文章前言
本篇文章是对《公链启动过程安全分析》的后续补充和扩展
源码分析
节点启动
startNode函数接受三个参数:ctx是上下文对象,stack是一个node.Node类型的指针,backend是ethapi.Backend类型的对象,该函数用于启动以太坊节点,并执行一系列操作
func startNode(ctx *cli.Context, stack *node.Node, backend ethapi.Backend) {
debug.Memsize.Add("node", stack)
// Start up the node itself
utils.StartNode(ctx, stack)
unlockAccounts函数则是用于解锁特定的账户
// Unlock any account specifically requested
unlockAccounts(ctx, stack)
随后创建了一个容量为16的通道events并将其注册为钱包事件处理程序,这也意味着当钱包相关的事件发生时会将事件发送到这个通道,
// Create a client to interact with local geth node.
rpcClient, err := stack.Attach()
if err != nil {
utils.Fatalf("Failed to attach to self: %v", err)
}
ethClient := ethclient.NewClient(rpcClient)
这里创建了一个与本地Geth节点进行交互的客户端,首先使用stack.Attach()方法获取一个RPC客户端并将其赋值给rpcClient变量,然后使用ethclient.NewClient()方法创建一个以太坊客户端,将RPC客户端传递给它,最后将返回的以太坊客户端赋值给ethClient变量
go func() {
// Open any wallets already attached
for _, wallet := range stack.AccountManager().Wallets() {
if err := wallet.Open(""); err != nil {
log.Warn("Failed to open wallet", "url", wallet.URL(), "err", err)
}
}
// Listen for wallet event till termination
for event := range events {
switch event.Kind {
case accounts.WalletArrived:
if err := event.Wallet.Open(""); err != nil {
log.Warn("New wallet appeared, failed to open", "url", event.Wallet.URL(), "err", err)
}
case accounts.WalletOpened:
status, _ := event.Wallet.Status()
log.Info("New wallet appeared", "url", event.Wallet.URL(), "status", status)
var derivationPaths []accounts.DerivationPath
if event.Wallet.URL().Scheme == "ledger" {
derivationPaths = append(derivationPaths, accounts.LegacyLedgerBaseDerivationPath)
}
derivationPaths = append(derivationPaths, accounts.DefaultBaseDerivationPath)
event.Wallet.SelfDerive(derivationPaths, ethClient)
case accounts.WalletDropped:
log.Info("Old wallet dropped", "url", event.Wallet.URL())
event.Wallet.Close()
}
}
}()
这段代码创建了一个匿名的goroutine(并发执行的函数),用于处理钱包相关的事件,首先它遍历已经附加的所有钱包并尝试打开它们,然后它开始监听钱包事件,直到终止,在事件的处理过程中根据事件的类型,执行相应的操作,例如:打开新的钱包、记录日志、关闭旧的钱包等
if ctx.GlobalBool(utils.ExitWhenSyncedFlag.Name) {
go func() {
sub := stack.EventMux().Subscribe(downloader.DoneEvent{})
defer sub.Unsubscribe()
for {
event := <-sub.Chan()
if event == nil {
continue
}
done, ok := event.Data.(downloader.DoneEvent)
if !ok {
continue
}
if timestamp := time.Unix(int64(done.Latest.Time), 0); time.Since(timestamp) < 10*time.Minute {
log.Info("Synchronisation completed", "latestnum", done.Latest.Number, "latesthash", done.Latest.Hash(),
"age", common.PrettyAge(timestamp))
stack.Close()
}
}
}()
}
如果设置了全局标志ExitWhenSyncedFlag,则会启动一个goroutine用于监视同步状态,它订阅了downloader.DoneEvent事件并在事件发生时执行相应的操作,如果最新区块的时间距离当前时间不到10分钟,则会打印同步完成的日志信息并关闭节点
if ctx.GlobalBool(utils.MiningEnabledFlag.Name) || ctx.GlobalBool(utils.DeveloperFlag.Name) {
// Mining only makes sense if a full Ethereum node is running
if ctx.GlobalString(utils.SyncModeFlag.Name) == "light" {
utils.Fatalf("Light clients do not support mining")
}
ethBackend, ok := backend.(*eth.EthAPIBackend)
if !ok {
utils.Fatalf("Ethereum service not running: %v", err)
}
// Set the gas price to the limits from the CLI and start mining
gasprice := utils.GlobalBig(ctx, utils.MinerGasPriceFlag.Name)
ethBackend.TxPool().SetGasPrice(gasprice)
// start mining
threads := ctx.GlobalInt(utils.MinerThreadsFlag.Name)
if err := ethBackend.StartMining(threads); err != nil {
utils.Fatalf("Failed to start mining: %v", err)
}
}
}
如果设置了全局标志MiningEnabledFlag或DeveloperFlag,则会检查节点的同步模式是否为"light",如果是"light"模式则会报错,因为轻客户端不支持挖矿,接着检查backend对象是否为eth.EthAPIBackend类型,如果不是,则会报错,然后根据命令行传入的Gas Price参数,设置交易池的Gas Price并启动挖矿,具体的挖矿操作需要通过ethBackend.StartMining(threads)来执行
startNode的具体实现如下:
// filedir:go-ethereum-1.10.2\cmd\utils\cmd.go
func StartNode(ctx *cli.Context, stack *node.Node) {
if err := stack.Start(); err != nil {
Fatalf("Error starting protocol stack: %v", err)
}
go func() {
sigc := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(sigc, syscall.SIGINT, syscall.SIGTERM)
defer signal.Stop(sigc)
minFreeDiskSpace := ethconfig.Defaults.TrieDirtyCache
if ctx.GlobalIsSet(MinFreeDiskSpaceFlag.Name) {
minFreeDiskSpace = ctx.GlobalInt(MinFreeDiskSpaceFlag.Name)
} else if ctx.GlobalIsSet(CacheFlag.Name) || ctx.GlobalIsSet(CacheGCFlag.Name) {
minFreeDiskSpace = ctx.GlobalInt(CacheFlag.Name) * ctx.GlobalInt(CacheGCFlag.Name) / 100
}
if minFreeDiskSpace > 0 {
go monitorFreeDiskSpace(sigc, stack.InstanceDir(), uint64(minFreeDiskSpace)*1024*1024)
}
<-sigc
log.Info("Got interrupt, shutting down...")
go stack.Close()
for i := 10; i > 0; i-- {
<-sigc
if i > 1 {
log.Warn("Already shutting down, interrupt more to panic.", "times", i-1)
}
}
debug.Exit() // ensure trace and CPU profile data is flushed.
debug.LoudPanic("boom")
}()
}
在这里会调用node的start方法启动所有注册的生命周期、RPC服务和P2P网络,这里对此进行逐行解析:
Start方法是Node结构体的一个方法,用于启动节点,在方法的开始和结束处使用了互斥锁,以确保在不同的线程中只有一个线程能够执行该方法
func (n *Node) Start() error {
n.startStopLock.Lock()
defer n.startStopLock.Unlock()
n.lock.Lock()
switch n.state {
case runningState:
n.lock.Unlock()
return ErrNodeRunning
case closedState:
n.lock.Unlock()
return ErrNodeStopped
}
n.state = runningState
在这里获取了节点的锁并根据节点的状态进行判断,如果节点已经处于运行状态,则解锁并返回ErrNodeRunning错误,如果节点已经处于关闭状态则解锁并返回ErrNodeStopped错误,否则将节点状态设置为运行状态
err := n.openEndpoints()
lifecycles := make([]Lifecycle, len(n.lifecycles))
copy(lifecycles, n.lifecycles)
n.lock.Unlock()
在此处调用n.openEndpoints()方法打开网络和RPC端点并创建一个lifecycles切片,用于存储节点中所有已注册的生命周期对象,然后将n.lifecycles切片的内容复制到lifecycles中并解锁节点的锁
if err != nil {
n.doClose(nil)
return err
}
如果打开端点的过程中出现错误,则调用n.doClose(nil)方法关闭节点并返回错误
var started []Lifecycle
for _, lifecycle := range lifecycles {
if err = lifecycle.Start(); err != nil {
break
}
started = append(started, lifecycle)
}
在这里遍历lifecycles切片中的每个生命周期对象并调用它们的Start()方法,如果某个生命周期启动失败,则终止遍历并将已启动的生命周期对象存储在started切片中,如果有生命周期启动失败,则调用n.stopServices(started)方法停止已启动的生命周期对象并调用n.doClose(nil)方法关闭节点,最后返回可能的错误
if err != nil {
n.stopServices(started)
n.doClose(nil)
}
return err
unlockAccounts解锁账户:
// filedir:go-ethereum-1.10.2\cmd\geth\main.go L426
// unlockAccounts unlocks any account specifically requested.
func unlockAccounts(ctx *cli.Context, stack *node.Node) {
var unlocks []string
inputs := strings.Split(ctx.GlobalString(utils.UnlockedAccountFlag.Name), ",")
for _, input := range inputs {
if trimmed := strings.TrimSpace(input); trimmed != "" {
unlocks = append(unlocks, trimmed)
}
}
// Short circuit if there is no account to unlock.
if len(unlocks) == 0 {
return
}
// If insecure account unlocking is not allowed if node's APIs are exposed to external.
// Print warning log to user and skip unlocking.
if !stack.Config().InsecureUnlockAllowed && stack.Config().ExtRPCEnabled() {
utils.Fatalf("Account unlock with HTTP access is forbidden!")
}
ks := stack.AccountManager().Backends(keystore.KeyStoreType)[0].(*keystore.KeyStore)
passwords := utils.MakePasswordList(ctx)
for i, account := range unlocks {
unlockAccount(ks, account, i, passwords)
}
}
注册钱包事件:
// Register wallet event handlers to open and auto-derive wallets
events := make(chan accounts.WalletEvent, 16)
stack.AccountManager().Subscribe(events)
之后监听钱包事件:
// Listen for wallet event till termination
for event := range events {
switch event.Kind {
case accounts.WalletArrived:
if err := event.Wallet.Open(""); err != nil {
log.Warn("New wallet appeared, failed to open", "url", event.Wallet.URL(), "err", err)
}
case accounts.WalletOpened:
status, _ := event.Wallet.Status()
log.Info("New wallet appeared", "url", event.Wallet.URL(), "status", status)
var derivationPaths []accounts.DerivationPath
if event.Wallet.URL().Scheme == "ledger" {
derivationPaths = append(derivationPaths, accounts.LegacyLedgerBaseDerivationPath)
}
derivationPaths = append(derivationPaths, accounts.DefaultBaseDerivationPath)
event.Wallet.SelfDerive(derivationPaths, ethClient)
case accounts.WalletDropped:
log.Info("Old wallet dropped", "url", event.Wallet.URL())
event.Wallet.Close()
}
}
}
生成用于状态同步监视的独立goroutine
// Spawn a standalone goroutine for status synchronization monitoring,
// close the node when synchronization is complete if user required.
if ctx.GlobalBool(utils.ExitWhenSyncedFlag.Name) {
go func() {
sub := stack.EventMux().Subscribe(downloader.DoneEvent{})
defer sub.Unsubscribe()
for {
event := <-sub.Chan()
if event == nil {
continue
}
done, ok := event.Data.(downloader.DoneEvent)
if !ok {
continue
}
if timestamp := time.Unix(int64(done.Latest.Time), 0); time.Since(timestamp) < 10*time.Minute {
log.Info("Synchronisation completed", "latestnum", done.Latest.Number, "latesthash", done.Latest.Hash(),
"age", common.PrettyAge(timestamp))
stack.Close()
}
}
}()
}
之后启动辅助服务(例如:挖矿):
// Start auxiliary services if enabled
if ctx.GlobalBool(utils.MiningEnabledFlag.Name) || ctx.GlobalBool(utils.DeveloperFlag.Name) {
// Mining only makes sense if a full Ethereum node is running
if ctx.GlobalString(utils.SyncModeFlag.Name) == "light" {
utils.Fatalf("Light clients do not support mining")
}
ethBackend, ok := backend.(*eth.EthAPIBackend)
if !ok {
utils.Fatalf("Ethereum service not running: %v", err)
}
// Set the gas price to the limits from the CLI and start mining
gasprice := utils.GlobalBig(ctx, utils.MinerGasPriceFlag.Name)
ethBackend.TxPool().SetGasPrice(gasprice)
// start mining
threads := ctx.GlobalInt(utils.MinerThreadsFlag.Name)
if err := ethBackend.StartMining(threads); err != nil {
utils.Fatalf("Failed to start mining: %v", err)
}
}
挖矿函数的具体逻辑代码如下,这里首先会检查矿工是否运行、配置本地挖矿奖励地址、最后执行挖矿:
// filedir:go-ethereum-1.10.2\eth\backend.go
// StartMining starts the miner with the given number of CPU threads. If mining
// is already running, this method adjust the number of threads allowed to use
// and updates the minimum price required by the transaction pool.
func (s *Ethereum) StartMining(threads int) error {
// Update the thread count within the consensus engine
type threaded interface {
SetThreads(threads int)
}
if th, ok := s.engine.(threaded); ok {
log.Info("Updated mining threads", "threads", threads)
if threads == 0 {
threads = -1 // Disable the miner from within
}
th.SetThreads(threads)
}
// If the miner was not running, initialize it
if !s.IsMining() {
// Propagate the initial price point to the transaction pool
s.lock.RLock()
price := s.gasPrice
s.lock.RUnlock()
s.txPool.SetGasPrice(price)
// Configure the local mining address
eb, err := s.Etherbase()
if err != nil {
log.Error("Cannot start mining without etherbase", "err", err)
return fmt.Errorf("etherbase missing: %v", err)
}
if clique, ok := s.engine.(*clique.Clique); ok {
wallet, err := s.accountManager.Find(accounts.Account{Address: eb})
if wallet == nil || err != nil {
log.Error("Etherbase account unavailable locally", "err", err)
return fmt.Errorf("signer missing: %v", err)
}
clique.Authorize(eb, wallet.SignData)
}
// If mining is started, we can disable the transaction rejection mechanism
// introduced to speed sync times.
atomic.StoreUint32(&s.handler.acceptTxs, 1)
go s.miner.Start(eb)
}
return nil
}
之后等待节点关闭:
// Wait blocks until the node is closed.
func (n *Node) Wait() {
<-n.stop
}
流程总览
根据对上面的流程进行分析我们可以绘制得出如下精简版本的流程示意图:
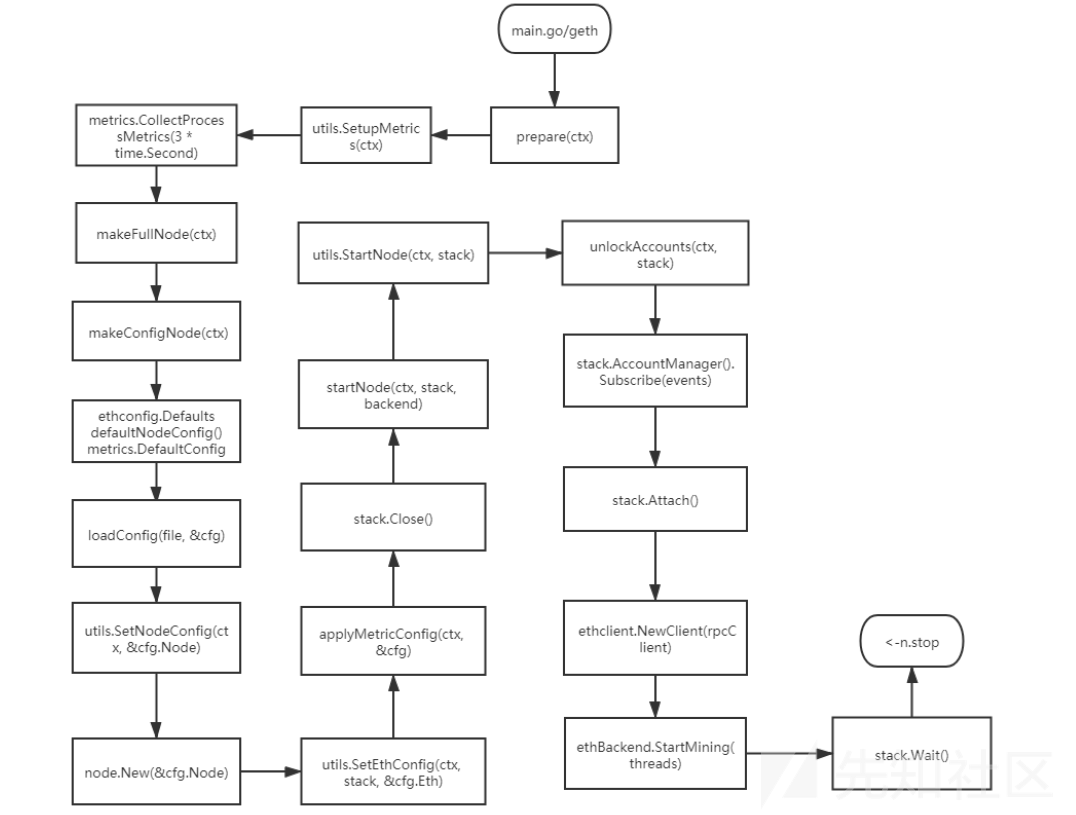
文末小结
本篇文章主要介绍了公链的启动过程并以以太坊源码为例对此进行了刨析,从上面可以看到公链的启动过程中的配置文件的加载、公链网络的选择适配、节点的创建、节点的启动、账户的创建、账户的锁定、账户的管理、事件的监听、挖矿操作等内容,期间我们需要重点注意的点主要有账户的管理、节点的创建和启动、挖矿操作等维度的安全性问题,例如:共识机制的设计、权限问题、数据同步问题等
 转载
转载
 分享
分享

